(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. – You may remember the color of your loved one's eyes for years. But how?
Scientists believe that long-term potentiation (LTP) – the long-lasting increase of signals across a connection between brain cells -- underlies our ability to remember over time and to learn, but how that happens is a central question in neuroscience.
Researchers at Duke University Medical Center have found a cascade of signaling molecules that allows a usually very brief signal to last for tens of minutes, providing the brain framework for stronger connections (synapses) that can summon a memory for a period of months or even years.
Their findings about how the synapses change the strength of connections could have a bearing on Alzheimer's disease, autism and mental retardation, said Ryohei Yasuda, Ph.D., assistant professor of neurobiology and senior author.
"We found that a biochemical process that lasts a long time is what causes memory storage," said Yasuda, who is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Early Career Scientist.
This work was published in the March 20 issue of Nature.
The researchers were investigating the signaling molecules that regulate the actin cytoskeleton, which serves as the structural framework of synapses.
"The signaling molecules could help to rearrange the framework, and give more volume and strength to the synapses," Yasuda said. "We reasoned that a long-lasting memory could possibly come from changes in the building block assemblies."
The Duke researchers knew that long-term potentiation, a long-lasting set of electrical impulses in nerve cells, is triggered by a transient increase of calcium (Ca2+) ions in a synapse. They devised experiments to learn exactly how the short Ca2+ signal, which lasts only for ~0.1s, is translated into long-lasting (more than an hour) change in synaptic transmission.
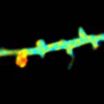
The team used a 2-photon microscopy technique to visualize molecular signaling within single synapses undergoing LTP, a method developed in the Yasuda lab. This microscopy method allowed the team to monitor molecular activity in single synapses while measuring the synapses for increase in their volume and strength of the connections.
They found that signaling molecules Rho and Cdc42, regulators of the actin cytoskeleton, are activated by CaMKII, and relay a CaMKII signal into signals lasting many minutes. These long-lasting signals are important for maintaining long-lasting plasticity of synapses, the ability of the brain to change during learning or memorization.
Many mental diseases such as mental retardation and Alzheimer's disease are associated with abnormal Rho and Cdc42 signals, Yasuda said. "Thus, our finding will provide many insights into these diseases."
INFORMATION:
Other authors include lead author Hideji Murakoshi and Hong Wang of the Duke Department of Neurobiology.
This study was funded by Howard Hughes Medical Institute, National Institute of Mental Health, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institute of Drug Abuse, the Alzheimer's Association and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Scientists discover major clue in long-term memory making
2011-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Nuts and Bolts of the Social Security Disability Appeals Process
2011-03-21
Social Security disability benefits provide an important safety net for thousands of Americans: studies cited by the Social Security Administration show that a 20-year-old worker has a 3-in-10 chance of becoming disabled at some point before reaching retirement. The benefits furnished through Social Security help disabled workers and their families maintain normal, productive lives. But what about those workers whose disability claims are denied by the SSA? Fortunately, a process is set forth that allows disabled workers to seek review of claims that may have been wrongly ...
Think globally, but act locally when studying plants, animals, global warming, researchers advise
2011-03-21
Contact: Camille Parmesan
parmesan@uts.cc.utexas.edu
512-232-1860
Michael C. Singer
sing@mail.utexas.edu
512-471-4506
University of Texas at Austin
Think globally, but act locally when studying plants, animals, global warming, researchers advise
AUSTIN, Texas—Global warming is clearly affecting plants and animals, but we should not try to tease apart the specific contribution of greenhouse gas driven climate change to extinctions or declines of species at local scales, biologists from The University of Texas at Austin advise.
Camille Parmesan, Michael ...
A Wrong Way Crash And A Wrongful Death
2011-03-21
A woman died because of a fatal accident, and her family has sued a Lynwood village clerk for negligence after the crash, the Chicago Sun Times reported.
Rolle Valle, driving the wrong way on Illinois Route 394 near East Lincoln Highway, crashed head-on into two cars.
Valle, the clerk in the village of Lynwood, has been charged with reckless homicide and aggravated DUI in connection with the fatal accident.
