(Press-News.org) In the business of concrete making, what's old—even ancient—is new again.
Almost 1,900 years ago, the Romans built what continues to be the world's largest unreinforced solid concrete dome in the world—the Pantheon. The secret, probably unknown to the Emperor Hadrian's engineers at the time, was that the lightweight concrete used to build the dome had set and hardened from the inside out. This internal curing process enhanced the material's strength, durability, resistance to cracking, and other properties so that the Pantheon continues to be used for special events to this day.
But it is only within the last decade or so that internally cured concrete has begun to have an impact on modern world infrastructure. Increasingly, internally cured concrete is being used in the construction of bridge decks, pavements, parking structures, water tanks, and railway yards, according to a review* of the current status of the new (or old) concrete technology just published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
The virtues of internally cured concrete stem from substituting light-weight, pre-wetted absorbent materials for some of the sand and/or coarse aggregates (stones) that are mixed with cement to make conventional concrete. Dispersed throughout the mixture, the water-filled lightweight aggregates serve as reservoirs that release water on an as-needed basis to nearby hydrating cement particles.
According to one study cited in the review, bridge decks made with internally cured, high-performance concrete were estimated to have a service life of 63 years, as compared with 22 years for conventional concrete and 40 years for high-performance concrete without internal curing.
"As with many new technologies, the path from research to practice has been a slow one, but as of 2010, hundreds of thousands of cubic meters" of the lighter and more durable material have been successfully used in U.S. construction, write the report's co-authors, NIST chemical engineer Dale Bentz and Jason Weiss, Purdue University civil engineering professor.
Compared with conventional varieties, internally cured concrete increases the cost of a project by 10 to 12 percent, Bentz and Weiss estimate on the basis of bridge-building projects in New York and Indiana. The increased front-end cost, they write, must be evaluated against the reduced risk of cracking, better protection against salt damage, and other improved properties that "should contribute to a more durable structure that has a longer life and lower life-cycle costs," they write. "Further, this could have substantial benefits in a reduced disruption to the traveling public, generally producing a more sustainable solution."
The 82-page report summarizes the current practice and theory of internal curing, reviews project experiences and material performance in the field, and describes opportunities for research that could lead to enhancements in the material.
INFORMATION:
* D.P. Bentz and W.J. Weiss. Internal Curing: A 2010 State-of-the-Art Review (NISTIR 7765). Feb. 2011. Available at: www.nist.gov/manuscript-publication-search.cfm?pub_id=907729.
High-tech concrete technology has a famous past
2011-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Viscous cycle: Quartz is key to plate tectonics
2011-03-18
More than 40 years ago, pioneering tectonic geophysicist J. Tuzo Wilson published a paper in the journal Nature describing how ocean basins opened and closed along North America's eastern seaboard.
His observations, dubbed "The Wilson Tectonic Cycle," suggested the process occurred many times during Earth's long history, most recently causing the giant supercontinent Pangaea to split into today's seven continents.
Wilson's ideas were central to the so-called Plate Tectonic Revolution, the foundation of contemporary theories for processes underlying mountain-building ...
NIST releases final report on Charleston sofa store fire
2011-03-18
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has released its final report on its study of the June 18, 2007, fire at the Sofa Super Store in Charleston, S.C., that trapped and killed nine firefighters, the highest number of firefighter deaths in a single event since 9/11. The final report is strengthened by clarifications and supplemental text based on comments provided by organizations and individuals in response to the draft report of the study, released for public comment on Oct. 28, 2010.
The revisions did not alter the study team's main finding: the ...
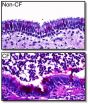
Pig model of cystic fibrosis improves understanding of disease
2011-03-18
It's been more than 20 years since scientists first discovered the gene that causes cystic fibrosis (CF), yet questions about how the mutated gene causes disease remain unanswered.
Using a newly created pig model that genetically replicates the most common form of cystic fibrosis, University of Iowa researchers have now shown that the CF protein is "misprocessed" in the pigs and does not end up in the correct cellular location. This glitch leads to disease symptoms, including gastrointestinal abnormalities and lung disease in the pigs, which mimic CF in humans. The findings ...
