(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, DC, January 25, 2011 – The tiger reserves of Asia could support more than 10,000 wild tigers – three times the current number – if they are managed as large-scale landscapes that allow for connectivity between core breeding sites, a new paper from some of the world's leading conservation scientists finds. The study, co-authored by World Wildlife Fund (WWF) scientists, is the first assessment of the political commitment made by all 13 tiger range countries at November's historic tiger summit to double the tiger population across Asia by 2022.
"A Landscape-Based Conservation Strategy to Double the Wild Tiger Population" in the current issue of Conservation Letters, finds that the commitment to double tiger numbers is not only possible, but can be exceeded. However, it will take a global effort to ensure that core breeding reserves are maintained and connected via habitat corridors.
"In the midst of a crisis, it's tempting to circle the wagons and only protect a limited number of core protected areas, but we can and should do better," said Dr. Eric Dinerstein, Chief Scientist at WWF and a co-author of the study. "We absolutely need to stop the bleeding, the poaching of tigers and their prey in core breeding areas, but we need to go much further and secure larger tiger landscapes before it is too late."
Wild tiger numbers have declined from about 100,000 in the early 1900s to as few as 3,200 today due to poaching of tigers and their prey, habitat destruction and human/tiger conflict. Most of the remaining tigers are scattered in small, isolated pockets across their range in 13 Asian countries.
"Tiger conservation is the face of biodiversity conservation and competent sustainable land-use management at the landscape level," said study co-author Dr. John Seidensticker of the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute. "By saving the tiger we save all the plants and animals that live under the tiger's umbrella."
The authors found that the 20 priority tiger conservation landscapes with the highest probability of long-term tiger survival could support more than 10,500 tigers, including about 3,400 breeding females. They also looked at historical examples to prove that a doubling or tripling is possible using large landscapes:
In the jungles of lowland Nepal, tiger numbers crashed during civil conflict from 2002 to 2006. However, tigers did not disappear because Nepal and India's tiger reserves are linked by forest corridors, which likely allowed for replenishment from India;
In the Russian Far East tigers, almost disappeared in the 1940s but the region was re-populated by tigers moving in from northeastern China. Recently designated habitat corridors across the Sino-Russia border are helping tigers re-establish themselves in China's Changbaishan mountains, where they had disappeared in the 1990s.
In India's Nagarahole National Park, tiger numbers are "healthy and resilient" because the park is connected to other reserves in the region. Tigers number almost 300 in this large landscape of connected parks and reserves.
In contrast, the authors point to two of India's premier tiger reserves to show how lack of connectivity can preclude tiger population recovery. Tigers disappeared from Sariska and Panna tiger reserves in 2005 and 2009 due to poaching and were not able to re-colonize because these reserves are not connected to other reserves through habitat corridors. Consequently, wild tigers had to be translocated into these reserves to attempt to re-establish populations.
Besides poaching and habitat loss, the $7.5 trillion in infrastructure projects like roads, dams and mines that will be invested in Asia over the next decade threatens tiger landscapes. A focus only on core sites and protected areas like reserves, instead of larger landscapes, could be seen by developers and politicians as a green light to move forward with harmful infrastructure projects outside of core sites.
"Without strong countervailing pressures, short-term economic gains will inevitably trump protection of the critical ecosystems necessary for sustainable development," said Keshav Varma, Program Director of the Global Tiger Initiative at the World Bank.
The authors insist that conservationists and governments must be involved in helping design infrastructure projects to mitigate their impacts on tigers both inside core sites and in current and potential forest corridors. A recently built oil depot in India's Terai Arc, for example, severed a vital elephant and tiger corridor. Conservationists are now in litigation to remove the depot. Early intervention could have avoided this.
"Following the St. Petersburg Declaration, Nepal has committed to the goal of doubling wild tiger numbers across our country by 2022," said Deepak Bohara, Nepal's Minister for Forests and Soil Conservation. "This analysis shows that it can be done, not just in Nepal, but, if done right with careful study and planning, across the entire tiger range. It is also worth noting that the tiger conservation provides carbon credits, protects water resources, and complements community development efforts. Thus, it is important to promote regional cooperation to maintain a healthy tiger corridor between different reserves."
###
Editor's Note: The study's authors are: Eric Wikramanayake, Eric Dinerstein, Bivash Pandev, Igor Chestin, Seng Teak, Peter Cutter and Utin Than of WWF; A.J.T. Johnsingh of Nature Conservation Foundation, India and WWF; Guangshun Jiang of WWF and Northeast Forestry University, P.R. China; John Seidensticker, Susan Lumpkin and Jonathan Ballou of the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute; Mahendra Shrestha of Save the Tiger Fund, National Fish and Wildlife Foundation; Hemanta Mishra of The Bridge Fund; Sunarto Sunarto and Kanchan Thapa of Virginia Polytechnic Institute; Sivananthan Elagupillay of Department of Wildlife and National Parks, Malaysia; Hemanta Kafley of the University of Missouri, Columbia; Narendra Man Babu Pradhan of the Department of National Parks and Wildlife, Nepal; Karma Jigme of the Department of Forests & Park Services, Bhutan; Md. Abdul Aziz, Jahangirnagar University & Wildlife Trust of Bangladesh.
