(Press-News.org) What should you do when you really, REALLY have to "go"? Make important life decisions, maybe. Controlling your bladder makes you better at controlling yourself when making decisions about your future, too, according to a study to be published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Sexual excitement, hunger, thirst—psychological scientists have found that activation of just one of these bodily desires can actually make people want other, seemingly unrelated, rewards more. Take, for example, a man who finds himself searching for a bag of potato chips after looking at sexy photos of women. If this man were able to suppress his sexual desire in this situation, would his hunger also subside? This is the sort of question Mirjam Tuk, of the University of Twente in the Netherlands, sought to answer in the laboratory.
Tuk came up with the idea for the study while attending a long lecture. In an effort to stay alert, she drank several cups of coffee. By the end of the talk, she says, "All the coffee had reached my bladder. And that raised the question: What happens when people experience higher levels of bladder control?" With her colleagues, Debra Trampe of the University of Groningen and Luk Warlop of the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Tuk designed experiments to test whether self-control over one bodily desire can generalize to other domains as well.
In one experiment, participants either drank five cups of water (about 750 milliliters), or took small sips of water from five separate cups. Then, after about 40 minutes—the amount of time it takes for water to reach the bladder—the researchers assessed participants' self-control. Participants were asked to make eight choices; each was between receiving a small, but immediate, reward and a larger, but delayed, reward. For example, they could choose to receive either $16 tomorrow or $30 in 35 days.
The researchers found that the people with full bladders were better at holding out for the larger reward later. Other experiments reinforced this link; for example, in one, just thinking about words related to urination triggered the same effect.
"You seem to make better decisions when you have a full bladder," Tuk says. So maybe you should drink a bottle of water before making a decision about your stock portfolio, for example. Or perhaps stores that count on impulse buys should keep a bathroom available to customers, since they might be more willing to go for the television with a bigger screen when they have an empty bladder.
The results were a little surprising from a theoretical point of view; a lot of research in psychology has supported the concept of "ego depletion"—that having to restrain yourself wears out your brain and makes it harder to exert self-control over something else. But Tuk says this seems to work in a different way, maybe because bladder control is largely an automatic, unconscious process.
###
For more information about this study, please contact Mirjam Tuk at m.a.tuk@utwente.nl.
The APS journal Psychological Science is the highest ranked empirical journal in psychology. For a copy of the article "Inhibitory Spillover: Increased Urination Urgency Facilitates Impulse Control in Unrelated Domains" and access to other Psychological Science research findings, please contact Keri Chiodo at 202-293-9300 or kchiodo@psychologicalscience.org.
Full bladder, better decisions? Controlling your bladder decreases impulsive choices
2011-03-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MIT-- parts of brain can switch functions
2011-03-01
Cambridge, MASS- When your brain encounters sensory stimuli, such as the scent of your morning coffee or the sound of a honking car, that input gets shuttled to the appropriate brain region for analysis. The coffee aroma goes to the olfactory cortex, while sounds are processed in the auditory cortex.
That division of labor suggests that the brain's structure follows a predetermined, genetic blueprint. However, evidence is mounting that brain regions can take over functions they were not genetically destined to perform. In a landmark 1996 study of people blinded early ...
Gut bacteria can control organ functions
2011-03-01
Bacteria in the human gut may not just be helping digest food but also could be exerting some level of control over the metabolic functions of other organs, like the liver, according to research published this week in the online journal mBio®. These findings offer new understanding of the symbiotic relationship between humans and their gut microbes and how changes to the microbiota can impact overall health.
"The gut microbiota enhances the host's metabolic capacity for processing nutrients and drugs and modulates the activities of multiple pathways in a variety of organ ...
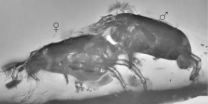
Mating mites trapped in amber reveal sex role reversal
2011-03-01
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---In the mating game, some female mites are mightier than their mates, new research at the University of Michigan and the Russian Academy of Sciences suggests. The evidence comes, in part, from 40 million-year-old mating mites preserved in Baltic amber.
