(Press-News.org) When doctors discover high concentrations of regulatory T cells in the tumors of breast cancer patients, the prognosis is often grim, though why exactly has long been unclear.
Now new research at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine suggests these regulatory T cells, whose job is to help mediate the body's immune response, produce a protein that appears to hasten and intensify the spread of breast cancer to distant organs and, in doing so, dramatically increase the risk of death.
The findings are reported in the Feb. 16 advance online edition of the journal Nature.
The researchers found that mice with breast cancer were more likely to develop metastatic lung cancer due to elevated levels of RANKL, an inflammatory protein normally involved in bone remodeling. Regulatory T cells were found to be the primary source of RANKL in these tumors. However, the same increase in metastasis was seen when synthetic RANKL was injected directly into tumors, suggesting that RANKL was the key to the ability of regulatory T cells to promote the spread of breast cancer. The scientists also determined that interfering with the ability of RANKL to interact with cancer cells seemed to block tumor progression, and may represent a potential target for drug therapy.
"What is exciting about this study is that now that we understand an increase in RANKL translates to an increase in metastasis, we can get to work on figuring out ways to stop or slow the production of RANKL in breast cancer patients," said Michael Karin, PhD, Distinguished Professor of Pharmacology and Pathology at UCSD's Laboratory of Gene Regulation and Signal Transduction and Moores Cancer Center.
RANKL is a well-known factor in a variety of degenerative bone diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and bone metastasis. In June 2010, the Food and Drug Administration approved the first RANKL-inhibiting drug for use in postmenopausal women at risk for osteoporosis.
"When we were able to control the RANKL production in the mice, we were able to slow or stop the spread of the cancer," Karin said. "The next logical step is to turn to drugs that block RANKL production to see how they might affect the spread of breast cancer."
Other breast cancer studies have linked RANKL to early stages in the development of synthetic progestin-driven breast tumors. According to the Women's Health Initiative and the Million Women Study, hormone replacement therapy and contraceptives with progestin significantly increase the risk of developing breast cancer. The findings from these studies and the new UCSD research suggest that drugs that block RANKL may be effective in preventing both the early stages of breast cancer and the advanced progression of the disease.
###
Collaborators on the study are first authors Wei Tan and Weizhou Zhang, Amy Strasner and Sergei Grivennikov, UCSD Laboratory of Gene Regulation and Signal Transduction; Jin Q. Cheng, Department of Molecular Oncology, H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, Fla.; and Robert M. Hoffman, AntiCancer Inc, San Diego.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation and Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America.
Key culprit identified in breast cancer metastasis
2011-02-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Regrowing hair: UCLA-VA researchers may have accidentally discovered a solution
2011-02-17
It has been long known that stress plays a part not just in the graying of hair but in hair loss as well. Over the years, numerous hair-restoration remedies have emerged, ranging from hucksters' "miracle solvents" to legitimate medications such as minoxidil. But even the best of these have shown limited effectiveness.
Now, a team led by researchers from UCLA and the Veterans Administration that was investigating how stress affects gastrointestinal function may have found a chemical compound that induces hair growth by blocking a stress-related hormone associated with ...
1 group of enzymes could have a positive impact on health, from cholesterol to osteoporosis
2011-02-17
Montreal, February 16, 2011 – Recent studies conducted at the Institut de recherches cliniques de Montréal (IRCM) on a group of PCSK enzymes could have a positive impact on health, from cholesterol to osteoporosis. A team led by Dr. Nabil G. Seidah, Director of the Biochemical Neuroendocrinology research unit, has published six articles in prestigious scientific journals over the past four months, all shedding light on novel functions of certain PCSK enzymes.
PCSK enzymes belong to the proprotein convertase family, responsible for the conversion of an inactive protein ...
