(Press-News.org) An international team of astronomers has identified for the first time a thick stellar disc in the Andromeda galaxy, the nearest large spiral galaxy to our own Milky Way.
The discovery of the thick disc, a major result from a five-year investigation, will help astronomers better understand the processes involved in the formation and evolution of large spiral galaxies like ours, according to the team, which includes UCLA research astronomer Michael Rich and colleagues from Europe and Australia.
Using the Keck Telescope in Hawaii, the astronomers analyzed the velocities of individual bright stars within the Andromeda galaxy and were able to observe a group of stars tracing a thick disc — distinct from those comprising the galaxy's already-known thin disc — and assessed how these stars differ from thin-disc stars in height, width and chemistry.
Approximately 70 percent of Andromeda's stars are contained in the galaxy's thin stellar disc. This disc structure contains the spiral arms traced by regions of active star formation, and it surrounds a central bulge of old stars at the core of the galaxy.
"From observations of our own Milky Way and other nearby spirals, we know that these galaxies typically possess two stellar discs, both a 'thin' and a 'thick' disc," said Michelle Collins, a doctoral student at the University of Cambridge's Institute of Astronomy, who led the study.
The thick disc consists of older stars whose orbits take them along a "thicker" path — one that extends both above and below the galaxy's thin disc.
"The classical thin stellar discs that we typically see in Hubble imaging result from the accretion of gas towards the end of a galaxy's formation, whereas thick discs are produced in a much earlier phase of the galaxy's life, making them ideal tracers of the processes involved in galactic evolution," Collins said.
The formation process of thick discs is not yet well understood. Previously, the best hope for understanding this structure was by studying the thick disc present in our own Milky Way. However, much of our galaxy's thick disc is obscured from view. The discovery of a similar thick disc in Andromeda presents a much clearer view of spiral structure.
Astronomers will be able to determine the properties of the disc across the galaxy and will search for signatures of the events related to its formation, the researchers said.
"Our initial study of this component already suggests that it is likely older than the thin disc, with a different chemical composition," said UCLA's Rich, who was the principal investigator at the Keck Observatory for the observations. "Future, more detailed observations should enable us to unravel the formation of the disc system in Andromeda, with the potential to apply this understanding to the formation of spiral galaxies throughout the universe."
"This result is one of the most exciting to emerge from the larger parent survey of the motions and chemistry of stars in the outskirts of Andromeda,'' said Scott Chapman of the Institute of Astronomy at Cambridge. "Finding this thick disc has afforded us a unique and spectacular view of the formation of the Andromeda system and will undoubtedly assist in our understanding of this complex process."
###
The study is currently available in the online version of Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society and will be published in a print edition of the journal later this year.
UCLA is California's largest university, with an enrollment of more than 38,000 undergraduate and graduate students. The UCLA College of Letters and Science and the university's 11 professional schools feature renowned faculty and offer 328 degree programs and majors. UCLA is a national and international leader in the breadth and quality of its academic, research, health care, cultural, continuing education and athletic programs. Six alumni and five faculty have been awarded the Nobel Prize.
For more news, visit the UCLA Newsroom and follow us on Twitter.
Astronomers identify thick disc of older stars in nearby Andromeda galaxy
2011-02-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Overabundance of protein expands breast cancer stem cells
2011-02-16
HOUSTON - An essential protein for normal stem cell renewal also promotes the growth of breast cancer stem cells when it's overproduced in those cells, researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center report in the February edition of Cancer Cell.
In mouse and lab experiments, the team also discovered that two drugs block the cascade of molecular events that they describe in the paper, thwarting formation of breast tumor-initiating cells.
"Overexpression of the EZH2 protein has been linked to breast cancer progression, but the molecular details of that ...
New material provides 25 percent greater thermoelectric conversion efficiency
2011-02-16
AMES, Iowa – Automobiles, military vehicles, even large-scale power generating facilities may someday operate far more efficiently thanks to a new alloy developed at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory. A team of researchers at the Lab that is jointly funded by the DOE Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, achieved a 25 percent improvement in the ability of a key material to convert heat into electrical energy.
"What happened here has not happened anywhere else," ...
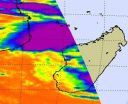
NASA Satellite sees most of Cyclone Bingiza's rainfall over Mozambique Channel
2011-02-16
Infrared data from NASA's AIRS instrument revealed that the low level center of Cyclone Bingiza was still over land in western Madagascar this morning, but the bulk of its rainfall was over the Mozambique Channel.
