(Press-News.org) Boston, MA – An estimated 10 million Americans suffer from knee osteoarthritis (OA), making it one of the most common causes of disability in the US. Due to obesity and symptomatic knee OA, Americans over the age of 50 will together lose the equivalent of 86 million healthy years of life, concluded researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), who investigated the potential gains in quality and quantity of life that could be achieved averting losses due to obesity and knee OA. These findings are published in the February 15 issue of Annals of Internal Medicine.
"Reducing obesity to levels observed in 2000 would prevent 172,792 cases of coronary heart disease, 710,942 cases of diabetes, and 269,934 total knee replacements," said Elena Losina, PhD lead author of the study and co-director of Orthopedics and Arthritis Center for Outcomes Research in the Dept of Orthopedic Surgery at BWH. "All told, it would save roughly 19.5 million years of life among US adults aged 50-84."
Experts have long known that knee osteoarthritis is on the rise among Americans, due in part to the growing obesity epidemic and longer life expectancy. Obesity and knee OA are among the most frequent chronic conditions in older Americans. However, how that translates into years of healthy life lost has not been accurately estimated. Dr. Losina and colleagues used a mathematical simulation model to assemble national data on the occurrence of knee OA, obesity and other important conditions such as coronary heart disease, diabetes, cancer and chronic lung disease. Their analysis examines the contribution of both obesity and knee OA to losses in quantity and quality of life. It also evaluates how those losses are distributed among racial and ethnic subpopulations in the United States.
"There are 86 million healthy years of life at stake, a disproportionate number of them being lost by Black and Hispanic women," said Jeffrey N. Katz, MD, Director of the Orthopedics and Arthritis Center for Outcomes Research at the BWH and a senior author of the study. "These staggering numbers may help patients and physicians to better grasp the scale of the problem and the potential benefits of behavior change."
###
This study was funded by grants from National Institute of Arthritis, Musculoskeletal and Skin Disease and the Arthritis Foundation. Contributing authors include Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, MPH, Massachusetts General Hospital, William M. Reichmann, MA, Holly L. Holt, Hanna Gerlovin, Daniel H. Solomon, MD, MPH and Jeffrey N. Katz, from Brigham and Women's Hospital, David Hunter MD from University of Sydney, Australia, Joanne M. Jordan, MD from University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, Drs. Lisa Suter and A. David Paltiel, from Yale University School of Medicine.
Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) is a 793-bed nonprofit teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School and a founding member of Partners HealthCare, an integrated health care delivery network. BWH is the home of the Carl J. and Ruth Shapiro Cardiovascular Center, the most advanced center of its kind. BWH is committed to excellence in patient care with expertise in virtually every specialty of medicine and surgery. The BWH medical preeminence dates back to 1832, and today that rich history in clinical care is coupled with its national leadership in quality improvement and patient safety initiatives and its dedication to educating and training the next generation of health care professionals. Through investigation and discovery conducted at its Biomedical Research Institute (BRI), BWH is an international leader in basic, clinical and translational research on human diseases, involving more than 900 physician-investigators and renowned biomedical scientists and faculty supported by more than $ 537 M in funding. BWH is also home to major landmark epidemiologic population studies, including the Nurses' and Physicians' Health Studies and the Women's Health Initiative. For more information about BWH, please visit www.brighamandwomens.org.
Obesity and knee osteoarthritis shorten healthy years of life
Researchers estimate healthy years of life losses due to obesity and knee osteoarthritis in Americans 50-84 years of age
2011-02-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
If greenhouse gas emissions stopped now, Earth still would likely get warmer
2011-02-16
While governments debate about potential policies that might curb the emission of greenhouse gases, new University of Washington research shows that the world is already committed to a warmer climate because of emissions that have occurred up to now.
There would continue to be warming even if the most stringent policy proposals were adopted, because there still would be some emission of heat-trapping greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. But the new research shows that even if all emissions were stopped now, temperatures would remain higher than pre-Industrial ...
Peer support offers promise for reducing depression symptoms
2011-02-16
Peer support offers promise as an effective, low-cost tool for fighting depression, a new study by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System and University of Michigan Health System finds.
Programs in which patients and volunteers share information were found to reduce symptoms of depression better than traditional care alone and were about as effective as cognitive behavioral therapy, researchers found after analyzing 10 randomized trials of peer support interventions for depression dating from 1987 to 2009.
