(Press-News.org) Most of us are familiar with the idea of image compression in computers. File extensions like ".jpg" or ".png" signify that millions of pixel values have been compressed into a more efficient format, reducing file size by a factor of 10 or more with little or no apparent change in image quality. The full set of original pixel values would occupy too much space in computer memory and take too long to transmit across networks.
The brain is faced with a similar problem. The images captured by light-sensitive cells in the retina are on the order of a megapixel. The brain does not have the transmission or memory capacity to deal with a lifetime of megapixel images. Instead, the brain must select out only the most vital information for understanding the visual world.
In today's online issue of Current Biology, a Johns Hopkins team led by neuroscientists Ed Connor and Kechen Zhang describes what appears to be the next step in understanding how the brain compresses visual information down to the essentials.
They found that cells in area "V4," a midlevel stage in the primate brain's object vision pathway, are highly selective for image regions containing acute curvature. Experiments by doctoral student Eric Carlson showed that V4 cells are very responsive to sharply curved or angled edges, and much less responsive to flat edges or shallow curves.
To understand how selectivity for acute curvature might help with compression of visual information, co-author Russell Rasquinha (now at University of Toronto) created a computer model of hundreds of V4-like cells, training them on thousands of natural object images. After training, each image evoked responses from a large proportion of the virtual V4 cells -- the opposite of a compressed format. And, somewhat surprisingly, these virtual V4 cells responded mostly to flat edges and shallow curvatures, just the opposite of what was observed for real V4 cells.
The results were quite different when the model was trained to limit the number of virtual V4 cells responding to each image. As this limit on responsive cells was tightened, the selectivity of the cells shifted from shallow to acute curvature. The tightest limit produced an eight-fold decrease in the number of cells responding to each image, comparable to the file size reduction achieved by compressing photographs into the .jpeg format. At this level, the computer model produced the same strong bias toward high curvature observed in the real V4 cells.
Why would focusing on acute curvature regions produce such savings? Because, as the group's analyses showed, high-curvature regions are relatively rare in natural objects, compared to flat and shallow curvature. Responding to rare features rather than common features is automatically economical.
Despite the fact that they are relatively rare, high-curvature regions are very useful for distinguishing and recognizing objects, said Connor, a professor in the Solomon H. Snyder Department of Neuroscience in the School of Medicine, and director of the Zanvyl Krieger Mind/Brain Institute.
"Psychological experiments have shown that subjects can still recognize line drawings of objects when flat edges are erased. But erasing angles and other regions of high curvature makes recognition difficult," he explained
Brain mechanisms such as the V4 coding scheme described by Connor and colleagues help explain why we are all visual geniuses.
"Computers can beat us at math and chess," said Connor, "but they can't match our ability to distinguish, recognize, understand, remember, and manipulate the objects that make up our world." This core human ability depends in part on condensing visual information to a tractable level. For now, at least, the .brain format seems to be the best compression algorithm around.
INFORMATION:
To learn more about the Mind/Brain Institute, go here:
http://krieger.jhu.edu/mbi/.
JPEG for the mind: How the brain compresses visual information
2011-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study examines phenomenon of women caring for ex-husbands
2011-02-14
COLUMBIA, Mo. – The aging population, 65 years and older, includes nearly 3.8 million divorced men and women, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. Illnesses and end-of-life issues can be particularly difficult for singles without spouses or designated caregivers. A new study from the University of Missouri provides insight into the experiences of exes who care for their former spouses, offering support, assistance with daily tasks and management of health needs.
"The concept of women as caregivers for their ex-husbands is largely unexplored," said Teresa Cooney, associate ...
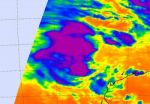
NASA infrared satellite data gives System 96S a fair shot at becoming a tropical cyclone
2011-02-14
A low pressure area located a couple of hundred miles northwest of Western Australia appears in a better position for development into a tropical cyclone according to infrared NASA satellite imagery. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows some strong convection in the low, named System 96S.
When Aqua passed over System 96S on Feb. 9 at 17:47 UTC (12:47 p.m. EST), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument showed some strong convection and strong thunderstorms with very cold cloud-top temperatures around the center of circulation. Those cloud top temperatures ...
