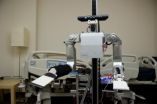
(Press-News.org) For people, being touched can initiate many different reactions from comfort to discomfort, from intimacy to aggression. But how might people react if they were touched by a robot? Would they recoil, or would they take it in stride? In an initial study, researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology found people generally had a positive response toward being touched by a robotic nurse, but that their perception of the robot's intent made a significant difference. The research is being presented today at the Human-Robot Interaction conference in Lausanne, Switzerland.
"What we found was that how people perceived the intent of the robot was really important to how they responded. So, even though the robot touched people in the same way, if people thought the robot was doing that to clean them, versus doing that to comfort them, it made a significant difference in the way they responded and whether they found that contact favorable or not," said Charlie Kemp, assistant professor in the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering at Georgia Tech and Emory University.
In the study, researchers looked at how people responded when a robotic nurse, known as Cody, touched and wiped a person's forearm. Although Cody touched the subjects in exactly the same way, they reacted more positively when they believed Cody intended to clean their arm versus when they believed Cody intended to comfort them.
These results echo similar studies done with nurses.
"There have been studies of nurses and they've looked at how people respond to physical contact with nurses," said Kemp, who is also an adjunct professor in Georgia Tech's College of Computing. "And they found that, in general, if people interpreted the touch of the nurse as being instrumental, as being important to the task, then people were OK with it. But if people interpreted the touch as being to provide comfort … people were not so comfortable with that."
In addition, Kemp and his research team tested whether people responded more favorably when the robot verbally indicated that it was about to touch them versus touching them without saying anything.
"The results suggest that people preferred when the robot did not actually give them the warning," said Tiffany Chen, doctoral student at Georgia Tech. "We think this might be because they were startled when the robot started speaking, but the results are generally inconclusive."
Since many useful tasks require that a robot touch a person, the team believes that future research should investigate ways to make robot touch more acceptable to people, especially in healthcare. Many important healthcare tasks, such as wound dressing and assisting with hygiene, would require a robotic nurse to touch the patient's body,
"If we want robots to be successful in healthcare, we're going to need to think about how do we make those robots communicate their intention and how do people interpret the intentions of the robot," added Kemp. "And I think people haven't been as focused on that until now. Primarily people have been focused on how can we make the robot safe, how can we make it do its task effectively. But that's not going to be enough if we actually want these robots out there helping people in the real world."
INFORMATION:
Video for this story is on our YouTube site at http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sKysoWzfZSI
In addition to Kemp and Chen, the research group consists of Andrea Thomaz, assistant professor in Georgia Tech's College of Computing, and postdoctoral fellow Chih-Hung Aaron King.
How do people respond to being touched by a robot?
2011-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Toward real time observation of electron dynamics in atoms and molecules
2011-03-10
Quebec City, March 9, 2011 – Another step has been taken in matter imaging. By using very short flashes of light produced by a technology developed at the national infrastructure Advanced Laser Light Source (ALLS) located at INRS University, researchers have obtained groundbreaking information on the electronic structure of atoms and molecules by observing for the first time ever electronic correlations using the method of high harmonic generation (HHG). Made by a team of researchers from the Energy, Materials, and Telecommunications Center of INRS and the National Research ...
Combating cucurbit yellow stunting disorder virus
2011-03-10
This release is available in Spanish.
U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists are working to give melon growers some relief from cucurbit yellow stunting disorder virus, or CYSDV.
In 2006, Agricultural Research Service (ARS) plant pathologist Bill Wintermantel with the U.S. Agricultural Research Station in Salinas, Calif., and university colleagues identified the plant disease that growers in California's Imperial Valley and nearby Yuma, Ariz., noticed was spreading through their cucurbit fields. Cucurbit crops affected included cantaloupe and honeydew melons.
ARS ...
Synthetic biology: TUM researchers develop novel kind of fluorescent protein
2011-03-10
This release is available in German.
