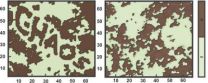
Breastfeeding tied to stronger maternal response to baby's cry
2011-04-21
(Press-News.org) A new study from the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry finds that mothers who feed their babies breast milk exclusively, as opposed to formula, are more likely to bond emotionally with their child during the first few months after delivery. The breastfeeding mothers surveyed for the study showed greater responses to their infant's cry in brain regions related to caregiving behavior and empathy than mothers who relied upon formula as the baby's main food source. This is the first paper to examine the underlying neurobiological mechanisms as a function of breastfeeding, and to connect brain activity with maternal behaviors among human mothers.
The fMRI-based findings suggest that breastfeeding and factors associated with breastfeeding, such has high levels of hormones (oxytocin, prolactin), stress, and culture may all play an important role for mothers' brain activity and parenting behaviours during the early postpartum period. The research shows that up to three or four months after delivery some of the brain regions originally observed at one month postpartum (amygdala, putamen, globus pallidus, and superior frontal gyrus) continued to activate and were correlated with maternal, sensitive behavior among the same group of mothers.
The findings highlight the dramatic relationship between breastfeeding, brain activity and parenting behaviours during the early postpartum period. Lead researcher Dr. Pilyoung Kim, "It is important for loved ones to support mothers and help them cope with challenges related to breastfeeding and parenting during this period. Mothers unable to breastfeed may benefit from extra encouragement to engage in sensitive, caring interactions with baby."
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-04-21
In February 2011, U.S. President Barack Obama made the ground-breaking announcement that his administration would no longer defend the Defense of Marriage Act (DOMA), which bans federal recognition of same-sex marriages. While the change in federal DOMA enforcement is a great stride forward in equal rights for the LGBT community, there are still alarming conflicts between federal law and Washington state law. If you are considering registering for a domestic partnership, are in a registered domestic partnership or if you advise people who are in a registered domestic partnerships, ...
2011-04-21
The passwords of the future could become more secure and, at the same time, simpler to use. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems in Dresden have been inspired by the physics of critical phenomena in their attempts to significantly improve password protection. The researchers split a password into two sections. With the first, easy to memorize section they encrypt a Captcha – an image that computer programs per se have difficulty in deciphering. The researchers also make it more difficult for computers, whose task it is to automatically ...
2011-04-21
When Congress' recent revisions to federal laws governing credit card usage went into effect, some consumers saw interest rates double or even triple. The law now allows for credit providers to be more flexible with interest rate raises, provided they give the cardholders notice of the action and share information about the total amount of the debt and approximately how long it will take to pay it off.
The changes in the law were initially introduced as a way to protect consumers, but, in practice they are much more biased toward lenders. Following the enacting of those ...
2011-04-21
New York, NY, April 20, 2011 - A 20-member blue-ribbon panel, the Study Group on Corporate Boards, co-sponsored by Columbia Business School and the John L. Weinberg Center for Corporate Governance at the University of Delaware, today released "Bridging Board Gaps," a report designed to improve board performance and effectiveness by offering a series of recommendations in critical areas of governance. The report calls for a renewed commitment to the purpose of corporate boards, and suggests guidelines to improve board practices and standards along seven core dimensions: ...
2011-04-21
WASHINGTON — Those childhood music lessons could pay off decades later - even for those who no longer play an instrument – by keeping the mind sharper as people age, according to a preliminary study published by the American Psychological Association.
The study recruited 70 healthy adults age 60 to 83 who were divided into groups based on their levels of musical experience. The musicians performed better on several cognitive tests than individuals who had never studied an instrument or learned how to read music. The research findings were published online in the APA ...
2011-04-21
Scientists are reporting development of a new battery that extracts and stores energy produced from the difference in saltiness at the point where freshwater in rivers flows into oceans. A report on the battery, which could supply about 13 percent of the world's energy needs, appears in ACS' journal Nano Letters.
Yi Cui and colleagues cite the intensive global scientific effort to develop renewable energy sources to supplement supplies of oil and other traditional fuels like coal, which contribute to global warming. Solar, wind, and geothermal are renewable, sustainable ...
2011-04-21
New technology that combines production of electricity with capture of carbon dioxide could make billions of barrels of oil shale — now regarded as off-limits because of the huge amounts of carbon dioxide released in its production — available as an energy source in a greenhouse world of the future. That's the conclusion of a report on "electricity production with in situ carbon capture" (EPICC) in ACS' journal Energy & Fuels.
Adam Brandt and Hiren Mulchandani explain that almost 3 trillion barrels of oil are trapped in the world's deposits of oil-shale, a dark-colored ...
2011-04-21
The North Carolina Legislature is considering proposed medical malpractice legislation that would limit damages for non-economic damages. The state has already enacted a law that caps monetary damages in negligence cases to $1 million where the parties agree to go to binding arbitration, but Bloomberg reports that few have actually exercised this option.
Proposed Malpractice Damage Cap
The legislation calls for a limit of $250,000 on non-economic damages, which include compensation for pain and suffering, disfigurement, mutilation, loss of a limb, paralysis, and death. ...
2011-04-21
A needle-in-the-haystack search through nearly 390,000 chemical compounds had led scientists to a substance that can sneak through the protective barrier surrounding the brain with effects promising for new drugs for Parkinson's and Huntington's disease. They report on the substance, which blocks formation of cholesterol in the brain, in the journal, ACS Chemical Biology.
Aleksey G. Kazantsev and colleagues previously discovered that blocking cholesterol formation in the brain could protect against some of the damage caused by chronic brain disorders like Parkinson's ...
2011-04-21
The costly, often-frustrating quest for new ways of preventing and treating diseases that strike vegetables, fruits, and other food crops bears striking similarity to the better-known saga of the pharmaceutical industry's pricey search for new drugs for humans. That's the topic of an article in the current edition of Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), ACS' weekly newsmagazine.
C&EN Senior Business Editor Melody M. Bomgardner points out that the R&D investment in new herbicides, fungicides, and other plant chemicals almost rivals that for human pharmaceuticals on a one ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Breastfeeding tied to stronger maternal response to baby's cry