(Press-News.org) Mild heart failure patients with a particular condition that results in disorganized electrical activity throughout the heart benefit substantially from cardiac resynchronization therapy with defibrillator (CRT–D), according to a study published in the American Heart Association journal Circulation.
In patients with the condition, known as left bundle branch block or LBBB, CRT-D therapy reduced heart failure progression and the risk of ventricular tachyarrhythmias, fast and potentially life-threatening heart rhythms. Heart failure patients without LBBB did not receive any benefit from the therapy.
The analysis, based on the major study which tested the device – the MADIT-CRT trial – led the FDA to extend the approval of the CRT-D in September 2010 to patients with mild heart failure and LBBB to prevent progression to advanced heart failure. The device, developed by Boston Scientific, was originally approved to treat patients with severe heart failure.
"This study allowed us to identify the specific set of patients that receive the greatest benefit from this device," said Wojciech Zareba, M.D., Ph.D., lead study author and director of the Heart Research Follow-up Program at the University of Rochester Medical Center. "Our analysis highlights the fact that this therapy is not equally effective in all mild heart failure patients and was the basis of the FDA's approval of the therapy only in patients with left bundle branch block."
Zareba's team found that patients with LBBB who received CRT-D therapy had a significant 53 percent reduction in the risk of a heart failure event, such as being hospitalized with heart failure symptoms, or death, compared to LBBB patients who only received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). The risk of ventricular tachyarrhythmias was also considerably less in LBBB patients with CRT-D.
CRT-D therapy combines an ICD, which senses dangerous abnormal heart rhythms and attempts to shock the heart back into a normal rhythm, with cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), which coordinates the beating of the heart so it can pump blood throughout the body more effectively.
The study included 1,817 patients and researchers analyzed electrocardiograms – maps of the heart's electrical activity – to determine which patients had electrical disturbances and what type. Seventy percent of study participants had LBBB. LBBB patients were more often female and had higher rates of non-ischemic heart disease, a disorder typically characterized by inflammatory scarring of the heart muscle.
Study authors evaluated the effects of CRT-D versus ICD therapy in patients with and without LBBB. They found that in LBBB patients, CRT-D therapy effectively prevented deterioration of the heart, otherwise known as cardiac remodeling, by preventing enlargement of the heart with more effective contraction of the heart.
"We believe this therapy is so effective in patients with LBBB because their hearts don't contract in a synchronous way, rather, the pumping action is quite out of sync," noted Zareba. "CRT-D therapy paces the heart and makes these patients much better very quickly."
Beyond mild heart failure patients, the results are leading experts to rethink current guidelines recommending the use of CRT-D therapy for all advanced heart failure patients. In this age of personalized medicine, as treatments are continually directed towards subsets of patients with particular characteristics or biologic markers, the group of advanced heart failure patients that receive CRT-D therapy may be narrowed to those with LBBB, as well.
INFORMATION: END
Researchers pinpoint patients who receive greatest benefit from heart failure treatment
2011-03-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists discover genetic switch that increases muscle blood supply
2011-03-02
Many people suffer from a devastating condition known as critical limb ischemia (CLI) that can lead to muscle wasting and even amputation. The disease is linked to the blockage of blood flow to the skeletal muscle and current treatment options include rehabilitative exercise and surgical bypass of blood vessels. New preclinical research suggests there may be a way to restore blood supply in skeletal muscle without traditional intervention.
Scientists at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) and the Salk Institute for Biological Studies ...
OFC/NFOEC 2011: Advances in wireless, data centers, cloud computing, network capacity
2011-03-02
WASHINGTON, March 1—The world's largest international conference on
optical communications will take place March 6-10 at the Los Angeles Convention Center. The Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exposition/National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference (OFC/NFOEC) is the premier telecom meeting where experts from industry and academia share their results, experiences, and insights on the future of electronic and wireless communication and optical technologies. More than 10,000 attendees and an exhibit with 500 companies are expected.
CONFERENCE HIGHLIGHTS
Plenary ...
For first time, scientists show an HIV vaccine impacts the genetic makeup of the virus
2011-03-02
An AIDS vaccine tested in people, but found to be ineffective, influenced the genetic makeup of the virus that slipped past. The findings suggest new ideas for developing HIV vaccines.
