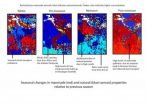
(Press-News.org) As the last ice age was ending, about 13,000 years ago, a final blast of cold hit Europe, and for a thousand years or more, it felt like the ice age had returned. But oddly, despite bitter cold winters in the north, Antarctica was heating up. For the two decades since ice core records revealed that Europe was cooling at the same time Antarctica was warming over this thousand-year period, scientists have looked for an explanation.
A new study in Nature brings them a step closer by establishing that New Zealand was also warming, indicating that the deep freeze up north, called the Younger Dryas for the white flower that grows near glaciers, bypassed much of the southern hemisphere.
"Glaciers in New Zealand receded dramatically at this time, suggesting that much of the southern hemisphere was warming with Antarctica," said study lead author, Michael Kaplan, a geochemist at Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory. "Knowing that the Younger Dryas cooling in the northern hemisphere was not a global event brings us closer to understanding how Earth finally came out of the ice age."
Ice core records show that warming of the southern hemisphere, starting 13,000 years ago, coincided with rising levels of the heat-trapping gas, carbon dioxide. The study in Nature is the first to link this spike in CO2 to the impressive shrinking of glaciers in New Zealand. The scientists estimate that glaciers lost more than half of their extent over a thousand years, and that their creep to higher elevations was a response to the local climate warming as much as 1 degree C.
To reconstruct New Zealand's past climate, the study's authors tracked one glacier's retreat on South Island's Irishman Basin. When glaciers advance, they drag mounds of rock and dirt with them. When they retreat, cosmic rays bombard these newly exposed ridges of rock and dirt, called moraines. By crushing this material and measuring the build-up of the cosmogenic isotope beryllium 10, scientists can pinpoint when the glacier receded. The beryllium-10 method allowed the researchers to track the glacier's retreat upslope through time and indirectly calculate how much the climate warmed.
The overall trigger for the end of the last ice age came as Earth's orientation toward the sun shifted, about 20,000 years ago, melting the northern hemisphere's large ice sheets. As fresh melt water flooded the North Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf Stream weakened, driving the north back into the ice age. During this time, temperatures in Greenland dropped by about 15 degrees C. For years, scientists have tried to explain how the so-called Younger Dryas cooling fit with the simultaneous warming of Antarctica that eventually spread across the globe.
The Nature paper discusses the two dominant explanations without taking sides. In one, the weakening of the Gulf Stream reconfigures the planet's wind belts, pushing warm air and seawater south, and pulling carbon dioxide from the deep ocean into the air, causing further warming. In the other, the weakened Gulf Stream triggers a global change in ocean currents, allowing warm water to pool in the south, heating up the climate.
Bob Anderson, a geochemist at Lamont-Doherty who argues the winds played the dominant role, says the Nature paper adds another piece to the puzzle. "This is one of the most pressing problems in paleoclimatology because it tells us about the fundamental processes linking climate changes in the northern and southern hemispheres," he said. "Understanding how regional changes influence global climate will allow scientists to more accurately predict regional variations in rain and snowfall."
INFORMATION:
Other researchers involved in the study: Joerg Schaefer and Roseanne Schwartz, also of Lamont-Doherty; George Denton and Aaron Putnam, University of Maine; David Barrell, GNS Science, New Zealand; Trevor Chinn, Alpine and Polar Processes Consultancy, New Zealand; Bjørn Andersen, University of Oslo; Robert Finkel, University of California, Berkeley; Alice Doughty, Victoria University of Wellington.
Study adds new clue to how last ice age ended
New Zealand glaciers melted as European glaciers briefly expanded
2010-09-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Investigating better endpoints for immunotherapy trials
2010-09-09
Cancer immunotherapy calls for revised clinical endpoints that differ from those used for chemotherapy, according to an article published online September 8 in The Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Unlike chemotherapy, which acts directly on tumors, cancer immunotherapies exert their effects on the immune system, which may delay or change response patterns, perhaps owing to the dynamics of the immune system itself. For example, initial tumor burden may increase due to lymphocytic infiltration, because of T-cell proliferation, which is followed by lymphocyte-induced ...
Researchers identify potential new drug for neurodegenerative disease
2010-09-09
BOSTON, Mass. (September 8, 2010)‹Scientists have discovered a small
molecule that helps human cells get rid of the misfolded, disfigured
proteins implicated in Alzheimer¹s disease and other neurodegenerative
ailments. This potential drug could have applications for other conditions
as well.
Cells create and discard proteins continuously, a process that relies on a
balance between the speed with which new proteins are created and damaged
ones destroyed. Protein destruction occurs through a sophisticated system
that marks proteins for disposal by tagging them with ...
