(Press-News.org) This release is available in French.
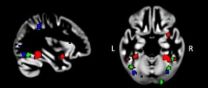
Researchers directed by Dr. Laurent Mottron at the University of Montreal's Centre for Excellence in Pervasive Development Disorders (CETEDUM) have determined that people with autism concentrate more brain resources in the areas associated with visual detection and identification, and conversely, have less activity in the areas used to plan and control thoughts and actions. This might explain their outstanding capacities in visual tasks. The team published their findings in Human Brain Mapping on April 4, 2011.
Aiming to understand why autistic individuals have strong abilities in terms of processing visual information, the researchers collated 15 years of data that covered the ways autistic brain works when interpreting faces, objects and written words. The data came from 26 independent brain imaging studies that looked at a total of 357 autistic and 370 non-autistic individuals. "Through this meta-analysis, we were able to observe that autistics exhibit more activity in the temporal and occipital regions and less activity in frontal cortex than non-autistics. The identified temporal and occipital regions are typically involved in perceiving and recognizing patterns and objects. The reported frontal areas subserve higher cognitive functions such as decision making, cognitive control, planning and execution,'' explained first author Fabienne Samson, who is also affiliated with the CETEDUM.
"This stronger engagement of the visual processing brain areas in autism is consistent with the well documented enhanced visuo-spatial abilities in this population," Samson said. The current findings suggest a general functional reorganization of the brain in favor of perception processes – the processes by which information is recorded the brain. This allows autistic individuals to successfully perform, albeit in their own way, higher-level cognitive tasks that would usually require a strong involvement of frontal areas in typical individuals. These are tasks that require reasoning – for example, a research participant would be asked if a statement is true or false, or to categorize a range of objects into groups.
"We synthesized the results of neuroimaging studies using visual stimuli from across the world. The results are strong enough to remain true despite the variability between the research designs, samples and tasks, making the perceptual account of autistic cognition currently the most validated model," Mottron said. "The stronger engagement of the visual system, whatever the task, represents the first physiological confirmation that enhanced perceptual processing is a core feature of neural organization in this population. We now have a very strong statement about autism functioning which may be ground for cognitive accounts of autistic perception, learning, memory and reasoning." This finding shows that the autistic brain successfully adapt by reallocating brain areas to visual perception, and offers many new lines of enquiry with regards to developmental brain plasticity and visual expertise in autistics.
INFORMATION:
Dr. Isabelle Soulières of the CETEDUM and the Neural Systems Group at the Massachusetts General Hospital (NSGMGH) and Dr.Thomas Zeffiro of the NSGMGH, also contributed to the findings. The CETEDUM is based at the University of Montreal affiliated Rivière-des-Prairies Hospital and is part of the Fernand-Seguin Research Centre. It is officially known as Centre d'Excellence en Troubles Envahissants du Développement de l'Université de Montréal. The research was financed in part by grants from Autism Speaks, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Fonds de la Recherche en Santé du Québec.
New research explains autistic's exceptional visual abilities
Mapping data shows enhanced activity in the 'perception' part of the brain
2011-04-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New test detects early-stage, asbestos-related pulmonary cancer
2011-04-04
Researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center have investigated a novel protein test to detect early-stage, asbestos-related pulmonary cancer. The test can accurately identify proteins secreted from cancerous tumors caused by asbestos exposure. The study was presented at the American Association for Cancer Research 102nd Annual Meeting 2011 on April 4th.
In a blinded test performed under the sponsorship of the National Cancer Institute's Early Detection Research Network Biomarker Discovery Lab, researchers detected 15 of 19 cases of stage 1 or stage 2 malignant pleural mesothelioma. ...
Nationwide utilization of virtual colonoscopy triples, study suggests
2011-04-04
Reston, VA (March 29, 2011) — Medicare coverage and nationwide utilization of computed tomographic colonography (CTC), commonly referred to as virtual colonoscopy, has tripled in recent years, according to a study in the April issue of the Journal of the American College of Radiology (www.jacr.org). CTC employs virtual reality technology to produce a three-dimensional visualization that permits a thorough and minimally invasive evaluation of the entire colon and rectum. CT colonography is an alternative to conventional optical colonoscopy for colorectal cancer screening ...
