(Press-News.org) First impressions are important, and they usually contain a healthy dose both of accuracy and misperception. But do people know when their first impressions are correct? They do reasonably well, according to a study in the current Social Psychological and Personality Science (published by SAGE).
Researchers had two separate groups of more than100 people meet in a "getting-acquainted" session much like speed-dating, until the people had spoken with everyone else in the group for three minutes each. At the end of each 3-minute chat, they rated each other's personalities, and rated how well they thought their impressions "would agree with someone who knows this person very well." To establish what the person was "really" like, the researchers had people fill out their own personality reports, which were bolstered with personality ratings that came either from friends or parents.
There is a large body of research that shows impressions can be accurate with short interactions, and the participants did a reasonably good job of seeing each other's personality. And the more accurate they felt, the closer their ratings to the friends' and parents' ratings (although this correlation was not perfect). The participants also found the highest accuracy from people who rated themselves moderately accurate—when people were highly confident of their judgment, accuracy was not greater than for moderate levels of confidence.
The research team, led by Jeremy Biesanz of the University of British Columbia, noted that there are two ways to be right about people's personality. We can know how people are different from each other, but a good judge of persons knows that people are mostly alike—for example, almost everyone would prefer being friendly to being quarrelsome. The more people rated their partner's personality in a way typical of most everyone, the more accurate they felt their perception was. And because most people are like most people, they were indeed being accurate.
"Many important decisions are made after very brief encounters—which job candidate to hire, which person to date, which student to accept," write the authors. "Although our first impressions are generally accurate, it is it critical for us to recognize when they may be lacking.
###
The article "Do we know when our impressions of others are valid? Evidence for realistic accuracy awareness in first impressions of personality" in Social Psychological and Personality Science is available free for a limited time at: http://spp.sagepub.com/content/early/2011/01/19/1948550610397211.full.pdf+html.
Social Psychological and Personality Science is a cutting-edge journal of succinct reports of research in social and personality psychology. SPPS is sponsored by a consortium of the world's leading organizations in social and personality psychology representing over 7,000 scholars on six continents worldwide. http://spps.sagepub.com
SAGE is a leading international publisher of journals, books, and electronic media for academic, educational, and professional markets. Since 1965, SAGE has helped inform and educate a global community of scholars, practitioners, researchers, and students spanning a wide range of subject areas including business, humanities, social sciences, and science, technology, and medicine. An independent company, SAGE has principal offices in Los Angeles, London, New Delhi, Singapore and Washington DC. www.sagepublications.com
Contact: Jeremy Biesanz, University of British Columbia, Department of Psychology, 2136 West Mall, Room 2037, Vancouver, British Columbia V6T 1Z4.Email: jbiesanz@psych.ubc.ca Phone: (604) 822-6493
Members of the media qualify for free access to this and 635+ other SAGE journals. Contact Ashley Wrye for further information.
People know when first impressions are accurate
2011-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Search for dark matters moves one step closer to detecting elusive particle
2011-04-15
Dark matter, the mysterious substance that may account for nearly 25 percent of the universe, has so far evaded direct observation. But researchers from UCLA, Columbia University and other institutions participating in the international XENON collaboration say they are now closer than ever before.
Their new results, announced today at the Gran Sasso National Laboratory in Italy, where the XENON experiment is housed deep beneath a mountain 70 miles west of Rome, represent the highest-sensitivity search for dark matter yet, with background noise 100 times lower than competing ...
Experimental drug inhibits cell signaling pathway and slows ovarian cancer growth
2011-04-15
An experimental drug that blocks two points of a crucial cancer cell signaling pathway inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells and significantly increases survival in an ovarian cancer mouse model, a study at UCLA's Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has found.
The drug, called NVP-BEZ235, also inhibits growth of ovarian cancer cells that have become resistant to the conventional treatment with platinum chemotherapy, and helps to re-sensitize the cancer cells to the therapy. It also enhances the effect of platinum chemotherapy on ovarian cancer cells that are still ...
