(Press-News.org) COLUMBIA, Mo. – Each year, 29,000 foster youths are released from care as they become adults. A University of Missouri foster care expert says these young people encounter tremendous challenges as they transition out of care. However, those who receive care benefits through age 21 have greatly improved outcomes. Clark Peters, assistant professor in the School of Social Work, says all states should consider extending benefits for foster youth.
"The transition between foster care and the real world leaves many 18-year-olds without a place to stay, money, a job or reliable transportation," Peters said. "Foster youths who continue to receive benefits through age 21 have improved outcomes including a greater likelihood of attending college and achieving financial stability."
Some states provide foster youths with continued benefits, such as educational aid, until age 21. Under the Fostering Connections to Success Act of 2009, the federal government matches states' expenditures for benefits through age 21. However, many states choose to discontinue foster benefits at age 18, Peters says.
Peters says foster youths lack personal assets or financial savings, making it difficult to secure housing, withstand unexpected changes or maintain jobs. Unlike other people their age, they often don't have a broad network of friends or family to rely on for help when they run out of gas or can't pay rent.
"Without families or established social networks, foster youths are faced with numerous difficulties in negotiating life on their own," Peters said. "They are forced to grow up faster than most kids because they don't have the same emotional or financial support when things go wrong or they make mistakes typical of youths their age."
Peters researched the costs and benefits to states that provide foster care benefits through age 21. In a 2009 study published by Chapin Hall at the University of Chicago, Peters found that the benefits of continued care outweighed the costs by a 2-1 ratio. Foster youths who receive extended benefits have more opportunities to make successful transitions to independent living. As a result, they utilize fewer government benefits and have higher incomes, resulting in more tax revenues for state and federal governments.
INFORMATION:
For more information about foster care and ways to help, visit the National Foster Care Coalition: www.nationalfostercare.org/about/; and the Jim Casey Foundation: www.jimcaseyyouth.org/need.
In 2011, Peters will research the operation of programs that help former foster youth develop financial skills and build assets. Peters is an assistant professor in the School of Social Work in the MU College of Human Environmental Sciences. He holds a law degree from Cornell University and master's and doctorate degrees in social work from the University of Chicago. His research interests include child welfare services, adolescent transition to adulthood and juvenile justice.
States should extend benefits for youth in foster care, MU expert says
2011-02-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Learning causes structural changes in affected neurons
2011-02-04
When a laboratory rat learns how to reach for and grab a food pellet – a pretty complex and unnatural act for a rodent – the acquired knowledge significantly alters the structure of the specific brain cells involved, which sprout a whopping 22 percent more dendritic spines connecting them to other motor neurons.
The finding, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by Mark H. Tuszynski, MD, PhD, professor of neurosciences and colleagues at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, underscores the brain's remarkable ability ...
'Tall order' sunlight-to-hydrogen system works, neutron analysis confirms
2011-02-04
OAK RIDGE, Tenn. Feb. 3, 2011 -- Researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed a biohybrid photoconversion system -- based on the interaction of photosynthetic plant proteins with synthetic polymers -- that can convert visible light into hydrogen fuel.
Photosynthesis, the natural process carried out by plants, algae and some bacterial species, converts sunlight energy into chemical energy and sustains much of the life on earth. Researchers have long sought inspiration from photosynthesis to develop new materials to harness the ...
Loss of oyster reefs a global problem, but one with solutions
2011-02-04
(February 3, 2011) Those familiar with Chesapeake Bay know that its once-vast oyster population stands at a tiny fraction of its historical abundance. A new study by an international team including professor Mark Luckenbach of the Virginia Institute of Marine Science shows that the decline of oyster reefs is not just a local problem.
The team's global comparison of oyster reefs past and present shows that oyster reefs are at less than 10% of their prior abundance in 70% of the 144 bays studied, ranging from China to England to Australia to Brazil. Overall, they estimate ...