Online messaging delivers follow-up care for depression
2011-03-18
SEATTLE—Online messaging can deliver organized follow-up care for depression effectively and efficiently, according to a randomized controlled trial of 208 Group Health patients that the Journal of General Internal Medicine e-published in advance of print.
After five months, compared to the half of the patients randomly assigned to receive usual care, the half who had three online care management contacts with a trained psychiatric nurse were significantly more likely to feel less depressed, take their antidepressant medication as prescribed, and be "very satisfied" ...
Book Marketing: 3 Ways To Tell If You Have a Good Book Promotion Strategy by Annie Jennings PR
2011-03-18
By national publicity expert, Annie Jennings, of the famous PR firm, Annie Jennings PR
Authors are flocking to print on demand publishing and other non-traditional methods of publishing their book. With this growth of authors hitting the scene, so do a myriad of ways to promote a book. With so many choices available to them, how do author choose the right book marketing and book promotion strategy for them.
National publicity expert, Annie Jennings PR, whose national PR firm has worked with thousands of book authors, shares 3 ways to tell if you like your book marketing ...
WHOI-led report links sonar to whale strandings
2011-03-18
Scientists have long been aware of a link between naval sonar exercises and unusual mass strandings of beaked whales. Evidence of such a link triggered a series of lawsuits in which environmental groups sued the U.S. Navy to limit sonar exercises to reduce risk to whales. In 2008, this conflict rose to the level of the US Supreme Court which had to balance potential threat to whales from sonar against the military risk posed by naval forces inadequately trained to use sonar to detect enemy submarines. The court ruled that the Navy could continue training, but that it was ...
2 new SCAP documents help improve automating computer security management
2011-03-18
It's increasingly difficult to keep up with all the vulnerabilities present in today's highly complex operating systems and applications. Attackers constantly search for and exploit these vulnerabilities to commit identity fraud, intellectual property theft and other attacks. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has released two updated publications that help organizations to find and manage vulnerabilities more effectively, by standardizing the way vulnerabilities are identified, prioritized and reported.
Computer security departments work behind ...
LateRooms.com - Head to Naples for The Aesthetics of Mould
2011-03-18
The Aesthetics of Mould is a new art exhibition in Naples that examines the creative process and compares it to the way nature evolves.
Running from March 25th to April 30th 2011, it will see the work of the production duo Ttozoi displayed at the Piazza S Eframo Vecchio.
The strange and captivating images created by the artists are very modern in their approach, but lean heavily on movements such as Gutai and abstract expressionism.
According to the organisers, the art on show is a perfect example of how a piece is born when the creator finishes painting it, but ...
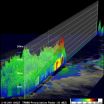
NASA satellites show towering thunderstorms in rare sub-tropical storm Arani
2011-03-18
NASA's Aqua and TRMM satellites are providing data to scientists about the Southern Atlantic Ocean Sub-tropical Storm Arani, a rare occurrence in the southern ocean. Rainfall data and cloud top temperatures revealed some heavy rain and strong thunderstorms exist in Arani as it continues to pull away from Brazil.
NOAA's Satellite and Information Service classified Arani as a T1 on the Dvorak intensity scale which would indicate an estimated wind speed of about 29 knots (~33 mph).
During the daytime on Tuesday, March 15 at 1820 UTC (2:20 p.m. EST) NASA's Tropical Rainfall ...
Physicists move closer to efficient single-photon sources
2011-03-18
Washington, D.C. (March 16, 2011) -- A team of physicists in the United Kingdom has taken a giant step toward realizing efficient single-photon sources, which are expected to enable much-coveted completely secure optical communications, also known as "quantum cryptography." The team presents its findings in Applied Physics Letters, a journal published by the American Institute of Physics.
Fluorescent "defect centers" in diamond act like atomic-scale light sources and are trapped in a transparent material that's large enough to be picked up manually. They don't need to ...