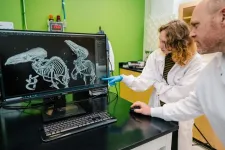
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the VIB-UGent Center for Medical Biotechnology have discovered a promising strategy to improve treatment responses in multiple myeloma patients by blocking a protein that plays a key role in drug resistance. The study, published in Pharmacological Research, offers a potential new strategy to improve outcomes for patients whose disease has become less responsive to standard therapies.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a type of blood cancer that affects the bone marrow. Patients are often treated with dexamethasone, a synthetic glucocorticoid frequently used in the clinic to regulate immune responses and slow cancer growth. However, as the disease progresses, many patients develop resistance to glucocorticoids.
The research team found that high levels of a protein, the chemokine receptor CCR1, are linked to worse outcomes in MM patients, particularly as the disease progresses. CCR1 is a receptor expressed on the surface of myeloma cells, through which the cells respond to chemical signals in the bone marrow environment and helps cancer cells to grow and survive.
Bert Luyckx, first author of the study, explains: “Our study shows that CCR1 is upregulated in MM patients with an unfavorable disease prognosis and plays a critical role in reducing glucocorticoid sensitivity in multiple myeloma cells. When we block CCR1 signaling, we see enhanced anti-cancer effects of dexamethasone in both lab models and patient samples.”
The team used a CCR1 inhibitor called BX471 and found that it helped to restore the effects of dexamethasone in cells that had started to become resistant. The drug combination pushed cancer cells towards programmed cell death and disrupted proteins involved in drug resistance.
“By targeting CCR1, we were able to partially reverse glucocorticoid resistance in multiple myeloma cells,” said Prof. Karolien De Bosscher. “This could offer new therapeutic opportunities for patients who no longer benefit from existing treatments.”
The findings suggest that CCR1 inhibitors could be used alongside current treatments to enhance their effectiveness. Further research is needed to explore how this approach can be applied in clinical settings.
END
Blocking chemokine receptor increases effectiveness of glucocorticoids in multiple myeloma treatment
Inhibiting CCR1 can reverse glucocorticoid resistance, offering a new strategy to improve myeloma treatment
2025-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Amount of sunlight reaching Earth’s surface varies over decades, researchers report
2025-04-15
The sun may rise every morning, but the amount of sunlight reaching the Earth’s surface can substantially vary over decades, according to a perspectives article led by an international research team. The article, published on March 15 in Advances in Atmospheric Science, suggests that stages of “dimming” and “brightening” correspond with increased air pollution and implementation of clean energy solutions, respectively.
“The amount of sunlight — which is solar ...
Heart valve abnormality is associated with malignant arrhythmias
2025-04-15
People with a certain heart valve abnormality are at increased risk of severe heart rhythm disorders, even after successful valve surgery. This is according to a new study from Karolinska Institutet and Karolinska University Hospital in Sweden published in the European Heart Journal. The condition is more common in women and younger patients with valve disorder and can, in the worst case, lead to sudden cardiac arrest.
Mitral annular disjunction, MAD, is a heart abnormality in which the mitral valve attachment ‘slides’. In recent years, the condition has ...
Explainable AI for ship navigation raises trust, decreases human error
2025-04-15
The Titanic sunk 113 years ago on April 14-15, after hitting an iceberg, with human error likely causing the ship to stray into those dangerous waters. Today, autonomous systems built on artificial intelligence can help ships avoid such accidents, but could such a system explain to the captain why it was maneuvering a certain way?
That’s the idea behind explainable AI, which should help human actors trust autonomous systems more. Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Engineering have developed an explainable AI model for ships that quantifies the collision risk for all vessels ...
Study reveals erasing inequality could prevent hundreds of adverse births annually in major UK city
2025-04-15
In Birmingham, 43% of the population live in the most deprived 10% of neighborhoods in England. It is well known that deprivation can lead to adverse pregnancy outcomes, including low birth weight, premature birth, stillbirths, and neonatal mortality.
Now, researchers there examined the association between demographic, socioeconomic, and lifestyle factors and the risk of adverse birth outcomes in Birmingham and neighboring Solihull, an area much less affected by deprivation.
“Within the study population, there were significant differences in the odds of adverse birth outcomes and the risk factors of adverse birth outcomes by ethnicity ...
