(Press-News.org) Vision is one of the most complex functions of our brain and requires a seamless interaction between many different brain structures to decode shapes, colours, depths, and movements and turn them into a meaningful whole. Just like other brain functions, vision also depends on a balanced and controlled interaction between the chemical signals that "activate" and "brake" activity in the eye's cells – much like the accelerator and brake of a car. In research, the "brake" is known as GABA, which stands for gamma-aminobutyric acid, and it is the primary neurotransmitter that inhibits nerve activity and helps regulate the balance between excitatory and inhibitory signals in the brain.
Neuroscientific researchers have long been particularly interested in understanding how networks of excitatory and inhibitory neurons work together. It has been a fundamental challenge to uncover how these complex interactions in neural circuits create the precise and targeted actions that underlie both vision and other cognitive processes.
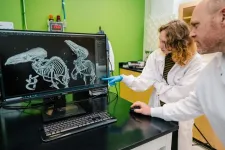
Together with colleagues from the USA, researchers from DANDRITE have, for the first time, conducted a comprehensive functional mapping of how the "brake" – inhibitory signaling – works in the part of the eye that processes and sends electrical signals to the brain, called the retina. It is in the retina that the first visual information is processed and then transmitted to the brain.
In total, the researchers mapped 44 different visual cells – some of which had never been described before. What was even more interesting was that these cells were characterized by a higher degree of systematic organization than previously known.
"Our result can be compared to finding a complicated map of an unknown landscape. Previously, we thought the landscape was randomly divided, but now we have mapped it, so we can see that each region has its own precise path and function," explains Professor Keisuke Yonehara, elaborating:
"By understanding how the different cells in the retina are organized and work in specific directions, we have revealed how the brain can precisely 'see' movement and orientation in our visual field – as if they have found the most efficient route through a complex network."
The key to this discovery was the development of a new GABA sensor, created by researchers in the USA, which allows for real-time observation and mapping of the precise activity of inhibitory neurons.
The research group's results have just been published in the prestigious journal Nature Neuroscience, and according to Keisuke Yonehara, this could be a breakthrough in understanding where and how certain eye disorders develop and occur.
"Many eye disorders are linked to imbalances in inhibitory signalling, including congenital nystagmus, where the eyes move involuntarily, quickly, and rhythmically. Now we have a 'map' that can give us deeper insights into this condition and hopefully also others related to this area."
END
Researchers have mapped the hidden control system of vision
2025-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Key to the high aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer identified
2025-04-15
Barcelona, 15th April 2025. – Pancreatic cancer is one of the most aggressive cancers and has one of the lowest survival rates—only 10% after five years. One of the factors contributing to its aggressiveness is its tumor microenvironment, known as the stroma, which makes up the majority of the tumor mass and consists of a network of proteins and different non-tumor cells. Among these, fibroblasts play a key role, helping tumor cells to grow and increasing their resistance to drugs. Now, a study led by researchers from the Hospital del Mar Research Institute, IIBB-CSIC-IDIBAPS, ...
How proactive salmon conservation in the North Pacific can deliver global benefits
2025-04-15
April 15, 2025 | Portland, Oregon—A new study in the journal Fisheries shows how a salmon-focused ecosystem protection strategy in the North Pacific can deliver meaningful results in the global drive to protect biodiversity.
The approach, called the stronghold strategy, aims to proactively protect the world’s greatest remaining “strongholds”—a select group of salmon, steelhead, and trout systems that collectively comprise 119 distinct watersheds. According to Wild Salmon Center President & CEO Guido Rahr—lead author of the peer-reviewed study—salmonids center the strategy because they are both iconic and globally recognized ...
Blocking chemokine receptor increases effectiveness of glucocorticoids in multiple myeloma treatment
2025-04-15
Researchers at the VIB-UGent Center for Medical Biotechnology have discovered a promising strategy to improve treatment responses in multiple myeloma patients by blocking a protein that plays a key role in drug resistance. The study, published in Pharmacological Research, offers a potential new strategy to improve outcomes for patients whose disease has become less responsive to standard therapies.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a type of blood cancer that affects the bone marrow. Patients are often treated with dexamethasone, a synthetic glucocorticoid frequently used in the clinic to regulate immune responses and slow cancer growth. However, as the disease progresses, many patients develop ...