When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Madagascar this morning, Feb. 15 at 11:11 UTC (6:11 a.m. EST), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument read the temperatures of the cold thunderstorm cloud tops in Cyclone Bingiza. Most of the strongest thunderstorms were north and west of the center of circulation already over the Mozambique Channel, while Bingiza's ...
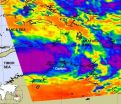
NASA Satellite sees two 'tropical fists' threatening Australia
2011-02-16
Australia is getting hit with two "tropical fists" as NASA satellites watch two low pressure areas develop near the Northern Territory and Western Australia. System 99S is currently strengthening near Darwin, Australia and another low pressure area called System 97S is strengthening near Western Australia.
System 97S was located about 210 nautical miles north-northwest of Learmonth, Western Australia, at 1800 UTC (1 p.m. EST), Feb. 15. It was centered near 19.2 South and 112.1 East. That puts the center of System 97S well to the northwest of Exmouth. System 97S is forecast ...
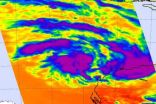
NASA Satellite catches a tropical cyclone forming near Darwin, Australia
2011-02-16
NASA's Aqua satellite captured a low pressure area known as System 99S that appears to be strengthening very close to Darwin, Australia. Aqua satellite data indicated that the strongest thunderstorms were over the Timor Sea on Feb. 15.
System 99S is a threat to Australia's Northern Territory because on Feb. 15 it was centered only 20 miles (32 km) south of Darwin, Australia, near 12.7 degrees South latitude and 130.7 degrees East longitude. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center gives System 99S a good chance for development in the next 24 hours, and NASA satellite imagery ...
Whole genome sequencing used to help inform cancer therapy
2011-02-16
SCOTTSDALE, Ariz. — Feb. 16, 2011 — Whole genome sequencing — spelling out a person's entire DNA genetic code — has moved one step closer to being a medical option for direct patient care.
Physicians and researchers at Mayo Clinic in Arizona and the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen) successfully completed sequencing both a single patients normal and cancer cells – a tour de force of more than 6 billion DNA chemical bases.
While the whole genomes of several individuals or their cancers have been sequenced in recent years, this is believed to be among the ...
Health care spending: Study shows high imaging costs for defensive purposes
2011-02-16
Nearly 35 percent of all the imaging costs ordered for 2,068 orthopaedic patient encounters in Pennsylvania were ordered for defensive purposes, according to a new study presented today at the 2011 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS).
For many years now, some physicians have ordered specific diagnostic procedures that are of little or no benefit to a patient, largely to protect themselves from a lawsuit. Until now, however, efforts to actually measure defensive medicine practices have been limited primarily to surveys sent to physicians. ...
How To Use "The Ex Back System" To Avoid The Valentine's Day Hangover Blues!
2011-02-16
There are three things women usually do when trying to get their ex boyfriend back, but those actions will only succeed in persuading them to run in the opposite direction. The comprehensive multimedia program by Brian Bold, "The Ex Back System," helps women avoid those pitfalls and points them in the right direction to avoiding the Valentine's Day Hangover Blues!
"Women make three mistakes when a relationship breaks up," said Bold. "They act desperate, they tell their ex that this time will be different, and they constantly try to contact their ex. Instead of bringing ...
New Treatment Now Available For Herniated And Degenerated Disc
2011-02-16
A relatively new treatment is available for difficult back pain, low back pain and neck pain in Atlanta. It is called spinal decompression. It is somewhat like traction, but more sophisticated in its engineering. The reason it usually helps patients is based on a simple, factual premise- as we age, our spines get more compressed. Eventually, this can cause pain and disability.
This new spinal decompression treatment is the most effective way we have had to reverse this process. Reversing spinal compression is the most direct way to treat pain and disability that arises ...
Top Realtor Ann Brizolis Partners with IDX MLS Technology to Make Finding a Home Easy
2011-02-16
Ann Brizolis, Southern California's top specialist in Rancho Santa Fe real Estate for sale partnered with Laguna Beach based Virtual Results to provide state-of-the-art IDX technology on her easy-to-use website last week. Designed to help Rancho Santa Fe home buyers improve their ability to research and find homes in record time, this website features innovative online technology sets Brizolis' team apart as they seek to improve and enhance the home buying experience for each and every client.
"At ranchosantaferealestatefinder.com we try hard to give our clients the ...