(Press-News.org) A study led by Baylor University geologists shows that a new method that uses different size and shape traits of leaves to reconstruct past climates over the last 120 million years is more accurate than other current methods.
The study appeared in the April issue of the journal New Phytologist and was funded by the National Science Foundation.
"Paleobotanists have long used models based on leaf size and shape to reconstruct ancient climates," said Dr. Daniel Peppe, assistant professor of geology at Baylor, College of Arts and Sciences, who is an expert in paleomagnetism, paleobotany and paleoclimatology. "However most of these models use just a single variable or variables that are not directly linked to climate, which obviously limits the models' predictive power. For that reason, they models often underestimate ancient temperatures."
Baylor geology researchers, along with 26 other co-authors from universities around the world, collected thousands of leaves from many different species of plants from 92 climatically-different and plant-diverse locations on every continent except Africa and Antarctica. Multiple linear regression models for mean annual temperature and mean annual precipitation were developed and then applied to nine well-studied fossil floras.
The results showed:
Leaves in cold climates typically have larger, more numerous teeth, and are more dissected. Leaves in wet climates are larger and have fewer, smaller teeth.
Leaf habit (deciduous vs. evergreen), local water availability and phylogenetic history all affect the relationships between climate and leaf size and shape.
The researchers' multivariate mean annual temperature and mean annual precipitation models offer strong improvements in accuracy and precision over single variable approaches. For example, the mean annual temperature estimates for most of North American fossil floras were considerably warmer and wetter and in better agreement with independent paleoclimate evidence. This suggests that these new models offer the potential to provide climate estimates that will help scientists better understand ancient climates.
"Our study demonstrates that the inclusion of additional leaf traits that are functionally linked to climate improves paleoclimate reconstructions," Peppe said. "This will help us to better reconstruct past climates and ecosystems, which will allow us to study how ecosystems respond to climate change and variations in climate on local, regional and global scales."
### END
New Baylor research shows using leaves' characteristics improves accuracy measuring past climates
NSF-funded study shows high promise for new method to estimate temperature, precipitation for ancient ecosystems
2011-04-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research turns the world upside down
2011-04-20
London, ON – When you think you see a face in the clouds or in the moon, you may wonder why it never seems to be upside down.
It turns out the answer to this seemingly minor detail is that your brain has been wired not to.
Using tests of visual perception and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), Lars Strother and colleagues at The University of Western Ontario's world-renowned Centre for Brain & Mind recently measured activity in two regions of the brain well known for facial recognition and found they were highly sensitive to the orientation of people's faces.
The ...
KLAS Report: Hospitals, Vendors Recognize Value of Patient Flow Systems
2011-04-20
Seeking to relieve increasing stress on their staff and financial resources, a fifth of hospitals have turned to patient flow products -- and 9 out of 10 current users say they'd make this same choice again, according to a new study by KLAS.
The new report, "Patient Flow 2011: Relieving Hospital Pressure," offers a detailed review of the three most prevalent patient flow vendors -- Allscripts, McKesson, and TeleTracking -- plus a brief overview of nearly a dozen up-and-comers. According to the report, 85 percent of the 200-plus providers interviewed reported ...
U-M experts: Gym gone but not forgotten? Parents want more physical activity at school for kids
2011-04-20
Ann Arbor, Mich., -- Childhood obesity affects 1 of every 6 kids in the United States, in part due to a lack of physical activity. Schools can play a key part in offering elementary-age kids lots of chances to be active—on the playground during recess and when they're in gym.
But recent increasing expectations about academic achievement, coupled with budget cuts, have prompted many schools to cut back on both recess and gym class.
The U-M C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health asked parents of children 6 to 11 years old for their views about ...
Learn to run a biorefinery in a virtual control room developed by Iowa State researchers
2011-04-20
AMES, Iowa – David Grewell flipped on the augers that carry corn from a truck to a biorefinery.