CleanFinancial Launches New Range of Financial Spread Betting Guides
2011-04-04
The leading financial spread betting website www.CleanFinancial.com has launched a brand new set of trading tutorials.
The guides, which cover the basics of spread betting, 24 hour trading, spread betting on stock markets and the value of tighter spreads, were introduced last week. The new tutorials have been added to the broad range of spread betting company reviews that the site already offers.
Jenna Cutly, Editor for CleanFinancial.com, said that the new trading guides will complement the range of information that service already offers. "Spread betting is an ...
Babies born earlier in areas near busy road junctions
2011-04-04
Babies are born earlier when their mothers live near a concentration of freeways and main roads, a study of 970 mothers and their newborn babies in Logan City, south of Brisbane, has found.
Senior research fellow Associate Professor Adrian Barnett from Queensland University of Technology's (QUT) Institute of Health and Biomedical Innovation (IHBI) said the study, published today in the online journal Environmental Health, showed that the more freeways and highways around a pregnant woman's home, the higher the likelihood of her baby being born prematurely.
"The most ...
Giant batteries for green power
2011-04-04
This press release is available in German.
Green power is an unstable commodity. Photovoltaic plants rest at night, and wind turbines stand still when there are lulls in the wind. This is why in the future there will be a need for intermediate storage of considerable amounts of environmentally friendly power. One of the hot topics at the moment is the use of electric cars for intermediate power storage. Experts agree that this alone will not suffice. Instead, large-scale stationary storage facilities will be needed, substations centrally located in the grid and capable ...
Clumsy kids who don't 'grow out of it'
2011-04-04
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, or ADHD, is widely recognized by the medical community, and there are a number of therapies in place. But as many as six percent of all children suffer from the less familiar Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD). Demonstrating a lack of refined motor skills, children with DCD tend to have a more difficult time playing sports and staying organized at school. They appear to be uncoordinated — and many parents think they'll grow out of it. But research shows that may not be true.
Now Dr. Orit Bart and her colleagues at Tel Aviv ...
Mobile with electricity
2011-04-04
This press release is available in German.
If electric vehicles are to become an alternative to traditional vehicles there is a lot of research and development work to be done. The Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft created the "System Research for Electromobility" project back in June 2009, an initiative involving a total of 33 Fraunhofer Institutes. The research is financed with € 34.4 million in funding from the federal economic stimulus program II from the German federal ministry of education and research (BMBF). In addition, the federal economic stimulus program I provided ...
Facial structure of men and women has become more similar over time
2011-04-04
Research from North Carolina State University shows that they really don't make women like they used to, at least in Spain. The study, which examined hundreds of Spanish and Portuguese skulls spanning four centuries, shows that differences in the craniofacial features of men and women have become less pronounced.
"Improving our understanding of the craniofacial features of regional groups can help us learn more from skeletal remains, or even help us identify an individual based on his or her remains," says Dr. Ann Ross, an associate professor of anthropology at NC State ...
Breast Augmentation for Older Women
2011-04-04
Traditionally, breast augmentation has been considered a procedure for young people. However, in recent years that stereotype has become obsolete. More than ever, older women are choosing to undergo breast augmentation to restore a more youthful breast appearance.
Age, pregnancy, and weight loss all affect the appearance of your breasts, causing them to sag or lose volume. Breast augmentation can be an effective way to neutralize the impact of these factors on your breast appearance. In general, breast augmentation for older women is more about restoring a youthful perkiness ...
Student confidence correlated with academic performance
2011-04-04
MANHATTAN, KS—Do those who know more also know that they know more? And does a student's confidence level correlate to academic performance? These questions have long inspired researchers in the fields of decisionmaking and education to study confidence. New research from Kansas State University professor Candice Shoemaker looked at the psychological constructs of "confidence" and "self-efficacy" to evaluate the effectiveness of targeted learning objectives on student achievement.
Shoemaker, from Kansas State University's Department of Horticulture, Forestry, and Recreation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
[Press-News.org] New research explains autistic's exceptional visual abilitiesMapping data shows enhanced activity in the 'perception' part of the brain