New study suggests changes in diagnosis and treatment of malaria
2010-09-09
LA JOLLA, CA - September 7, 2010 –A team of scientists from The Scripps Research Institute, the Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation (GNF), and the U. S. Naval Research Detachment in Peru has completed a study that could improve the efficacy of diagnosis and treatment strategies for drug-resistant malaria.
In the new study—published online on September 9, 2010 by the journal Genome Research—the scientists analyzed the genomic features of a population of malaria parasites in Peru, identifying the genetic basis for resistance to a common antibiotic.
Malaria ...
NIST researchers hear puzzling new physics from graphene quartet's quantum harmonies
2010-09-09
GAITHERSBURG, Md. – Using a one-of-a-kind instrument designed and built at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), an international team of researchers have "unveiled" a quartet of graphene's electron states and discovered that electrons in graphene can split up into an unexpected and tantalizing set of energy levels when exposed to extremely low temperatures and extremely high magnetic fields. Published in this week's issue of Nature,* the new research raises several intriguing questions about the fundamental physics of this exciting material and reveals ...
New sickle cell screening program for college athletes comes with serious pitfalls, experts say
2010-09-09
The Johns Hopkins Children's Center top pediatrician is urging a "rethink" of a new sickle cell screening program, calling it an enlightened but somewhat rushed step toward improving the health of young people who carry the sickle cell mutation.
Beginning this fall, all Division I college athletes will undergo mandatory screening for the sickle cell trait. The program, rolled out by the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA), is an attempt to prevent rare but often-lethal complications triggered by intense exercise in those who carry the genetic mutation yet ...
Liver defect likely cause of DHA deficiency in Alzheimer's patients, UCI study finds
2010-09-09
Irvine, Calif. — UC Irvine researchers have discovered that markedly depleted amounts of an omega-3 fatty acid in brain tissue samples from Alzheimer's patients may be due to the liver's inability to produce the complex fat, also contained in fish-oil supplements.
Low levels of docosahexaenoic acid, or DHA, have been associated with the chronic neurodegenerative disease affecting millions of Americans, but no cause had been identified.
In postmortem liver tissue from Alzheimer's patients, the UCI team found a defect in the organ's ability to make DHA from shorter molecules ...
The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB) Local and Regional Policy Makers report launched at major biodiversity conference in Ghent
2010-09-09
Ghent, 9 September 2010 – Factoring the planet's multi-trillion dollar ecosystem services into policy-making can help save cities and regional authorities money while boosting the local economy, enhancing quality of life, securing livelihoods and generating employment.
This is the finding from a major international study, launched in a report by TEEB for Local and Regional Policy Makers, being released in Belgium, Brazil, India, Japan and South Africa.
In the Framework of the Belgian Presidency of the European Union, the Flemish Ministry of Environment, Nature and ...
Unauthorized population would soar if birthright citizenship repealed
2010-09-09
University Park, Pa. -- Repeal of birthright citizenship for the U.S.-born children of unauthorized immigrants would expand the nation's unauthorized population by at least 5 million over the next decade, according to a new report from the Migration Policy Institute.
The report's principal author is Jennifer Van Hook, professor of sociology and demographics at Penn State and non-resident fellow at the Washington, D.C.-based institute.
"While some are discussing an end to birthright citizenship as a means to reduce illegal immigration," Van Hook said, "repeal of birthright ...
Satellite data reveal seasonal pollution changes over India
2010-09-09
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Armed with a decade's worth of satellite data, University of Illinois atmospheric scientists have documented some surprising trends in aerosol pollution concentration, distribution and composition over the Indian subcontinent.
In addition to environmental impact, aerosol pollution, or tiny particles suspended in the air, can be detrimental to human health by causing a range of respiratory problems. Aerosols can come from natural sources, such as dust and pollen carried on the wind, but the most hazardous aerosols are generated by human activity – soot ...
Why the biological clock? Penn study says aging reduces centromere cohesion, disrupts reproduction
2010-09-09
PHILADELPHIA –- University of Pennsylvania biologists studying human reproduction have identified what is likely the major contributing factor to the maternal age-associated increase in aneuploidy, the term for an abnormal number of chromosomes during reproductive cell division.
Using naturally aging mouse models, researchers showed that this basic fact of reproductive life is most likely caused by weakened chromosome cohesion. Older oocytes, or egg cells, have dramatically reduced amounts of a protein, REC8, that is essential for chromosomes to segregate correctly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
[Press-News.org] Study adds new clue to how last ice age endedNew Zealand glaciers melted as European glaciers briefly expanded