(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.H. – People who feel more secure in receiving love and acceptance from others place less monetary value on their possessions, according to new research from the University of New Hampshire.
The research was conducted by Edward Lemay, assistant professor of psychology at UNH, and colleagues at Yale University. The research is presented in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology in the article "Heightened interpersonal security diminishes the monetary value of possessions."
Lemay and his colleagues found that people who had heightened feelings of interpersonal security – a sense of being loved and accepted by others – placed a lower monetary value on their possession than people who did not.
In their experiments, the researchers measured how much people valued specific items, such as a blanket and a pen. In some instances, people who did not feel secure placed a value on an item that was five times greater than the value placed on the same item by more secure people.
"People value possessions, in part, because they afford a sense of protection, insurance, and comfort," Lemay says. "But what we found was that if people already have a feeling of being loved and accepted by others, which also can provide a sense of protection, insurance, and comfort, those possessions decrease in value."
The researchers theorize that the study results could be used to help people with hoarding disorders.
"These findings seem particularly relevant to understanding why people may hang onto goods that are no longer useful. They also may be relevant to understanding why family members often fight over items from estates that they feel are rightfully theirs and to which they are already attached. Inherited items may be especially valued because the associated death threatens a person's sense of personal security," Lemay says.
###
The research was conducted by Lemay; Margaret Clark, Aaron Greenberg, Emily Hill, and David Roosth, all from Yale University; and Elizabeth Clark-Polner, from Université de Genève, Switzerland.
The University of New Hampshire, founded in 1866, is a world-class public research university with the feel of a New England liberal arts college. A land, sea, and space-grant university, UNH is the state's flagship public institution, enrolling 12,200 undergraduate and 2,300 graduate students.
PHOTO
Edward Lemay, assistant professor of psychology at UNH.
http://www.unh.edu/news/img/edward_lemay.jpg
END
According to a study conducted at the Department of Pedagogy of the University of Granada, about six out of ten male drug-abusers direct some type of violence against their intimate partners. Thus, the study revealed a high rate of domestic violence –both pysical and psychological– by male drug-abusers against women. The study also detailed the most recurrent forms of abuse, as well as the variables associated to them.
The study revealed that between 6.5 and 72.4% of the population admits to having committed some form of violence against their partner. The less prevalent ...
Washington, DC, March 3, 2011 – Community gym surfaces do not appear to be reservoirs for MRSA transmission, according to a study published in the March issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of APIC – the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology.
The purpose of the study, conducted by researchers from the University of Florida College of Medicine, was to determine whether community gymnasium equipment surfaces could harbor staphylococcal colonies and to assess whether disinfection lowers the rate of bacterial ...
Researchers at Queen's University Belfast are taking the first step towards discovering the true effectiveness of brain training exercises with the release of their own app aimed at those over 50.
The Brain Jog application is available to download free for iPhone, iPod or iPad. It is the product of 18 months of work by researchers at Queen's School of Music and Sonic Arts to find out what the over 50's are looking for in a brain training app.
Queen's researchers are encouraging as many people as possible to download and use the application. During the process, users ...
Researchers determined that carotid artery stenting (CAS) with embolic protection is an economically attractive alternative to endarterectomy (END) for patients at increased surgical risk. The study, based on data from the Stenting and Angioplasty with Protection in Patients at High Risk for Endarterectomy (SAPPHIRE) trial, found that initial procedural cost was higher with CAS, but post-procedure hospital stay was shorter which significantly offset associated costs compared to END. Details of the study—the first to evaluate the long-term cost-effectiveness of CAS versus ...
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- As carbon dioxide levels have risen during the last 150 years, the density of pores that allow plants to breathe has dwindled by 34 percent, restricting the amount of water vapor the plants release to the atmosphere, report scientists from Indiana University Bloomington and Utrecht University in the Netherlands in an upcoming issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (now online).
In a separate paper, also to be published by PNAS, many of the same scientists describe a model they devised that predicts doubling today's carbon dioxide ...
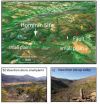
Our earliest ancestors preferred to settle in locations that have something in common with cities such as San Francisco, Naples and Istanbul -- they are often on active tectonic faults in areas that have an earthquake risk or volcanoes, or both.
An international team of scientists has established a link between the shape of the landscape and the habitats preferred by our earliest ancestors. The research, by scientists at the University of the Witwatersrand, South Africa, the University of York and the Institut de Physique du Globe Paris (IPGP), is published in the ...
Microsoft SharePoint experts have joined forces at www.sharepoint-blog.com to provide reviews, comparisons and opinions to assist clients in selecting the right collaboration software.
Group blog sites combine resources of firms to create active blog sites that build trust, get attention and attract visitors. Following the model of successful group blog sites for Microsoft Dynamics Partners including www.erpsoftwareblog.com and www.crmsoftwareblog.com this blog site will provide objective articles from Microsoft SharePoint experts nationwide. Rather than being focused ...
People in marginalized groups, such as the disabled or racial minorities, feel stigmatized—condemned, feared, or excluded—when other people stigmatize them. That's obvious. But they can also feel stigma when nobody blatantly discriminates against them or says a negative word.
These folks aren't paranoid, suggests a new study of HIV-positive people and their communities to be published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association of Psychological Science. Rather, they're picking up subtle clues from their communities.
"Society is changing when it comes to ...
Escape the humdrum tedium of everyday life, and enter Next's magical world of fabulous fragrances and indulgent beauty treats. In this deliciously sweet-smelling universe, feminine allure is complemented by olfactory art.
GET THE LOOK showcases on-trend additions to Next's RUNWAY COLLECTION colour cosmetics range including a volumising black mascara for truly luscious lashes... and oh-so-very-kissable cherry lip glosses that will certainly pump up a pout! While lush fashion lashes are wonderfully seductive, there's a terrific new dry shampoo kissed with OH MY GORGEOUS ...
A new study provides fascinating insight into the genetic basis of bipolar disorder, a highly heritable mood disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of mania and depression. The research, published by Cell Press online February 24 in the American Journal of Human Genetics, identifies a previously unrecognized susceptibility factor for bipolar disorder.
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) provide a way to systematically sort through all the DNA of many individuals in order to identify genetic variations associated with a particular disease. However, thus far these ...