(Press-News.org) ST. PAUL, Minn. –New research shows men and women who regularly eat berries may have a lower risk of developing Parkinson's disease, while men may also further lower their risk by regularly eating apples, oranges and other sources rich in dietary components called flavonoids. The study was released today and will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 63rd Annual Meeting in Honolulu April 9 to April 16, 2011.
Flavonoids are found in plants and fruits and are also known collectively as vitamin P and citrin. They can also be found in berry fruits, chocolate, and citrus fruits such as grapefruit.
The study involved 49,281 men and 80,336 women. Researchers gave participants questionnaires and used a database to calculate intake amount of flavonoids. They then analyzed the association between flavonoid intakes and risk of developing Parkinson's disease. They also analyzed consumption of five major sources of foods rich in flavonoids: tea, berries, apples, red wine and oranges or orange juice. The participants were followed for 20 to 22 years.
During that time, 805 people developed Parkinson's disease. In men, the top 20 percent who consumed the most flavonoids were about 40 percent less likely to develop Parkinson's disease than the bottom 20 percent of male participants who consumed the least amount of flavonoids. In women, there was no relationship between overall flavonoid consumption and developing Parkinson's disease. However, when sub-classes of flavonoids were examined, regular consumption of anthocyanins, which are mainly obtained from berries, were found to be associated with a lower risk of Parkinson's disease in both men and women.
"This is the first study in humans to examine the association between flavonoids and risk of developing Parkinson's disease," said study author Xiang Gao, MD, PhD, with the Harvard School of Public Health in Boston. "Our findings suggest that flavonoids, specifically a group called anthocyanins, may have neuroprotective effects. If confirmed, flavonoids may be a natural and healthy way to reduce your risk of developing Parkinson's disease."
###
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health.
The American Academy of Neurology, an association of more than 22,500 neurologists and neuroscience professionals, is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, brain injury, epilepsy and Parkinson's disease. For more information about the American Academy of Neurology and its upcoming Annual Meeting, visit http://www.aan.com
Eating berries may lower risk of Parkinson's
2011-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scripps Research study sheds light on RNA 'on/off switches'
2011-02-14
LA JOLLA, CA – Embargoed by the journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology until February 13, 2011, 1 PM Eastern time – Scientists from The Scripps Research Institute have shed new light on a molecular switch that turns genes on or off in response to a cell's energy needs.
The study—published February 13, 2011 in an Advance Online Publication of the journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology—shows these recently discovered RNA "riboswitches" are capable of more complex functions than originally thought. In addition, because riboswitches so far have been found ...
Prayer/Life Up for eWorld Music Award
2011-02-14
Infusing soul and incredible depth into an intoxicating blend of contemporary folk and new age music—this is the rock solid foundation for one of the hottest up and coming groups in the Christian genre. The duo of Andrea Davis-Griffin and John Stallworth teamed up to form the inspiring and thought-provoking creation known as Prayer/Life while delivering a positive message driven by faith. Their initial success is reaching new heights, and the group is asking fans to help vote for them in the eWorld Music Awards via the Boomerang Media Station.
Drawing comparisons to ...
Fleeting fluctuations in superconductivity disappear close to transition temperature
2011-02-14
UPTON, NY — As part of an ongoing effort to uncover details of how high-temperature superconductors carry electrical current with no resistance, scientists at Johns Hopkins University and the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory have measured fluctuations in superconductivity across a wide range of temperatures using terahertz spectroscopy. Their technique allows them to see fluctuations lasting mere billionths of a billionth of a second, and reveals that these fleeting fluctuations disappear 10-15 Kelvin (K) above the transition temperature (Tc) at ...
Study finds massive flux of gas, in addition to liquid oil, at BP well blowout in Gulf
2011-02-14
Athens, Ga. – A new University of Georgia study that is the first to examine comprehensively the magnitude of hydrocarbon gases released during the Deepwater Horizon Gulf of Mexico oil discharge has found that up to 500,000 tons of gaseous hydrocarbons were emitted into the deep ocean. The authors conclude that such a large gas discharge—which generated concentrations 75,000 times the norm—could result in small-scale zones of "extensive and persistent depletion of oxygen" as microbial processes degrade the gaseous hydrocarbons.
The study, led by UGA Professor of Marine ...
Aspira Continuing Education Offers The Courses Required for Already Licensed Mental Health Professionals Seeking the CA BBS Grandparenting Path to LPCC Licensure
2011-02-14
For those previously seeking MFT continuing education, there is a new path available in California. The California Board of Behavioral Sciences (CA BBS) has created a new licensing category, LPCC (licensed professional clinical counselor). This new license can be obtained not only from existing licensed professionals in California, but from those licensed in other states as well. For a short period of time, the CA BBS has made available a process to apply for their LPCC license, called the "grandparenting" path. This path will differ for those licensed outside of California ...
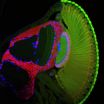
Partnership of genes affects the brain's development
2011-02-14
VIDEO:
This is a 3D-rotation through the optic lobe of a fly larva's brain. Blue are axons of the photoreceptor nerve cells, the two guidance proteins are shown in green (GoGo)...
Click here for more information.
The human brain consists of approximately one hundred billion nerve cells. Each of these cells needs to connect to specific other cells during the brain's development in order to form a fully functional organism. Yet how does a nerve cell know where it should ...
Green Vanity Provides On-Set Alternative to Environmentally Insensitive Production Units
2011-02-14
Whether it's Leonardo DiCaprio, Angelina Jolie or Natalie Portman, it seems that just about every Hollywood celebrity champions a noble environmental cause these days. But how often is this environmental concern brought directly to the film sets that such A-level stars work on? Green Vanity is a full-service mobile vanity unit that delivers environmental awareness directly to any Hollywood film set, project or event.
"The Hollywood film community has done a tremendous amount of work for the environment and raised awareness of many of the most urgent issues that concern ...
Mummies' false toes helped ancient Egyptians walk
2011-02-14
Two artificial big toes – one found attached to the foot of an ancient Egyptian mummy – may have been the world's earliest functional prosthetic body parts, says the scientist who tested replicas on volunteers.
University of Manchester researcher, Dr Jacky Finch, has shown that a three-part wood and leather artefact housed in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo, along with a second one, the Greville Chester artificial toe on display in the British Museum, not only looked the part but also helped their toeless owners walk like Egyptians.
The toes date from before 600BC, predating ...
Gonorrhea acquires a piece of human DNA
2011-02-14
CHICAGO --- If a human cell and a bacterial cell met at a speed-dating event, they would never be expected to exchange phone numbers, much less genetic material. In more scientific terms, a direct transfer of DNA has never been recorded from humans to bacteria.
Until now. Northwestern Medicine researchers have discovered the first evidence of a human DNA fragment in a bacterial genome – in this case, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the bacterium that causes gonorrhea. Further research showed the gene transfer appears to be a recent evolutionary event.
The discovery offers insight ...
Obesity takes heavy toll on knee arthritis
2011-02-14
More than 14 million visits were made to physicians' offices in 2008 by patients with knee problems. Five new studies presented at the 2011 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) look at the effect that obesity has on knee arthritis and a patient's ability to recover from knee surgery.
Does Obesity Cause Irreparable Damage To Knees Despite Weight Loss? (Embargo: February 15)
One new study found that while weight loss via bariatric surgery may improve knee pain in obese patients with knee osteoarthritis, there may be permanent damage ...