(Press-News.org) The previously unknown species of ribbon worm discovered in Kosterhavet National Park in 2007 has now been scientifically named using a new method. Pseudomicrura afzelii, a form of nemertean or ribbon worm, has been described and registered by researchers at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, using DNA technology.
"We've shown that it's possible to move away from the traditional, highly labour-intensive way of describing a new species. Developments in molecular biology have made it possible to determine the genetic code for selected parts of DNA both quickly and cheaply." So says Malin Strand who, together with Per Sundberg, had the non-traditional description of the new nemertean published in a scientific journal. They have also deposited a type specimen of the species at the Gothenburg Museum of Natural History together with a test tube containing the species' unique DNA. Thus the species has been given its valid formal name and can be counted as a Swedish species – and the two researchers have opened the door to new methods for determining species.
There are currently around 1.7 million known species of plant and animal, though the actual number is many times higher. To date, every new species has been described and named using the system introduced by Linnaeus in the 18th century, in other words on the basis of similarities of appearance. A species name is valid only once a detailed description of the species has been published and a type specimen has been deposited with a museum. This guarantees the link between the name and the species, and prevents the same name from being used for different species. An international committee keeps track of all valid species names.
"The description of the species is an extremely important part of the naming process. A species without a name just doesn't 'exist'. Without valid names for species, our perception of biological diversity is skewed."
However, this is a time-consuming process that in many cases involves expensive special techniques and specialist expertise. As a result, many new species are not described, but instead remain unprocessed.
Ribbon worms are an example of creatures that are traditionally described using anatomical characteristics, in other words how their internal organs such as intestines, blood vessels and brain are organised and what they look like. The recently published species description means that the two Gothenburg researchers are paving the way for more new species to be registered by linking a species-specific DNA code to a name.
INFORMATION:
Malin Strand and Per Sundberg from the University of Gothenburg both have links with the Swedish Species Information Centre. The article A DNA-based description of a new nemertean (phylum Nemertea) species has been published in the scientific journal Marine Biology Research.
Researchers register new species using DNA-based description
2011-01-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
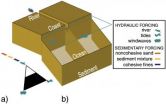
A clearer picture of how rivers and deltas develop
2011-01-26
By adding information about the subsoil to an existing sedimentation and erosion model, researchers at Delft University of Technology (TU Delft, The Netherlands) have obtained a clearer picture of how rivers and deltas develop over time. A better understanding of the interaction between the subsoil and flow processes in a river-delta system can play a key role in civil engineering (delta management), but also in geology (especially in the work of reservoir geologists). Nathanaël Geleynse et al. recently published in the journals Geophysical Research Letters and Earth and ...
Insects that deter predators produce fewer offspring
2011-01-26
Scientists studied the defences used by caterpillars that transform into large white butterflies, called Pieris brassicae. The insects regurgitate semi-digested cabbage leaves to make them smell and taste unpleasant to predators. The team found, however, that frequent use of this defence reduces the caterpillars' growth rate and the number of eggs they produce. It remains unclear why their defences affect them in this way, but the loss of nutrition from frequent regurgitation is thought to play a part.
Caterpillars are a target of pest control, as they destroy food ...
Increased marginalization of students
2011-01-26
The successful Swedish model of reducing the impact of students' different social, cultural and economic backgrounds on academic outcome is severely threatened after 20 years of educational reforms. This is the main point made by Docent (Reader) Girma Berhanu from the University of Gothenburg in International Journal of Special Education.
Some of the previously very positive trends in the Swedish school system seem to have been put in reverse over the past 20 years, and students with special needs, immigrant students and socially disadvantaged students are getting the ...
A psychopath lacks empathy just like a person with frontal head injury
2011-01-26
"Seeing as psychopathic behavior is similar to that of a person with brain damage, it could be that it could benefit from similar forms of treatment," said Dr. Simone Shamay-Tsoory, who conducted the study.
People diagnosed as psychopathic have difficulty showing empathy, just like patients who have suffered frontal head injury. This has been shown in a new study from the University of Haifa. "Our findings show that people who have psychopathic symptoms behave as though they are suffering frontal brain damage," said Dr. Simone Shamay-Tsoory, who conducted the study.
Psychopathy ...
CSI: Manchester -- University team gets forensic on dinosaurs
2011-01-26
A new TV series featuring dinosaur detectives from The University of Manchester looking at how dinosaurs once lived, looked and functioned begins in the UK this week.
Presented by University of Manchester palaeontologist Dr Phil Manning, the series will be aired on the National Geographic Channel, starting in the UK on Thursday February 3rd, before being transmitted to many countries around the world.
It is the first ever series on dinosaurs commissioned by National Geographic, as previously documentaries have only aired as one or two-hour specials.
Jurassic CSI ...
Asian tiger numbers could triple if large-scale landscapes are protected
2011-01-26
The tiger reserves of Asia could support more than 10,000 wild tigers – three times the current number – if they are managed as large-scale landscapes that allow for connectivity between core breeding sites, a new study from some of the world's leading conservation scientists finds. The study, published in Conservation Letters, is the first assessment of the political commitment made by all 13 tiger range countries last November to double the tiger population across Asia by 2022.
"A Landscape-Based Conservation Strategy to Double the Wild Tiger Population" finds that ...
Patients infected with HIV have higher drop-out rate for liver transplantation
2011-01-26
French researchers determined that infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) impaired results of transplant surgery for liver cancer, with more HIV infected patients dropping off the transplantation wait list. The team found that overall survival and recurrence-free survival was not impacted following liver transplantation in patients with controlled HIV disease. Details of this single center study—the largest to date—are published in the February issue of Hepatology, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD).
More ...
Researchers identify gene variants linked to hepatitis C treatment-related anemia
2011-01-26
In two recent studies, researchers have identified two functional variants in the inosine triphosphatase (ITPA) gene that protect patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) against anemia brought on by antiviral treatment. The ability to identify those patients protected against treatment-induced anemia will ensure completion of antiviral therapy and successful elimination of the virus. Full findings of these studies appear in the February issue of Hepatology, a journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Chronic ...
Climate tax on meat and milk results in less greenhouse gases
2011-01-26
A climate tax corresponding to €60/ton CO2eq on meat and milk could reduce
greenhouse gas emissions from European agriculture by around seven per cent. If the land made available is used for bioenergy production, the decrease in emissions can be six times greater. This is shown by the researchers Kristina Mohlin, Stefan Wirsenius and Fredrik Hedenus, University of Gothenburg, Sweden, in an article published in the scientific journal Climatic Change.
Kristina Mohlin is a PhD student at the Department of Economics at the University of Gothenburg. She wrote the article ...
The embryogenesis evidence of foregut duplication cyst
2011-01-26
Foregut duplication cyst of the stomach is rare. Foregut duplications may or may not communicate with the gastrointestinal tract, and are usually diagnosed at a young age. There have been relatively few case reports describing this entity. Adenocarcinoma has been reported in four cases of gastric duplication cyst, but not in cysts that have a ciliated epithelium. Controversy exists concerning the embryological origin of these anomalies.
A research article to be published on January 7, 2011 in the World Journal of Gastroenterology addresses this question. The authors presented ...