(Press-News.org) This release is available in German.
FRANKFURT. Creating artificial structures from DNA is the objective of DNA nanotechnology. This new discipline, which combines biology, physics, chemistry and material science makes use of the ability of the natural DNA-strains' capacity for self assembly. Smileys or small boxes, measuring only 10s of nanometers (10 one-billionths of a meter) were created from DNA in a drop of water. Prof Alexander Heckel and his doctoral student Thorsten Schmidt from the "Cluster of Excellence for Macromolecular Complexes" at Goethe University were able to create two rings of DNA only 18 nanometers in size, and to interlock them like two links in a chain. Such a structure is called catenan, a term derived from the Latin word catena (chain). Schmidt, who got married during the time he was working on the nano-rings, believes that they are probably the world's smallest wedding rings.
From a scientific perspective, the structure is a milestone in the field of DNA nanotechnology, since the two rings of the catenan are, as opposed to the majority of the DNA nanoarchitechtures that have already been realized, not fixed formations, but – depending on the environmental conditions – freely pivotable. They are therefore suitable as components of molecular machines or of a molecular motor. "We still have a long way to go before DNA structures such as the catenan can be used in everyday items", says Prof Alexander Heckel, "but structures of DNA can, in the near future, be used to arrange and study proteins or other molecules that are too small for a direct manipulation, by means of auto-organization." This way, DNA nano-architectures could become a versatile tool for the nanometer world, to which access is difficult.
In the manufacture of DNA nano-architecture, the scientists take advantage of the pairing rules of the four DNA nucleobases, according to which two natural DNA strands can also find each other (in DNA nano-architecture, the base order is without biological significance). An A on one strand pairs with T on the other strand and C is complementary to G. The trick is to create the sequences of the DNA strands involved in such a manner as to ensure that the desired structure builds up on its own without direct intervention on the experimenter's part. If only certain parts of the strands used complement each other, branches and junctions can be created.
As reported by Schmidt and Heckel in the journal "Nano Letters" (online advance publication, dx.doi.org/10.1021/nl200303m), they first created two C-shaped DNA-fragments for the catenans. With the help of special molecules that act as sequence-specific glue for the double helix, they arranged the "Cs" in such a ways as to create two junctions, with the open ends of the "Cs" pointing away from each other (see images). The catenan was created by adding two strands that attach to the ends of the two ring fragments, which are still open. Thorsten Schmidt dedicated the publication to his wife Dr Diana Gonçalves Schmidt, who also appreciates the work on scientific level, since she was also a part of Alexander Heckel's work group.
Since they are much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light, the rings cannot be seen with a standard microscope. "You would have to string together about 4000 such rings to even achieve the diameter of a human hair", says Thorsten Schmidt. He therefore displays the catenans with a scanning force microscope, which scans the rings that have been placed on a surface with an extremely fine tip.
INFORMATION:
Information: Prof Alexander Heckel, Cluster of Excellence for Macromolecular Complexes, Campus Riedberg, phone: +49 (0)69 798- 29821 (secretary's office); heckel@em.uni-frankfurt.de;
Dr Thorsten Schmidt is now at Harvard University, USA, phone: +1 (0)857-334-9212 Thorsten.Schmidt@wyss.harvard.edu, interviews are possible via Skype, Skype name t.l.schmidt
http://www.uni-frankfurt.de/~heckel
Goethe University, with its strong research focus, is situated in the European financial metropolis of Frankfurt. Founded in 1914 by Frankfurt citizens, it is now one of Germany's ten largest universities and among the ten German universities with the highest amount of third-party funds. On 1 January 2008 it returned to its historical roots as a university financed by foundations, guaranteeing it an unrivalled degree of autonomy. At the same time, the university is receiving a new look thanks to extensive construction work. A new campus is taking shape around the historical ensemble of buildings designed by Julius Poelzig in Frankfurt's Westend that sets new aesthetic and functional standards. The "Science City" on the Riedberg Campus brings together the science faculties in direct proximity to two Max Planck Institutes. With over 55 foundation-financed professorships and visiting professorships, Goethe University is, according to the Association of Sponsors for the Promotion of German Science, leading the way.
The world's smallest wedding rings
2 interlocking rings of DNA are only visible through the scanning force microscope
2011-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tuberculosis strain spread by the fur trade reveals stealthy approach of epidemics
2011-04-12
Patience may be a virtue in a person, but in an infectious disease, it is insidious. Witness tuberculosis, which can lie dormant in a human host for decades before bursting forth into infection. TB's stealthy nature has made it difficult to decipher how it spreads, seriously hampering efforts to control it. The World Health Organization estimates that a third of the people on Earth are infected.
Now, a study led by Stanford scientists has provided new insights into the behavior of tuberculosis by tracing the travels of a particular strain of the disease that was unintentionally ...