No “uncanny valley” effect in science-telling AI avatars
2025-04-15
If you’re among the 1.5 billion people worldwide using TikTok, you may have come across exceptional “testimonials” like Nikola Tesla or Marie Curie delivering short science-related messages that have garnered millions of views. This is just one of many examples where AI-generated avatars are used to communicate science — a strategy that might also have its drawbacks.
The generation of images and animations through artificial intelligence is a rapidly growing field, constantly improving in quality. Yet many avatars, though realistic, still present minor flaws — glitches, delays, inconsistent ...
New UNCG research shows southern shrews shrink in winter
2025-04-15
Newly published research from UNC Greensboro biology professor Dr. Bryan McLean and colleagues shows that the masked shrew, a small, mole-like mammal found in the Appalachian Mountains, shrinks its body and braincase to conserve energy during winter months. The study, published in the May 2025 issue of The American Naturalist, found that the masked shrew (Sorex cinereus) reduces its body mass by 13 percent in the colder months; the creature then grows larger in spring when conditions improve. In addition to a shrinking body, the team also found seasonal changes in the height of the creature’s ...
Children exposed to brain-harming chemicals while sleeping
2025-04-15
Babies and young children may breathe and absorb plasticizers called phthalates, flame retardants, and other harmful chemicals from their mattresses while they sleep, according to a pair of peer-reviewed studies published today from the University of Toronto in Environmental Science & Technology and Environmental Science & Technology Letters. These chemicals are linked to neurological and reproductive problems, asthma, hormone disruption, and cancer.
"Sleep is vital for brain development, ...
Emotions and levels of threat affect communities’ resilience during extreme events
2025-04-15
Hoboken, N.J., April 14, 2025 — Tightly connected communities tend to be more resilient when facing extreme events such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods or wildfires, says Jose Ramirez-Marquez, who develops metrics to analyze, quantify and ultimately improve performance of urban systems.
Ramirez-Marquez, associate professor and division director of Enterprise Science and Engineering at Stevens, who grew up in the earthquake-prone Mexico City knows this first-hand. “Whenever there's an earthquake, a city-wide alarm goes off and everybody leaves wherever they are and stays in the middle of the street — that’s a prevention phase,” he says. ...
New CONSORT reporting guidelines published today in five medical journals
2025-04-14
Under embargo until 23:30 (UK), Monday April 14, 2025
An updated set of guidelines to improve transparency and clarity in the reporting of randomised controlled trials have been published today. The CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) 2025 statement provides a minimum set of essential items that should be included when reporting the results of randomised trials.
First published in 1996, the CONSORT guidelines saw additional updates in 2001 and 2010. Becoming the gold standard for reporting randomised trials, ...
Experts stress importance of vaccination amidst measles outbreaks
2025-04-14
Pediatric infectious diseases experts stress the importance of vaccination against measles, one of the most contagious viruses, which is once more spreading in the United States. In the article published in Pediatrics, they update pediatricians on this vaccine-preventable disease, which was previously declared non-endemic in the U.S.
“The most effective way to prevent measles is vaccination,” said lead author Caitlin Naureckas Li, MD MHQS, infectious diseases specialist at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and Assistant Professor of Pediatrics at Northwestern University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
ACMG Foundation to present adaptive bikes to Baltimore-area children with genetic conditions at heartwarming “Day of Caring” event on March 13
Racial disparities in food insecurity for high- and low-income households
Incidence of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest on a postholiday weekday
Prior authorization bans for buprenorphine alone may not improve treatment retention
When light boosts protein evolution
New model may predict preeclampsia in late pregnancy
Lifestyle medicine experts call meaning, purpose, and spirituality foundational to evidence-based, whole-person lifestyle change
Significant acceleration of global warming since 2015
FAU awarded $2.4M NIH grant to study immune signaling and social behavior
Deep learning-enabled virtual multiplexed immunostaining of label-free tissue for vascular invasion assessment
New PET imaging study reveals how ketamine relieves treatment-resistant depression
New study reveals differences between anime bamboo muzzle and actual bamboo
The ‘Great Texas Freeze’ killed thousands of purple martins; biologists worry recovery could take decades
Cancer has a unique nuclear metabolic fingerprint
Tiny thermometers offer on-chip temperature monitoring for processors
New compound stops common complications after intestinal surgery
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
[Press-News.org] Blocking chemokine receptor increases effectiveness of glucocorticoids in multiple myeloma treatmentInhibiting CCR1 can reverse glucocorticoid resistance, offering a new strategy to improve myeloma treatment