The analysis was the first of its kind to look at peer support specifically ...
4.7 million Californians to gain coverage under health reform, new study estimates
2011-02-16
Up to two-thirds of California's 7 million uninsured residents will become eligible for health insurance coverage when health care reform is implemented in 2014, according to a new policy brief from the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research.
The study draws on the latest data from the California Health Interview Survey (CHIS), which will be released shortly.
The policy brief, "Two-thirds of California's 7 Million Uninsured May Obtain Coverage Under Health Care Reform," finds that 4.7 million Californians, including both adults and children, will likely be eligible ...
Payoffs of long-term investment in education research
2011-02-16
WASHINGTON, D.C.—Leading scholars and private foundation presidents shared the Capitol Hill stage to highlight the payoffs of long-term investment in education research at a Capitol Hill briefing on Monday, February 14, 2011. Speakers emphasized that education research based on long-term funding has led to important payoffs for education policy and practice in such areas as resource allocation, school and classroom organization, and the education and evaluation of teachers.
The Education Deans Alliance, American Educational Research Association, and the National Academy ...
NIH-funded study finds new possible risk factor of heart disease
2011-02-16
Abnormal heart rate turbulence is associated with an increased risk of heart disease death in otherwise low-risk older individuals, according to a study funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), part of the National Institutes of Health.
This study appears in the Feb. 15 edition of the Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology.
Among the nearly 1,300 study participants, heart rate turbulence, which reflects how well the heart reacts to occasional premature contractions, was an even stronger heart disease risk factor than elevated levels of C-reactive ...
Designing new molecular tools to study the life and death of a cancer cell
2011-02-16
Basic and translational research on cancer, and development of new cancer therapeutics, has focused on different aspects of cancer cellular function. One area of focus is the life and death of a cancer cell. Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a fundamental process of cells including cancer cells. The signal transduction pathways of apoptosis involve many different proteins and their interactions with each other. Protein-protein interactions involved in these apoptotic signals, like those in many other biological processes, are often determined or influenced ...
Astronomers identify thick disc of older stars in nearby Andromeda galaxy
2011-02-16
An international team of astronomers has identified for the first time a thick stellar disc in the Andromeda galaxy, the nearest large spiral galaxy to our own Milky Way.
The discovery of the thick disc, a major result from a five-year investigation, will help astronomers better understand the processes involved in the formation and evolution of large spiral galaxies like ours, according to the team, which includes UCLA research astronomer Michael Rich and colleagues from Europe and Australia.
Using the Keck Telescope in Hawaii, the astronomers analyzed the velocities ...
Overabundance of protein expands breast cancer stem cells
2011-02-16
HOUSTON - An essential protein for normal stem cell renewal also promotes the growth of breast cancer stem cells when it's overproduced in those cells, researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center report in the February edition of Cancer Cell.
In mouse and lab experiments, the team also discovered that two drugs block the cascade of molecular events that they describe in the paper, thwarting formation of breast tumor-initiating cells.
"Overexpression of the EZH2 protein has been linked to breast cancer progression, but the molecular details of that ...
New material provides 25 percent greater thermoelectric conversion efficiency
2011-02-16
AMES, Iowa – Automobiles, military vehicles, even large-scale power generating facilities may someday operate far more efficiently thanks to a new alloy developed at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory. A team of researchers at the Lab that is jointly funded by the DOE Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, achieved a 25 percent improvement in the ability of a key material to convert heat into electrical energy.
"What happened here has not happened anywhere else," ...
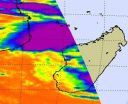
NASA Satellite sees most of Cyclone Bingiza's rainfall over Mozambique Channel
2011-02-16
Infrared data from NASA's AIRS instrument revealed that the low level center of Cyclone Bingiza was still over land in western Madagascar this morning, but the bulk of its rainfall was over the Mozambique Channel.
When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Madagascar this morning, Feb. 15 at 11:11 UTC (6:11 a.m. EST), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument read the temperatures of the cold thunderstorm cloud tops in Cyclone Bingiza. Most of the strongest thunderstorms were north and west of the center of circulation already over the Mozambique Channel, while Bingiza's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Obesity and knee osteoarthritis shorten healthy years of lifeResearchers estimate healthy years of life losses due to obesity and knee osteoarthritis in Americans 50-84 years of age