The results were published Feb. 27 in Nature Medicine.
This is the first evidence that vaccine-induced cellular immune responses against HIV-1 infection exert selective pressure on the virus. "Selective pressure" refers to environmental demands that favor certain genetic traits over others.
The senior author of the multi-institutional study is Dr. James I. Mullins, University of Washington ...
NASA tracks the brief life of Tropical Cyclone Atu in the southern Pacific
2011-03-02
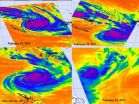
Tropical Cyclone Atu had a brief but memorable life last week, and NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a day-by-day look at its growth and death.
AIRS provides infrared images of atmospheric phenomena, oceans and land areas around the world. Basically, infrared data takes the temperature of these things. When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Cyclone Atu from February 21 through the 25 it saw thunderstorm cloud tops grow colder as the clouds grew higher and thunderstorms became more powerful. When ...
NASA's Glory Satellite scheduled for launch March 4
2011-03-02
WASHINGTON -- NASA's Glory spacecraft is scheduled for launch on Friday, March 4. Technical issues with ground support equipment for the Taurus XL launch vehicle led to the scrub of the original Feb. 23 launch attempt. Those issues have been resolved.
The March 4 liftoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., is targeted for 5:09:43 a.m. EST, in the middle of a 48-second launch window. Spacecraft separation occurs 13 minutes after launch.
Data from the Glory mission will allow scientists to better understand how the sun and tiny atmospheric particles called aerosols ...
Tanning bed exposure can be deadly when complicated by medication reactions
2011-03-02
INDIANAPOLIS – Tanning bed exposure can produce more than some tanners may bargain for, especially when they self-diagnose and use the radiation to treat skin eruptions, according to research conducted by the Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Dermatology.
"There are many reasons to be cautious of tanning bed radiation but some people use tanning beds to 'self-treat' skin eruptions," said Jeffrey B. Travers, M.D., Ph.D., senior author of a study published online in the Archives of Dermatology. "If the skin eruption is eczema or even psoriasis, a tanning ...
Discovery of source of glycogen 'manufacturing' errors sheds light on fatal disease
2011-03-02
Indiana University scientists have solved a perplexing mystery regarding one of the body's main energy storage molecules, in the process shedding light on a possible route to treatment of a rare but deadly disease in teenagers.
The disease occurs when a genetic mutation causes excessive amounts of phosphate to build up in glycogen. Glycogen is a chain-like molecule the body uses to temporarily store glucose when it's not needed to provide energy for cellular activities. The excess phosphate causes unnatural glycogen structures to appear in the body, including the brain, ...
Emergency mental health lessons learned from Continental Flight 3407 disaster
2011-03-02
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- When a disaster's physical evidence is gone -- debris removed, shooter arrested, ashes cold -- the psychological effects of the disaster on emergency responders and civilians involved still may burn.
Emergency mental health, a field often overlooked in the chaos, is a vital component of any disaster response, but may not be well represented in emergency preparedness planning.
Trained mental health responders to the Continental Flight 3407 disaster outside Buffalo in 2009 share their lessons learned on mental health preparedness in an article that ...
Queen's University professor uses nanotechnology to prolong machine and engine life
2011-03-02
Guojun Liu has discovered a way to use nanotechnology to reduce friction in automobile engines and machines.
"The technology should be useful in a wide range of machineries other than automobile engines," says Dr. Liu, a professor in the Department of Chemistry and an expert in polymer synthesis. "If implemented industrially, this nanotechnology should help prolong machine life and improve energy efficiency."
Dr Liu's team prepared miniscule polymer particles that were only tens of nanometers in size. These particles were then dispersed in automobile engine base oils. ...
Relaxation leads to lower elasticity
2011-03-02
This press release is available in German.
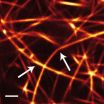
Many materials, when observed over a sufficiently long period of time, show changes in their mechanical properties. The exact course of these developments depends on the underlying microscopic mechanisms. However, the microscopic structure and the complexity of the systems make direct observation extremely difficult.
That is why a team led by Professor Andreas Bausch from the Chair of Cellular Biophysics resorted to a model system that can be precisely controlled using actin filaments, a biopolymer that, among other things, ...