Proteins are the most important functional biomolecules in nature with numerous applications in life science research, biotechnology and medicine. So how can they be modified in the most effective way to attain certain desired properties? In the past, the modifications were usually carried out either chemically or via genetic engineering. The team of Professor Arne Skerra from the TUM Chair of Biological Chemistry has now developed a more elegant combined solution: By extending the otherwise universal genetic code, the scientists are ...
Banana peels get a second life as water purifier
2011-03-10
To the surprisingly inventive uses for banana peels — which include polishing silverware, leather shoes, and the leaves of house plants — scientists have added purification of drinking water contaminated with potentially toxic metals. Their report, which concludes that minced banana peel performs better than an array of other purification materials, appears in ACS's journal Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.
Gustavo Castro and colleagues note that mining processes, runoff from farms, and industrial wastes can all put heavy metals, such as lead and copper, into ...
An advance toward blood transfusions that require no typing
2011-03-10
Scientists are reporting an "important step" toward development of a universal blood product that would eliminate the need to "type" blood to match donor and recipient before transfusions. A report on the "immunocamouflage" technique, which hides blood cells from antibodies that could trigger a potentially fatal immune reaction that occurs when blood types do not match, appears in the ACS journal, Biomacromolecules.
Maryam Tabrizian and colleagues note that blood transfusions require a correct match between a donor and the recipient's blood. This can be a tricky proposition ...
New study shows government spending preferences of Americans
2011-03-10
In its 27th survey of American spending priorities since 1973 conducted as part of its General Social Survey (GSS), NORC at the University of Chicago Wednesday released a report on its most recent findings. By a notable margin, education and health care were the top two spending priorities of Americans. And Americans are consistent in that: those two categories have finished in the top two in each of the ten surveys since 1990.
The spending priorities report is derived from recently released data of the 2010 General Social Survey which NORC has conducted for forty years. ...
New molecular robot can be programmed to follow instructions
2011-03-10
Scientists have developed a programmable "molecular robot" — a sub-microscopic molecular machine made of synthetic DNA that moves between track locations separated by 6nm. The robot, a short strand of DNA, follows instructions programmed into a set of fuel molecules determining its destination, for example, to turn left or right at a junction in the track. The report, which represents a step toward futuristic nanomachines and nanofactories, appears in ACS's Nano Letters.
Andrew Turberfield and colleagues point out that other scientists have developed similar DNA-based ...
Battling the bedbug epidemic
2011-03-10
Mom's comforting tuck-them-in-words — "Sleep tight, don't let the bedbugs bite"— is becoming an impossible dream for millions of people as the world experiences a resurgence of an ancient scourge that is fostering human misery, financial burdens and the risk of exposure to potentially toxic materials. That's the message from the cover story of the current edition of Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), ACS' weekly newsmagazine.
In the article, C&EN News Editor William G. Schulz points out that bedbugs represent a growing epidemic that is difficult to control. The bugs ...
Pinpointing air pollution's effects on the heart
2011-03-10
Scientists are untangling how the tiniest pollution particles – which we take in with every breath we breathe – affect our health, making people more vulnerable to cardiovascular and respiratory problems. While scientists know that air pollution can aggravate heart problems, showing exactly how it does so has been challenging.
In a study published recently in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, scientists showed that in people with diabetes, breathing ultrafine particles can activate platelets, cells in the blood that normally reduce bleeding from a wound, ...
Study shows how plants sort and eliminate genes over millennia
2011-03-10
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Hybrid plants with multiple genome copies show evidence of preferential treatment of the genes from one ancient parent over the genes of the other parent, even to the point where some of the unfavored genes eventually are deleted.
Brian Dilkes, an assistant professor of genetics at Purdue University, worked with a team of scientists at the University of California Davis and University of Southern California to study the genome of Arabidopsis suecica, a hybrid species with four chromosome sets formed tens of thousands of years ago from a cross between ...