In a paper published March 1 in the Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, researchers Pavel Klimov and Ekaterina Sidorchuk describe an extinct mite species in which the traditional sex roles were reversed.
"In this species, it is the female who has partial or complete control of mating," said Klimov, ...
Dry lake reveals evidence of southwestern 'megadroughts'
2011-03-01
LOS ALAMOS, New Mexico, February 28, 2011—There's an old saying that if you don't like the weather in New Mexico, wait five minutes. Maybe it should be amended to 10,000 years, according to new research.
In a letter published recently in the journal Nature, Los Alamos National Laboratory researchers and an international team of scientists report that the Southwest region of the United States undergoes "megadroughts"—warmer, more arid periods lasting hundreds of years or longer. More significantly, a portion of the research indicates that an ancient period of warming may ...
Silk moth's antenna inspires new nanotech tool with applications in Alzheimer's research
2011-03-01
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---By mimicking the structure of the silk moth's antenna, University of Michigan researchers led the development of a better nanopore---a tiny tunnel-shaped tool that could advance understanding of a class of neurodegenerative diseases that includes Alzheimer's.
A paper on the work is newly published online in Nature Nanotechnology. This project is headed by Michael Mayer, an associate professor in the U-M departments of Biomedical Engineering and Chemical Engineering. Also collaborating are Jerry Yang, an associate professor at the University of California, ...
Neighborhood barbers can influence black men to seek blood-pressure treatment
2011-03-01
DALLAS – March 1, 2011 – Will Marshall saw a physician about his blood pressure at his barber's urging.
Yes, his barber.
"The barber and beauty shops for men and women are kind of their own private escapes," Mr. Marshall said. "Every conversation you can imagine goes on in the barbershop. I wouldn't have put the barbershop and blood pressure together – but that visit to my physician for my blood pressure saved my life."
Mr. Marshall now has a healthy blood pressure thanks to lifestyle and dietary changes.
He is one of about 1,300 participants in a study described ...
Researchers looking at a rare disease make breakthrough that could benefit everyone
2011-03-01
This release is available in French.
MONTREAL, March 1, 2011 – By working with Canadians of French ancestry who suffer a rare genetic disease, researchers have discovered how three genes contribute to abnormal growth, making a breakthrough that will improve our understanding of many disorders such as foetal and childhood growth retardation, abnormal development of body parts and cancer. "As a result of the Human Genome Project, we know the basic identity of essentially all the genes in the human body, but we don't automatically know what they do in detail," explained ...
Quality of life significantly increases after uterine fibroid treatment
2011-03-01
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Women who received one of three treatments for uterine fibroids at Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston said their symptoms diminished and their quality of life significantly increased, according to a new study published in the May issue of Radiology.
Uterine fibroids are benign pelvic tumors that occur in as many as one in five women during their childbearing years. Although not all fibroids cause symptoms, some women experience heavy bleeding, pain and infertility. Treatment options include hysterectomy, minimally invasive uterine artery embolization ...
Hospital use of virtual colonoscopy is on the rise, study suggests
2011-03-01
Reston, VA (Feb. 23, 2011) — Despite the absence of Medicare coverage, hospital use of computed tomographic colonography (CTC), commonly referred to as virtual colonoscopy, is on the rise, according to a study in the March issue of the Journal of the American College of Radiology (www.jacr.org). Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. CTC, a minimally invasive alternative to optical colonoscopy for colorectal cancer screening, employs virtual reality technology to produce a 3-D visualization that permits a thorough evaluation of the entire ...
Is March Madness always the same?
2011-03-01
DURHAM, N.C. – Why is it that the same teams seem to dominate the annual men's collegiate basketball tournament? For that matter, why does the same small group of institutions seem to top annual best-college rankings?
According to a theory developed by a Duke University engineer, these hierarchies are not only natural, but predictable. Just as continually growing streams flow into a larger river, or smaller and smaller branches grow out from a single tree trunk, examples of these hierarchies abound in the natural world.
Whether it is a river or basketball rankings, ...