Safety of stored blood among chief concerns for transfusion medicine community
2011-04-15
In light of recent studies that suggest the use of stored blood during transfusions may cause adverse effects in patients, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) funded a number of research projects to examine the safety of transfusing older red cells and the impact of stored blood on respiratory gases. These papers discussing potential adverse effects of stored blood and related concerns for oxygen delivery by transfusion are now available online in TRANSFUSION, a journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of AABB.
Blood banks are responsible for ...
Genital herpes more virulent in Africa than in US
2011-04-15
BOSTON, Mass. (April 15, 2011) — Strains of genital herpes in Africa are far more virulent than those in the United States, researchers at Harvard Medical School report, a striking insight into a common disease with important implications for preventing HIV transmission in a region staggered by the HIV/AIDS epidemic. The researchers arrived at this finding by testing mouse model strains of the disease against vaccine candidates. All vaccines were far more efficacious in abating the U.S. strain.
The researchers say identification of the properties of the African viruses ...
Jefferson researchers unlock key to personalized cancer medicine using tumor metabolism
2011-04-15
PHILADELPHIA—Identifying gene mutations in cancer patients to predict clinical outcome has been the cornerstone of cancer research for nearly three decades, but now researchers at the Kimmel Cancer Center at Jefferson have invented a new approach that instead links cancer cell metabolism with poor clinical outcome. This approach can now be applied to virtually any type of human cancer cell.
The researchers demonstrate that recurrence, metastasis, and poor clinical outcome in breast cancer patients can be identified by simply gene profiling cancer cells that are using ...
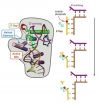
Secrets of a precision protein machine
2011-04-15
VIDEO:
Much of the FEN1 structure was solved by Sakurai et al, but how FEN1 works was not apparent in the DNA-free structure. The presence of DNA appears to induce the...
Click here for more information.
DNA replication is critical to the life of all organisms, insuring that each new cell, as well as each new offspring, gets an accurate copy of the genome. Among the legions of proteins that do the work so essential to a cell's survival, the DNA-slicing "flap endonuclease" ...
Colorado Supreme Court to Review Wal-Mart Personal Injury Damages Issue
2011-04-15
The Colorado Supreme Court recently decided to review a 2010 Colorado Court of Appeals decision involving the collateral source rule. The central issue is whether a Colorado personal injury defendant can introduce evidence of the actual amount a health provider received for a plaintiff's injuries.
Under common law, compensation or indemnity paid to an injured party by a collateral source (that is, not the alleged wrongdoer in the lawsuit) does not reduce the damages that could otherwise be recovered from the wrongdoer. In Crossgrove v. Wal-Mart Stores, Inc., a delivery ...
Crash rates may be higher for teen drivers who start school earlier in the morning
2011-04-15
DARIEN, IL – A study in the April 15 issue of the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine shows increased automobile crash rates among teen drivers who start school earlier in the morning.
Results indicate that in 2008 the weekday crash rate for 16- to 18-year-olds was about 41 percent higher in Virginia Beach, Va., where high school classes began at 7:20 - 7:25 a.m., than in adjacent Chesapeake, Va., where classes started at 8:40 - 8:45 a.m. There were 65.8 automobile crashes for every 1,000 teen drivers in Virginia Beach, and 46.6 crashes for every 1,000 teen drivers in ...
A safer treatment could be realized for millions suffering from parasite infection
2011-04-15
A safer and more effective treatment for 10 million people in developing countries who suffer from infections caused by trypanosome parasites could become a reality thanks to new research from Queen Mary, University of London published today (15 April).
Scientists have uncovered the mechanisms behind a drug used to treat African sleeping sickness and Chagas disease, infections caused by trypanosome parasites which result in 60,000 deaths each year.
The study, appearing in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, investigated how the drug nifurtimox works to kill off the ...
NYC Bicyclists May Face New Laws, Challenges
2011-04-15
An editorial in the New York Post gave City Councilman Eric Ulrich a "Knucklehead Award" for his proposal to license all bicycles in New York City. Ulrich, from Queens (and the youngest serving member of the council at age 24), proposed the licensing system after receiving complaints from senior citizens who said, according to Ulrich, that bicyclists "scare the hell out of them."
While some rogue cyclists may tarnish the reputation of all riders, cycling is up across the city, with Department of Transportation figures showing the number of everyday bicycle commuters ...