Ambulatory Providers Overly Optimistic about Reaching Meaningful Use
2011-04-12
Although nearly 80 percent of ambulatory providers that have purchased an EMR are confident they will qualify for meaningful use (MU) in 2011, a closer look at what functionalities they have actually implemented reveals that most still have significant holes to fill, according to a KLAS report. Over two thirds of the surveyed providers are not sharing medical records electronically with patients, and nearly half have not implemented clinical decision support (CDS) rules, two key MU requirements.
The report, "Ambulatory EMR: A KLAS Guide to Meaningful Use Success," presents ...
Excessive nitrogen harms the economy and environment -- first Europe-wide assessment published
2011-04-12
A major new study finds that nitrogen pollution is costing each person in Europe around £130 - £650 (€150 – €740 Euros) a year. The first European Nitrogen Assessment (ENA) is launched at a conference today in Edinburgh, Scotland.
The study, carried out by 200 experts from 21 countries and 89 organizations, estimates that the annual cost of damage caused by nitrogen across Europe is £60 - £280 billion (€70 -320 billion), more than double the extra income gained from using nitrogen fertilizers in European agriculture.
Professor Bob Watson Chief Scientific Advisor to ...
Berkeley Lab researchers report tandem catalysis in nanocrystal interfaces
2011-04-12
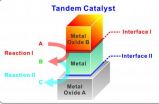
In a development that holds intriguing possibilities for the future of industrial catalysis, as well as for such promising clean green energy technologies as artificial photosynthesis, researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have created bilayered nanocrystals of a
metal-metal oxide that are the first to feature multiple catalytic sites on nanocrystal interfaces. These multiple catalytic sites allow for multiple, sequential catalytic reactions to be carried out selectively and in tandem.
"The demonstration ...
Pop Cult Studio's Mark Mushkin is Currently Producing TV Shows to be Pitched to Google and YouTube as Content for a New Wave of Media Headed for America's Living Room
2011-04-12
Pop Cult Studio's Mark Mushkin is currently producing TV shows as content for a new wave of media headed for America's living room.
The Internet and TV are engaged to be married and there are big name companies scheduled to attend. Google and YouTube are looking to purchase TV shows to distribute on a network of channels being set up in preparation for the next generation of TV's that will connect to the Internet.
Pop Cult Studios' Executive Producer Mark Mushkin says, "We plan to take advantage of this opportunity to get our new TV shows seen by these major distributors." ...
Shootingstars provide clues to likely response of plants to global warming
2011-04-12
Many scientists are concerned that plant and animal species may face extinction due to global warming, but biologists at Washington University in St. Louis are trying to predict exactly what will happen to them. Which species will migrate? Which evolve? Which change their behavior? Which become extinct?
Rather than peer into the future, they are looking backward, exploring how species alive today survived global warming at the end of the Pleistocene and asking whether their responses provide any guidance for us today.
For his dissertation Brad Oberle, a doctoral candidate ...
MedWOW Offers 10 Free Business Leads to Global Medical Equipment Professionals
2011-04-12
MedWOW.com, the global online marketplace for medical equipment, announces the promotion of their upgraded business leads program. Any medical equipment professional in the world can claim a gift of 10 free business leads. All of the business leads generated are highly verified, pre-qualified, registered buyers who are looking for medical equipment, as well as devices and related services.
Leads' types include: buying leads (available for complete systems, as well as parts and accessories), leasing & financing leads and shipping leads. Leads are kept fresh and current, ...
Vitamin D levels associated with age-related macular degeneration
2011-04-12
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Women under the age of 75 with high vitamin D status were less likely to have early age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the leading cause of irreversible vision loss in adults, a University at Buffalo study has shown. The disease affects approximately 9 percent of Americans aged 40 and older.
The paper is published in the April issue of "Archives of Ophthalmology," one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Vitamin D status was assessed using the blood measure of 25-hydroxyvitamin D or 25 (OH) D. The 25 (OH) D level is generally considered the means by which ...
Creative, online learning tool helps students tackle real-world problems
2011-04-12
AMES, Iowa – Solving problems for clients in any field usually requires gathering information and creative thinking that leads to practical and inventive solutions.
A new computer interface developed at Iowa State University is helping students use what they've learned in the horticulture classroom and apply it to problems they'll face when they are on the job site.
The project, called ThinkSpace, is led by a group of ISU faculty including Ann Marie VanDerZanden, professor of horticulture and associate director of ISU's Center for Excellence in Learning and Teaching.
ThinkSpace ...
Spacify Offers Sustainable Modern Furniture and Introduces Modern New Bar Stools and Counter Stools
2011-04-12
What can be more intriguing than a furniture item that seemingly has come straight out of the house of a fashion stylist? If you love the planet, you will want to explore the new modern designs of the collection from Emco, now available at Spacify. Such is the creation of Emco and its Icon Bar/Counter stool is known to be an avant garde design amongst all the modern bar stools and contemporary counter stools. But this is not the only design that is intriguing. You may pick up any designer bar stool from Emco and you will find that all the stools have been created keeping ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] The world's smallest wedding rings2 interlocking rings of DNA are only visible through the scanning force microscope