Amount of sunlight reaching Earth’s surface varies over decades, researchers report
2025-04-15
The sun may rise every morning, but the amount of sunlight reaching the Earth’s surface can substantially vary over decades, according to a perspectives article led by an international research team. The article, published on March 15 in Advances in Atmospheric Science, suggests that stages of “dimming” and “brightening” correspond with increased air pollution and implementation of clean energy solutions, respectively.
“The amount of sunlight — which is solar ...
Heart valve abnormality is associated with malignant arrhythmias
2025-04-15
People with a certain heart valve abnormality are at increased risk of severe heart rhythm disorders, even after successful valve surgery. This is according to a new study from Karolinska Institutet and Karolinska University Hospital in Sweden published in the European Heart Journal. The condition is more common in women and younger patients with valve disorder and can, in the worst case, lead to sudden cardiac arrest.
Mitral annular disjunction, MAD, is a heart abnormality in which the mitral valve attachment ‘slides’. In recent years, the condition has ...
Explainable AI for ship navigation raises trust, decreases human error
2025-04-15
The Titanic sunk 113 years ago on April 14-15, after hitting an iceberg, with human error likely causing the ship to stray into those dangerous waters. Today, autonomous systems built on artificial intelligence can help ships avoid such accidents, but could such a system explain to the captain why it was maneuvering a certain way?
That’s the idea behind explainable AI, which should help human actors trust autonomous systems more. Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Engineering have developed an explainable AI model for ships that quantifies the collision risk for all vessels ...
Study reveals erasing inequality could prevent hundreds of adverse births annually in major UK city
2025-04-15
In Birmingham, 43% of the population live in the most deprived 10% of neighborhoods in England. It is well known that deprivation can lead to adverse pregnancy outcomes, including low birth weight, premature birth, stillbirths, and neonatal mortality.
Now, researchers there examined the association between demographic, socioeconomic, and lifestyle factors and the risk of adverse birth outcomes in Birmingham and neighboring Solihull, an area much less affected by deprivation.
“Within the study population, there were significant differences in the odds of adverse birth outcomes and the risk factors of adverse birth outcomes by ethnicity ...
No “uncanny valley” effect in science-telling AI avatars
2025-04-15
If you’re among the 1.5 billion people worldwide using TikTok, you may have come across exceptional “testimonials” like Nikola Tesla or Marie Curie delivering short science-related messages that have garnered millions of views. This is just one of many examples where AI-generated avatars are used to communicate science — a strategy that might also have its drawbacks.
The generation of images and animations through artificial intelligence is a rapidly growing field, constantly improving in quality. Yet many avatars, though realistic, still present minor flaws — glitches, delays, inconsistent ...
New UNCG research shows southern shrews shrink in winter
2025-04-15
Newly published research from UNC Greensboro biology professor Dr. Bryan McLean and colleagues shows that the masked shrew, a small, mole-like mammal found in the Appalachian Mountains, shrinks its body and braincase to conserve energy during winter months. The study, published in the May 2025 issue of The American Naturalist, found that the masked shrew (Sorex cinereus) reduces its body mass by 13 percent in the colder months; the creature then grows larger in spring when conditions improve. In addition to a shrinking body, the team also found seasonal changes in the height of the creature’s ...
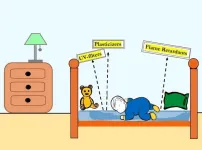
Children exposed to brain-harming chemicals while sleeping
2025-04-15
Babies and young children may breathe and absorb plasticizers called phthalates, flame retardants, and other harmful chemicals from their mattresses while they sleep, according to a pair of peer-reviewed studies published today from the University of Toronto in Environmental Science & Technology and Environmental Science & Technology Letters. These chemicals are linked to neurological and reproductive problems, asthma, hormone disruption, and cancer.
"Sleep is vital for brain development, ...