State Police said Valle was driving northbound in the southbound lane. His vehicle struck the other car head-on and the impact caused the car to roll over in ...
Metabolite levels may be able to improve diabetes risk prediction
2011-03-21
Measuring the levels of small molecules in the blood may be able to identify individuals at elevated risk of developing type 2 diabetes as much as a decade before symptoms of the disorder appear. In a report receiving advance online release in Nature Medicine, a team led by Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) researchers describes finding that levels of five amino acids not only indicated increased diabetes risk in a general population but also could differentiate, among individuals with traditional risk factors such as obesity, those most likely to actually develop diabetes. ...
New data published in Nature Genetics demonstrate that tiny LNA-based compounds developed by Santaris Pharma A/S inhibit entire disease-associated microRNA families
2011-03-21
Tiny Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) based compounds, which are 8-mer LNA oligonucleotides, successfully inhibit entire microRNA families, providing potential new approach for treating a variety of diseases, including cancer, viral infections, cardiovascular and muscle diseases
Data show high affinity and target specificity of tiny LNA-based compounds enabled functional inhibition of entire microRNA families in a range of tissues without off-target effects
Tiny LNA-based compounds are well tolerated in preclinical studies and can be delivered without the use of complex ...
Men fuel rebound in plastic surgery
2011-03-21
Contact: Lisa Arledge Powell
larledge@mediasourcetv.com
614-932-9950, ext. 12
American Society of Plastic Surgeons
Men fuel rebound in plastic surgery
New ASPS statistics show sizeable increases in facelifts and other surgical procedures for men
Statistics released today by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) show that more men are going under the knife. Overall cosmetic plastic surgery procedures in men were up 2 percent in 2010 compared to 2009. However, many male surgical procedures increased significantly. Facelifts for men rose 14 percent in 2010 ...
Roberts Law Group Client's DWI Charge Dismissed
2011-03-21
Raleigh criminal lawyer Patrick Roberts successfully obtained a dismissal of a Driving While Under the Influence (DWI) charge in a Wake County Criminal Court. After a challenge to certain circumstantial evidence in the case, including a challenge to the field sobriety test administered by the arresting officer, the Wake County District Attorney's Office determined that the case was flawed. The charges against Mr. Roberts' client were dropped.
According to Mr. Roberts, a criminal lawyer with the Roberts Law Group PLLC, the dismissal was based on the fact that the state ...
Traffic accidents linked to increased risk of chronic widespread pain
2011-03-21
Individuals with poorer health or psychological issues may be prone to developing chronic widespread pain following a traumatic event. This new research, published today in Arthritis Care & Research, a peer-reviewed journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), found that the onset of chronic pain was more often reported following a traffic accident than from other physically traumatic triggers.
The ACR defines chronic widespread pain as the presence of pain above and below the waist, or on both the left and right sides of the body, for three months or longer. ...
Invitation To Foodies - Don't Go To Hawaii...
2011-03-21
Don't go to Hawaii to just eat great food. TasteHawaiiOnline.com wants travelers to journey to Hawaii for a little more than the usual vacation options.
In September on Maui at the Makena Beach and Golf Resort, the first annual "Invitation To Foodies" seminar will ask conscientious travelers to not only go to Hawaii for snorkeling, surfing and helicopter rides but to take some time to meet local non-profits who help provide identity to local communities.
"We started shining a spotlight on Hawaii non-profits in 2009 by putting some of them on our website. We gave them ...
Advocate Law Group Says Northwestern Mutual Life, By Claiming "Only The Fine Print" Matters, Admits What Insurance Companies Long Denied
2011-03-21
At a press briefing today, one of the plaintiff's attorneys in the case of Smith v. Northwestern Mutual Life -- now pending in Federal District Court in Milwaukee -- labeled the somewhat novel "you can't believe anything we say" defense offered by Northwestern Mutual Life and its lawyers as the "Wizard of Oz Defense."
The lawsuit asserts Northwestern Mutual Life has been significantly overcharging hundreds of thousands of policyholders it promised a "flexible" policy loan interest rate "based on long term economic conditions." Instead the company has been charging an ...