Huge ocean 'Frisbees' spin off Brazil's coast
University of Miami researchers find that rings are bigger, faster than previously thought
2011-03-22
(Press-News.org) MIAMI – March 21, 2011 -- As the North Brazil Current (NBC) moves northward along the northeastern coast of Brazil, it draws water from the South Equatorial Current and the freshwater outflow from the Amazon River, providing a source for warm, nutrient-rich water. Just northwest of Brazil, part of the NBC banks a hard right and flows east along the equator. Occasionally, the turn is especially sharp and the current loops around, pinching off an independently- traveling parcel of warm water. This portion travels northwest with a clockwise rotation, moving through the ocean like a Frisbee™ travels through air.
These current rings have been known to exist for decades, but knowledge of their basic properties such as size, speed, depth, and rotation velocity has been limited. Drawing on current profiles from both shipboard and stationary instruments, University of Miami researchers Guilherme Castelão and Bill Johns describe the basic properties of ten rings sampled between 1998 and 2000. The authors find that the rings are best described as solid, clockwise-rotating parcels of water enclosed within a band of lower-speed water that tends to protect them from the surrounding environment.
Overall, this research has established that the NBC rings seem to be bigger, faster, and taller than previous observations suggested.
INFORMATION:
The study, titled "Sea surface structure of North Brazil Current rings derived from shipboard and moored acoustic Doppler current profiler observations" appears in the Journal of Geophysical Research – Oceans, a publication of the American Geophysical Union.
About the University of Miami's Rosenstiel School
The University of Miami's mission is to educate and nurture students, to create knowledge, and to provide service to our community and beyond. Committed to excellence and proud of the diversity of our University family, we strive to develop future leaders of our nation and the world. Founded in the 1940's, the Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science has grown into one of the world's premier marine and atmospheric research institutions. Offering dynamic interdisciplinary academics, the Rosenstiel School is dedicated to helping communities to better understand the planet, participating in the establishment of environmental policies, and aiding in the improvement of society and quality of life. For more information, please visit www.rsmas.miami.edu.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-03-22
Mashed potatoes, macaroni and cheese, meatloaf…they may be bad for your arteries, but according to an upcoming study in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, they're good for your heart and emotions. The study focuses on "comfort food" and how it makes people feel.
"For me personally, food has always been big in my family," says Jordan Troisi, a graduate student at the University of Buffalo. The study came out of the research program of his co-author Shira Gabriel, which has looked at social surrogates—things that make people ...
2011-03-22
MIG BANK, the first Forex broker to have obtained a Swiss banking license in December 2009, has announced today it has been granted the Securities Dealer License by the FINMA, the Swiss Financial Market Regulatory Authority. Since its foundation in 2003, MIG BANK has been offering online Forex trading services to private and institutional clients and has become, within a short period, one of the global leaders in the area of online Forex trading.
Swiss financial institutions are required to have the Securities Dealer License in order to offer securities trading facilities ...
2011-03-22
WASHINGTON -- Recent research aboard the Space Shuttle is giving scientists a better understanding of how infectious disease occurs in space and could someday improve astronaut health and provide novel treatments for people on Earth.
The research involves an opportunistic pathogen known as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the same bacterium that caused astronaut Fred Haise to become sick during the Apollo 13 mission to the moon in 1970.
Scientists studying the bacterium aboard the Shuttle hope to unlock the mysteries of how disease-causing agents work. They believe the research ...
2011-03-22
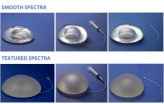
Dr. Hilton Becker, a Board Certified Plastic Surgeon and international specialist practicing Reconstructive, Cosmetic and Corrective Surgery in Boca Raton, Florida, recently presented studies and technical data about Spectra to the Brazilian medical community. Dr. Becker spoke at the 47th Brazilian Congress of Plastic Surgery in Vitoria in the State of Espiritu Santo on November 14. Dr. Becker is the inventor of Spectra, the first adjustable aesthetic breast implant, which is considered ideal for women with breast asymmetry.
Spectra's unique feature is its innovative ...
2011-03-22
A paper announcing a breakthrough discovery in the fight against Niemann-Pick Type C, coauthored by Olaf Wiest and Paul Helquist of the University of Notre Dame's Department Chemistry & Biochemistry and Frederick Maxfield, Chair of Biochemistry at Cornell University Weill College of Medicine, appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences this week. The paper shows how use of a histone deacetylase inhibitor correct the damage done by the genetic disorder and allowed once-diseased cells to function normally.
Niemann-PickType C (NPC) involves a genetic flaw ...
2011-03-22
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Monday, March 21, 2011 – For a patient at high risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), keeping up with what pills to take at different times of the day can be tedious. Window sills lined with prescription bottles – a pill for cholesterol, another for blood pressure, and an aspirin to keep blood thin and flowing – the list can get quite long and, as a result, many people, especially the elderly, often forget doses or take the wrong pill at the wrong time.
But what if there was a single pill that had all the benefits of multiple medications in one dose? ...
2011-03-22
PHILADELPHIA -- Patients who've been hurt in car or bike crashes, been shot or stabbed, or suffered other injuries are more likely to live if they arrive at the hospital on the weekend than during the week, according to new University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine research published in the March 21 issue of Archives of Surgery. The findings, which also showed that trauma patients who present to the hospital on weeknights are no more likely to die than those who presented during the day, contrast with previous studies showing a so-called "weekend effect" in which patients ...
2011-03-22
The James Webb Space Telescope has a unique shield to protect its sensitive instruments from the heat and light of the sun. The sunshield is like an umbrella popping open on the shores of the cosmos that allows the instruments beneath it to see far into the universe.
Like a beach umbrella protects people from the sun's heat and ultraviolet radiation, the sunshield protects the telescope and the sensitive infrared instruments that fly beneath the Webb telescope's sunshield from our sun's heat and light. "Each of the five layers of the shield is less than half the thickness ...
2011-03-22
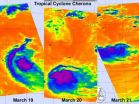
Three days of NASA infrared satellite imagery provides a clear picture to forecasters of the effect wind shear has had on former Cyclone Cherono. Wind shear increased near Cyclone Cherono this weekend and weakened it down to a remnant low pressure area in the Southern Indian Ocean. Today, March 21, Cherono's remnants are moving away from Mauritius and still causing ocean swells.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over former Tropical Cyclone Cherono each day over the last three days and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured the effects of the increased ...
2011-03-22
Calls to the police reporting men's assaults on their wives or intimate partners rose 10 percent in areas where the local National Football League team lost a game they were favored to win, according to an analysis of 900 regular-season NFL games reports researchers in a paper in the Quarterly Journal of Economics.
Football games are emotionally laden events of widespread interest, typically garnering 25 percent or more of a local television viewing audience. The disappointment of an unexpected loss, the researchers concluded, raises the risk that football fans may react ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Huge ocean 'Frisbees' spin off Brazil's coast
University of Miami researchers find that rings are bigger, faster than previously thought