Neurologists develop software application to help identify subtle epileptic lesions
2011-02-17
Researchers from the Department of Neurology at NYU Langone Medical Center identified potential benefits of a new computer application that automatically detects subtle brain lesions in MRI scans in patients with epilepsy. In a study published in the February 2011 issue of PLoS ONE, the authors discuss the software's potential to assist radiologists in better identifying and locating visually undetectable, operable lesions.
"Our method automatically identified abnormal areas in MRI scans in 92 percent of the patients sampled, which were previously identified by expert ...
Increasing brain enzyme may slow Alzheimer's disease progression
2011-02-17
LOS ANGELES – Increasing puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase, the most abundant brain peptidase in mammals, slowed the damaging accumulation of tau proteins that are toxic to nerve cells and eventually lead to the neurofibrillary tangles, a major pathological hallmark of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia, according to a study published online in the journal, Human Molecular Genetics.
Researchers found they could safely increase the puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase, PSA/NPEPPS, by two to three times the usual amount in animal models, and it removed the ...
Hip, thigh implants can raise bone fracture risk in children
2011-02-17
Children with hip and thigh implants designed to help heal a broken bone or correct other bone conditions are at risk for subsequent fractures of the very bones that the implants were intended to treat, according to new research from Johns Hopkins Children's Center.
Findings of the Johns Hopkins study, based on an analysis of more than 7,500 pediatric bone implants performed at Hopkins over 15 years, will be presented Feb. 16 at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Although the absolute risk among the patients was relatively small — nine ...
Erg gene key to blood stem cell 'self-renewal'
2011-02-17
Scientists from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute have begun to unravel how blood stem cells regenerate themselves, identifying a key gene required for the process.
The discovery that the Erg gene is vitally important to blood stem cells' unique ability to self-renew could give scientists new opportunities to use blood stem cells for tissue repair, transplantation and other therapeutic applications.
Professor Doug Hilton, Dr Samir Taoudi and colleagues from the institute's Molecular Medicine and Cancer and Haematology divisions led the study. Dr Taoudi said the research ...
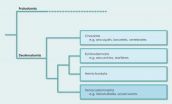
Xenacoelomorpha -- a new phylum in the animal kingdom
2011-02-17
An international team of scientists including Albert Poustka from the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics in Berlin has discovered that Xenoturbellida and the acoelomorph worms, both simple marine worms, are more closely related to complex organisms like humans and sea urchins than was previously assumed. As a result they have made a major revision to the phylogenetic history of animals. Up to now, the acoelomate worms were viewed as the crucial link between simple animals like sponges and jellyfish and more complex organisms. It has now emerged that these animals ...
Tau-induced memory loss in Alzheimer's mice is reversible
2011-02-17
VIDEO:
To test their capacity to learn, the mice are trained to find an underwater platform which is not visible to them from the edge of a water basin. The swimming...
Click here for more information.
Amyloid-beta and tau protein deposits in the brain are characteristic features of Alzheimer disease. The effect on the hippocampus, the area of the brain that plays a central role in learning and memory, is particularly severe. However, it appears that the toxic effect of tau ...
Insects hold atomic clues about the type of habitats in which they live
2011-02-17
Scientists have discovered that insects contain atomic clues as to the habitats in which they are most able to survive. The research has important implications for predicting the effects of climate change on the insects, which make up three-quarters of the animal kingdom.
Applying a method previously only used to examine the possible effects of climate change on plants, scientists from the University of Cambridge can now determine the climatic tolerances of individual insects. Their research was published today, 16 February, in the scientific journal Biology Letters.
Because ...
Researchers link gene mutations to Ebstein's anomaly
2011-02-17
Ebstein's anomaly is a rare congenital valvular heart disease. Now, in patients with this disease, researchers of the Academic Medical Center Amsterdam in the Netherlands, the University of Newcastle, UK and the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch have identified mutations in a gene which plays an important role in the structure of the heart. The researchers hope that these findings will lead to faster diagnosis and novel, more specifically targeted treatment methods (Circulation Cardiovascular Genetics, DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.110.957985)*.
Ebstein's ...