WSU researcher designs multilingual instruction materials for world's largest mall
2011-02-14
Housing 1,200 stores, an underwater zoo, a SEGA indoor theme park, an Olympic-size ice rink, a 22-screen Cineplex and the world's largest gold market, the Dubai Mall is a retail marvel that attracts tourists from around the world. Thanks to one Wayne State researcher, its multilingual, multicultural employees are using an efficient, cost-effective instructional process to learn their job duties.
Monica W. Tracey, Ph.D., associate professor of instructional technology and administrative and organizational studies in WSU's College of Education and resident of Farmington ...
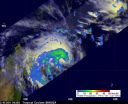
2 NASA satellites see a newborn tropical storm near Madagascar
2011-02-14
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center were keeping a close eye on a low pressure area known as System 94S yesterday, and satellite data helped confirm that today it has strengthened into Tropical Storm Bingiza.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured this image of Tropical Storm Bingiza at 06:30 UTC (1:30 a.m. EST) on its approach to Madagascar. The highest, strongest thunderstorms appeared almost bubble-like near the center of the storm's circulation.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission ...
321Soft Announces New Release of Data Recovery for Mac 5.0.0
2011-02-14
321Soft Data Recovery for Mac is professional and user-friendly Mac data recovery software to recover data lost due to accidental deleting, formatting, virus infection, unexpected power failure, and other unknown reasons. It compatible with HFS+, FAT16/32, NTFS ISO9660, UDF, and EXT2/3 file system volumes, It is non-destructive data recovery software and will not write or make changes to the drive it is recovering from. all recovered files must be saved to another storage device or another drive letter in the system.
Key Features of 321Soft Data Recovery for Mac 5.0.0 ...
Changing views about saturated fat and cardiovascular disease
2011-02-14
(Rosemont, IL) Feb. 10 – For generations, the consumption of dairy products has been positively associated with the health and wellness of families and communities. Nevertheless, the recent shift in dietary trends has focused on "what not to eat" instead of emphasizing "what to eat," resulting in demonizing the naturally occurring fats in dairy, while overlooking its many essential nutrients.
However, the long-held beliefs about the impact of saturated fatty acids (SFA) on the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) are being challenged by a new perspectives paper from ...
123Decal Acquires The Banner Factory.
2011-02-14
123Decal a consistent leader in the Custom Decal industry has recently announed the aquistion of The Banner Factory.
The Banner Factory is a wholesale provider of Custom Banners, Vinyl Banners Flag Banners and More. They have provided banners to clients locally as well as on a national basis. Althought the details of the aquisition were not yet available, it is rumored that 123Decal is looking to expand their product lines after explosive growth in the custom decal industry.
123Decal just finished a year of their highest sales in company history. They are well position ...
Trial will test whether surgery is the best option for type 2 diabetes
2011-02-14
NEW YORK (Feb. 10, 2011) -- A new clinical trial at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center is among the first to test surgery specifically for Type 2 diabetes. The aim of the study is to understand whether surgery can control diabetes, as well or even better than the best medical treatment available today. This is the first study of its kind open to patients who are overweight or mildly obese.
Under current guidelines, bariatric surgery is only indicated for the treatment of severe or morbid obesity, defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of ...
Seismology highlights from BSSA February issue
2011-02-14
A sequence of small earthquakes that occurred at the Dallas-Fort Worth Airport between October 30, 2008 and May 31, 2009 were likely triggered by the disposal of brines accompanying natural gas production at a nearby well that had recently been completed, according to research published in the February issue of the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America (BSSA).
Many residents of the Dallas-Fort Worth area felt small earthquakes, which had magnitudes between 2.2 and 3.3, prompting scientists to investigate. The area, home to more than four million residents, ...
New On-Line Media Expert/Source Directory Now In Use By Major Media Outlets
2011-02-14
Media professionals across North America are using the new http://www.guestmatch.com as a quick and easy resource when searching for interview guests, story sources and experts in a variety of topics.
GuestMatch.com features on-line media kits for hundreds of expert sources in all fields, and includes backgrounders, hi res photos, video and audio samples and best of all, direct contact phone numbers and email addresses for each GuestMatch member.
In addition to a search feature that allows media members to sort both by topic, name, program idea and area of expertise, ...