Nanotech milling produces dramatic increase in thermoelectric performance of bulk semiconductor
2011-01-26
(Press-News.org) CHESTNUT HILL, MA (1/25/11) -- Researchers from Boston College, MIT, Clemson and Virginia have used nanotechnology to achieve a 60-90 percent increase in the thermoelectric figure of merit of p-type half-Heusler, a common bulk semiconductor compound, the team reported in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
The dramatic increase in the figure of merit, used to measure a material's relative thermoelectric performance, could pave the way for a new generation of products – from car exhaust systems and power plants to solar power technology – that that runs cleaner, according to co-author Yan Xiao, a researcher in the Department of Physics at Boston College.
The team registered improvement in half-Heusler, which has been under study for its thermal stability, mechanical sturdiness, non-toxicity and low cost. However, the application of half-Heusler has been limited because of its poor thermoelectric performance: it previously registered a peak figure of merit of approximately 0.5 at 700 degrees Celsius for bulk ingots.
Xiao, working with BC Professor of Physics Zhifeng Ren and MIT's Soderberg Professor of Power Engineering Gang Chen, said the team produced an increase in the figure of merit value of p-type half-Heusler to 0.8 at 700 degrees Celsius. Moreover, the groups' material preparation methods proved to save time and expense compared with conventional methods.
"This method is low cost and can be scaled for mass production," Ren said. "This represents an exciting opportunity to improve the performance of thermoelectric materials in a cost-effective manner."
The researchers obtained their results by first forming alloyed ingots using arc melting technique and then creating nanoscale powders by ball milling the ingots and finally obtaining dense bulk by hot pressing. Transport property measurements together with microstructure studies on the nanostructured samples, in comparison with that of bulk ingots, showed that the thermoelectric performance improves largely because of low thermal conductivity produced by enhanced phonon scattering at grain boundaries and defects in the material. The material was also found to have a high Seebeck coefficient, a measure of thermoelectric power.
Researchers in the BC and MIT labs are still trying to prevent grain growth during press, which accounts for the still large thermal conductivity of half-Heusler.
"Even lower thermal conductivity and improved thermoelectric performance can be expected when average grain sizes are made smaller than 100 nm," said Ren, who was joined on the team by fellow Boston College researchers Giri Joshi, Weishu Liu, Yucheng Lan and Hui Wang, MIT's Sangyeop Lee, Virginia's Rogers Professor of Physics Joe Poons and J.W. Simonson and Clemson Professor of Physics Terry M. Tritt.
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-01-26
Washington, D.C. (January 25, 2011) -- A team of physicists has taken a big step toward the development of useful graphene spintronic devices. The physicists, from the City University of Hong Kong and the University of Science and Technology of China, present their findings in the American Institute of Physics' Applied Physics Letters.
Graphene, a two-dimensional crystalline form of carbon, is being touted as a sort of "Holy Grail" of materials. It boasts properties such as a breaking strength 200 times greater than steel and, of great interest to the semiconductor and ...
2011-01-26
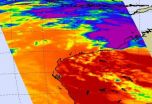
NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of the very cold clouds that house powerful thunderstorms within the Southern Indian Ocean's newest tropical depression, number 10S. The depression quickly strengthened into a tropical storm and continues to affect the northern coast of Western Australia.
When Aqua passed over the Tropical Storm 10S on January 25 at 05:53 UTC (12:53 a.m. EST), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the storm's clouds. The image showed that most of the coldest cloud tops (-63 Fahrenheit/-52 Celsius) ...
2011-01-26
Boulder, CO, USA – The February issue of Geology is online now. Articles cover Patagonian glaciations, the Younger Dryas cold period, paleodiversity, submarine gullies, the Transantarctic Mountain micrometeorite collection, the "fastest glacier on Earth," salt diapirs in the Nordkapp Basin, reinterpretation of James Hutton's historic discovery on the Isle of Arran, a new tool to directly date dinosaur-bone fossils, ancient megalakes in Australia, Egypt's Kamil Crater, and more. GSA TODAY examines seismic activity to gain insights into the Rio Grande Rift.
Keywords: Ammonoids, ...
2011-01-26
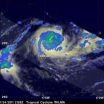
Wilma caught the eye of NASA. NASA's Aqua satellite captured visible and infrared images of Cyclone Wilma in the Southwestern Pacific Ocean and her eye was clearly visible from space.
On January 25 at 00:59 UTC (8:59 p.m. EST on Jan. 24), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured data that was used to create infrared and visible images at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. The images showed Cyclone Wilma had strengthened overnight and now has a visible eye.
AIRS Infrared imagery showed strong, very cold thunderstorm cloud tops around ...
2011-01-26
SEATTLE – Women who have experienced hot flushes and other symptoms of menopause may have a 50 percent lower risk of developing the most common forms of breast cancer than postmenopausal women who have never had such symptoms, according to a recent study by researchers at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center.
The results of the first study to examine the relationship between menopausal symptoms and breast cancer risk are available online ahead of the February print issue of Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention.
The protective effect appeared to increase along ...
2011-01-26
Charles Darwin based his groundbreaking theory of natural selection on the realization that genetic variation among organisms is the key to evolution.
Some individuals are better adapted to a given environment than others, making them more likely to survive and pass on their genes to future generations. But exactly how nature creates variation in the first place still poses somewhat of a puzzle to evolutionary biologists.
Now, Joanna Masel, associate professor in the UA's department of ecology and evolutionary biology, and postdoctoral fellow Etienne Rajon discovered ...
2011-01-26
Measuring the attractive forces between atoms and surfaces with unprecedented precision, University of Arizona physicists have produced data that could refine our understanding of the structure of atoms and improve nanotechnology. The discovery has been published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Van der Waals forces are fundamental for chemistry, biology and physics. However, they are among the weakest known chemical interactions, so they are notoriously hard to study. This force is so weak that it is hard to notice in everyday life. But delve into the world of ...
2011-01-26
In an effort to better understand the dynamics of complex networks, scientists have developed a mathematical model to describe interactions within ecological food webs. This research, performed by Northwestern University physics professor Adilson Motter and his student, Sagar Sahasrabudhe, is published in the January 25 issue of Nature Communications. The work illustrates how human intervention may effectively aid species conservation efforts.
"Our study provides a theoretical basis for management efforts that would aim to mitigate extinction cascades in food web networks. ...
2011-01-26
Aneesoft Corporation, a leading digital multimedia software company, announces the release of Aneesoft Free Image Editor today, a free image editing software which fulfills all the basic needs of the average users.
Like a review from Softpedia.com, the second largest download site in Europe, said of Aneesoft Free Image Editor, "Image editing was never simpler". Aneesoft Free Image Editor supports most common image file format, such as .JPG, .PNG, .BMP, .GIF, etc. It provides some basic functions for image editing: crop, rotate, watermark and most attractive of all, various ...
2011-01-26
Agora Gallery is delighted to announce the opening of the Chelsea International Fine Art Competition. This will be the 26th year of the well-known annual competition, which will begin accepting entries on February 2nd, 2011. The submission deadline is March 14th, 2011, and the results will be announced on April 5th, 2011. Details of how to enter can be found here - http://www.agora-gallery.com/competition/default.aspx.
The prizes total a value of $38,000, and include a range of awards, all designed to aid in promoting the careers of the artists whose work will be selected ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nanotech milling produces dramatic increase in thermoelectric performance of bulk semiconductor