Future surgeons may use robotic nurse, 'gesture recognition'
2011-02-04
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- Surgeons of the future might use a system that recognizes hand gestures as commands to control a robotic scrub nurse or tell a computer to display medical images of the patient during an operation.
Both the hand-gesture recognition and robotic nurse innovations might help to reduce the length of surgeries and the potential for infection, said Juan Pablo Wachs, an assistant professor of industrial engineering at Purdue University.
The "vision-based hand gesture recognition" technology could have other applications, including the coordination of ...
Morning-after spike in ozone air pollution from Super Bowl XLV?
2011-02-04
WASHINGTON, Feb. 3, 2011 — Not even the most avid fans could notice, but those spectacular aerial images of a brightly-lit Cowboys Stadium during Sunday's Super Bowl XLV symbolize one of the hottest new pieces of scientific intelligence about air pollution:
Researchers have discovered — in a classic case of scientific serendipity — that the bright light from sports stadiums and urban street lights may boost daytime levels of ozone, a key air pollutant in many heavily populated areas. That's among the topics included in a broader article about the chemistry of air pollution ...
Scientists urge new research policies in wake of Gulf disaster
2011-02-04
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Scientists are having a difficult time gauging the recovery of marine species from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico because they lack sufficient data about historical population size and the distribution, growth rates and reproduction rates of many species.
In a forum paper published this week in the journal Science, they call for a new research agenda that prioritizes systematic acquisition of baseline data for marine species.
"It is impossible to diagnose whether a species is recovering or floundering if you don't have good data ...
Oil in Gulf of Mexico: Biologists cite need for critical data to determine ecological consequences
2011-02-04
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — Twenty years after biologists attempted to determine the ecological damages to marine life from the Exxon Valdez oil spill, scientists dealing with the BP disaster find themselves with the same problem: the lack of critical data to determine the ecological consequences of human-induced environmental disasters, a University of Florida researcher said.
Writing in the Feb. 4 issue of the journal Science, Karen A. Bjorndal, a University of Florida biology professor and director of the Archie Carr Center for Sea Turtle Research, and other biologists said ...
New clue to lupus: Failed autoimmune suppression mechanism
2011-02-04
Bar Harbor, Maine — Researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Cambridge, Mass., in collaboration with Jackson Laboratory scientists, have identified a regulatory defect that drives lupus.
Correcting the defect "may represent an effective therapeutic approach to systemic lupus erythematosus-like autoimmune disease," the researchers state in their research paper, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The research team was led by Harvey Cantor, M.D., chair of the department of cancer immunology and AIDS at Dana-Farber, in collaboration with ...
Surprise hidden in Titan's smog: Cirrus-like clouds
2011-02-04
Every day is a bad-air day on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Blanketed by haze far worse than any smog belched out in Los Angeles, Beijing or even Sherlock Holmes's London, the moon looks like a dirty orange ball. Described once as crude oil without the sulfur, the haze is made of tiny droplets of hydrocarbons with other, more noxious chemicals mixed in. Gunk.
Icky as it may sound, Titan is really the rarest of gems: the only moon in our solar system with an atmosphere worthy of a planet. This atmosphere comes complete with lightning, drizzle and occasionally a big, summer-downpour ...
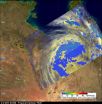
NASA measuring Tropical Storm Yasi's inland rainfall from space
2011-02-04
Tropical Cyclone Yasi has continued moving through inland Queensland, Australia and has weakened to a tropical depression today. NASA and JAXA's TRMM satellite passed over Yasi as it continued to drop moderate to heavy rainfall.
On February 3 at 0300 UTC (Feb. 2 at 10 p.m. EST/1 p.m. Australia local time) Tropical cyclone Yasi continued over land as a tropical storm. Yasi's maximum sustained winds were near 60 knots (69 mph/111 kmh). It was moving west-southwest near 20 knots/23 mph/37 kmh). It was located about 200 miles (321 km) southwest of Cairns, Australia near ...