Then, with a few more clicks of his computer mouse, he turned on the pumps that send grain all the way through an ethanol plant, from storage to hammer mill to slurry tanks to jet cooker to liquefaction, fermentation, distillation, water separation and ultimately to ethanol storage.
Don't forget the centrifuges, evaporators and driers that recover distillers grains for livestock feed.
All of this happened in a small office on the north side of the Food Sciences Building ...
Ross-Simons Unveils New Spring Collection
2011-04-20
Ross-Simons Jewelers' just-released Spring 2011 Jewelry Catalog includes hundreds of ways to put spring in your step. The vast collection ranges from floral gemstone jewelry inspired by spring's budding blossoms to exotic showpieces from around the world. Whether you are looking for a Mother's Day present, a graduation gift, or a treat for yourself, you'll find it in this catalog -and at a legendary low price!
"I love the jewelry we found for the spring catalog. It's so colorful and new. Year after year, spring inspires some of the most liberating, special jewelry ...
Too many relatives ruining your picnic? Be glad the flies don't invite their cousins
2011-04-20
AMES, Iowa – When your family members gather at a picnic in your backyard, there may be 10 to 20 people -- maybe more -- enjoying your barbecue.
When flies visit your party, be glad they don't bring their entire family.
Houseflies have more than 152,000 cousins. And those are just the ones we know about.
An Iowa State University researcher is one of a team of scientists who have recently researched the fly family tree -- one of the most complicated in the animal world.
"It really isn't a tree, it's sort of a bush," said Gregory Courtney, professor of entomology, ...
Straighterline and New England College of Business and Finance (NECB) Partner to Provide Students Seeking to Major in Business with Access to an Online Business Degree
2011-04-20
StraighterLine (www.straighterline.com) announced today that New England College of Business and Finance (NECB) (http://necb.edu/) in Boston, MA, has joined StraighterLine's network of partner colleges. Founded in 1909, New England College of Business and Finance (NECB) is a leading Boston institution offering Associate's, Bachelor's and Master's business degrees online. The school is accredited by the New England Association of Schools and Colleges (NEASC), and is licensed by the Massachusetts Department of Higher Education.
Through this partnership, students who successfully ...
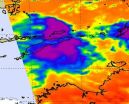
NASA's Aqua satellite sees weaker Tropical Depression Errol crossing West Timor
2011-04-20
NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Tropical Depression Errol's warming cloud temperatures as it was crossing the southern tip of West Timor today.
West Timor is the western and Indonesian portion of the island of Timor. To the east lies the Timor Sea, to the west is the Southern Indian Ocean.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image on April 18 at 04:53 UTC (12:53 a.m. EDT) that showed very little strong convection (rapidly rising air that forms thunderstorms) remained in Errol. The ...
Cosmetic Dentist in Park Ridge Makes Appointment Requesting as Easy as Point and Click
2011-04-20
Leading Park Ridge dentist, Dr. Daniel Hogan, has enhanced his patients' ability to seek treatment through online appointment requesting. The online appointment feature was created in order to make routine appointment setting quick and convenient, as well as to increase the quality of care patients receive. Patients can easily access the appointment requesting feature via the practice's educational website.
Providing patients with the opportunity to easily request appointments for various procedures and treatments creates a welcoming environment for this cosmetic dentist ...
GOES-13 satellite animation shows US severe storms and tornado outbreak
2011-04-20
The GOES-13 satellite captured images of the powerful weather system that triggered severe weather in the southern U.S. this weekend, and NASA created an animation to show its progression. GOES-13 satellite data showed the strong cold front as it moved eastward from Saturday through Monday and generated tornadoes before moving off-shore into the Atlantic Ocean. NASA's Aqua satellite also captured data from the system and took the temperature of the cold front's cloud tops and revealing severely cold temperatures of some of the thunderstorms.
The Geostationary Operational ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
[Press-News.org] New Baylor research shows using leaves' characteristics improves accuracy measuring past climatesNSF-funded study shows high promise for new method to estimate temperature, precipitation for ancient ecosystems