ABOUT WORLD WILDLIFE FUND
WWF is the world's leading conservation organization, working in 100 countries for nearly half a century. With the support of almost 5 million members worldwide, WWF is dedicated to delivering science-based solutions to preserve the diversity and abundance of life on Earth, halt the degradation of the environment and combat climate change. Visit www.worldwildlife.org to learn more.
END
VIDEO:
Jerry Nick, M.D., associate professor of medicine at National Jewish Health, discusses recent research on biofilms, bacterial infections and contact lenses.
Click here for more information.
Researchers at National Jewish Health and the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center have discovered a new method to fight bacterial infections associated with contact lenses. The method may also have applications for bacterial infections associated with severe burns and ...
A study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has raised safety concerns about an investigational approach to treating cancer.
The strategy takes aim at a key signaling pathway, called Notch, involved in forming new blood vessels that feed tumor growth. When researchers targeted the Notch1 signaling pathway in mice, the animals developed vascular tumors, primarily in the liver, which led to massive hemorrhages that caused their death.
Their findings are reported online Jan. 25 in the Journal of Clinical Investigation and will appear ...
New Rochelle, NY, January 25, 2011—Give caffeine to cells engineered to produce viruses used for gene therapy and the cells can generate 3- to 8-times more virus, according to a paper published in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. (www.liebertpub.com). The paper is available free online at www.liebertpub.com/hum
This simple and inexpensive strategy for increasing lentivirus production was developed by Brian Ellis, Patrick Ryan Potts, and Matthew Porteus, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas. In their paper, ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers have invented a technique that uses inexpensive paper to make "microfluidic" devices for rapid medical diagnostics and chemical analysis.
The innovation represents a way to enhance commercially available diagnostic devices that use paper-strip assays like those that test for diabetes and pregnancy.
"With current systems that use paper test strips you can measure things like pH or blood sugar, but you can't perform more complex chemical assays," said Babak Ziaie, a Purdue University professor of electrical and computer engineering and ...
Washington, D.C. (January 25, 2011) -- In a development that may revolutionize handheld electronics, flat-panel displays, touch panels, electronic ink, and solar cells, as well as drastically reduce their manufacturing costs, physicists in Iran have created a spintronic device based on "armchair" graphene nanoribbons. Spintronic devices are being pursued by the semiconductor and electronics industries because they promise to be smaller, more versatile, and much faster than today's electronics.
As described in the American Institute of Physics journal Applied Physics Letters, ...
CHESTNUT HILL, MA (1/25/11) -- Researchers from Boston College, MIT, Clemson and Virginia have used nanotechnology to achieve a 60-90 percent increase in the thermoelectric figure of merit of p-type half-Heusler, a common bulk semiconductor compound, the team reported in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
The dramatic increase in the figure of merit, used to measure a material's relative thermoelectric performance, could pave the way for a new generation of products – from car exhaust systems and power plants to solar power technology – that that runs ...
Washington, D.C. (January 25, 2011) -- A team of physicists has taken a big step toward the development of useful graphene spintronic devices. The physicists, from the City University of Hong Kong and the University of Science and Technology of China, present their findings in the American Institute of Physics' Applied Physics Letters.
Graphene, a two-dimensional crystalline form of carbon, is being touted as a sort of "Holy Grail" of materials. It boasts properties such as a breaking strength 200 times greater than steel and, of great interest to the semiconductor and ...
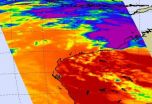
NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of the very cold clouds that house powerful thunderstorms within the Southern Indian Ocean's newest tropical depression, number 10S. The depression quickly strengthened into a tropical storm and continues to affect the northern coast of Western Australia.
When Aqua passed over the Tropical Storm 10S on January 25 at 05:53 UTC (12:53 a.m. EST), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the storm's clouds. The image showed that most of the coldest cloud tops (-63 Fahrenheit/-52 Celsius) ...
Boulder, CO, USA – The February issue of Geology is online now. Articles cover Patagonian glaciations, the Younger Dryas cold period, paleodiversity, submarine gullies, the Transantarctic Mountain micrometeorite collection, the "fastest glacier on Earth," salt diapirs in the Nordkapp Basin, reinterpretation of James Hutton's historic discovery on the Isle of Arran, a new tool to directly date dinosaur-bone fossils, ancient megalakes in Australia, Egypt's Kamil Crater, and more. GSA TODAY examines seismic activity to gain insights into the Rio Grande Rift.
Keywords: Ammonoids, ...
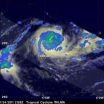
Wilma caught the eye of NASA. NASA's Aqua satellite captured visible and infrared images of Cyclone Wilma in the Southwestern Pacific Ocean and her eye was clearly visible from space.
On January 25 at 00:59 UTC (8:59 p.m. EST on Jan. 24), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured data that was used to create infrared and visible images at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. The images showed Cyclone Wilma had strengthened overnight and now has a visible eye.
AIRS Infrared imagery showed strong, very cold thunderstorm cloud tops around ...