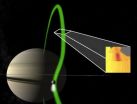
(Press-News.org) Data from NASA's Cassini spacecraft have revealed that Enceladus, one of Saturn's diminutive moons, is linked to Saturn by powerful electrical currents - beams of electrons that flow back and forth between the planet and moon. The finding is part of a paper published in Nature today.
CAPS, one of the instruments on board Cassini which made the electron beam discovery, includes a electron sensor called CAPS-ELS – led by UCL (University College London).
Since Cassini's arrival at Saturn in 2004 it has passed 500km-wide Enceladus 14 times, gradually discovering more of its secrets on each visit. Research has found that jets of gas and icy grains emanate from the south pole of Enceladus, which become electrically charged and form an ionosphere. The motion of Enceladus and its ionosphere through the magnetic bubble that surrounds Saturn acts like a dynamo, setting up the newly-discovered current system.
Scientists already knew that the giant planet Jupiter is linked to three of its moons by charged current systems set up by the satellites orbiting inside its giant magnetic bubble, the magnetosphere, and that these current systems form glowing spots in the planet's upper atmosphere. The latest discovery at Enceladus shows that similar processes take place at the Saturnian system too.
The detection of the beams was made by the Cassini Plasma Spectrometer's electron spectrometer, CAPS-ELS, the design and building of which was led at UCL's Mullard Space Science Laboratory. UCL co-authors of the Nature paper, Dr Geraint Jones and Professor Andrew Coates, are delighted with this new finding.
Dr Jones said: "Onboard Cassini, only CAPS-ELS has the capability of directly detecting the electron beams at the energies they're seen; this finding marks a great leap forward in our understanding of what exactly is going on at mysterious Enceladus."
Lead co-investigator of CAPS-ELS, Professor Coates, added: "This now looks like a universal process – Jupiter's moon Io is the most volcanic object in the solar system, and produces a bright spot in Jupiter's aurora. Now, we see the same thing at Saturn – the variable and majestic water-rich Enceladus plumes, probably driven by cryovolcanism, cause electron beams which create a significant spot in Saturn's aurora too."
The Nature paper in which the discovery is reported is co-led by Dr Wayne Pryor of Central Arizona College and Dr Abigail Rymer of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. The work also reports the presence of an ultraviolet auroral spot in Saturn's upper atmosphere, and of energetic ions flowing towards Enceladus: discoveries made using other Cassini instruments.
INFORMATION:
Cassini-related work at UCL-MSSL is supported by the UK Space Agency, the Science and Technology Facilities Council, and the European Space Agency. Geraint Jones is supported by a STFC Advanced Fellowship.
Notes for Editors
1. For more information or to interview Dr Geraint Jones or Professor Andrew Coates, please contact Clare Ryan in the UCL Media Relations Office on tel: +44 (0)20 3108 3846, mobile: +44 07747 565 056, out of hours +44 (0)7917 271 364, e-mail: clare.ryan@ucl.ac.uk.
2. 'The Enceladus Auroral Footprint at Saturn' is published in the April 21st issue of Nature. For copies of the paper please contact UCL Media Relations.
3. The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Italian Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter was designed, developed and assembled at JPL. For information about Cassini, please contact the JPL Media Relations Office on tel: +1 818 354 5011. More information is also available at http://www.nasa.gov/cassini and http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov.
4. Cassini-related work at UCL-MSSL is supported by the UK Space Agency, the Science and Technology Facilities Council, and the European Space Agency. Geraint Jones is supported by a STFC Advanced Fellowship. www.stfc.ac.uk
About UCL (University College London)
Founded in 1826, UCL was the first English university established after Oxford and Cambridge, the first to admit students regardless of race, class, religion or gender, and the first to provide systematic teaching of law, architecture and medicine. UCL is among the world's top universities, as reflected by performance in a range of international rankings and tables. Alumni include Marie Stopes, Jonathan Dimbleby, Lord Woolf, Alexander Graham Bell, and members of the band Coldplay. UCL currently has over 13,000 undergraduate and 9,000 postgraduate students. Its annual income is over £700 million. www.ucl.ac.uk
UCL Mullard Space Science Laboratory
The UCL Mullard Space Science Laboratory delivers a cutting-edge science programme, underpinned by a capability in space science instrumentation, systems engineering and project management. Its staff are committed to a broad outreach programme and are very happy to receive enquiries from the public and fellow space science professionals alike. http://www.mssl.ucl.ac.uk/
Beams of electrons link Saturn with its moon Enceladus
2011-04-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Avoiding Home Loan Modification Scams
2011-04-21
The nationwide economic recession has cost tens of thousands their jobs, forced millions into foreclosure and resulted in countless bankruptcy filings. Despite their best efforts, many people are falling behind on mortgage payments due to financial circumstances beyond their control. In an effort to avoid foreclosure, more and more people are seeking loan modifications as a way to lower payments temporarily (or permanently), making them more affordable and making keeping the home a real possibility.
Unfortunately, at a time when foreclosures are at a record high, unscrupulous ...
Molecule Nutlin-3a activates a signal inducing cell death and senescence in primary brain tumors
2011-04-21
Researchers of Apoptosis and Cancer Group of the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) have found that a small molecule, Nutlin-3a, an antagonist of MDM2 protein, stimulates the signalling pathway of another protein, p53. By this way, it induces cell death and senescence (loss of proliferative capacity) in brain cancer, a fact that slows its growth. These results open the door for MDM2 agonists as new treatments for glioblastomas. The study has been published at the journal PLoS ONE.
Glioblastoma multiforme is the most common brain tumour in adults and the ...
How molecules get to the right place at the right time
2011-04-21
In a multicellular organism, different cells fulfill a range of diversified functions. Often such specialization depends on the delivery of molecular goods to distinct places within a cell. It ensures that particular functions only occur at defined cellular sites. This establishment of intracellular asymmetry in the otherwise fluid environment of the cell cytoplasm requires active transport processes. Messenger RNAs (mRNA) represent an especially important type of freight. They are copies of genetic information stored in the nucleus. In the cytoplasm the information encoded ...
Lightning-fast materials testing using ultrasound
2011-04-21
Expectant mothers are familiar with the procedure: the physician examines them with an ultrasound apparatus that displays lifelike images of the fetus on the monitor. The application of this technology has been customary in medicine for years; in materials testing though, it has been used only in relatively rudimentary form to date. Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Non-Destructive Testing IZFP in Saarbrücken have adapted the conventional sonar procedure – a simple ultrasound method – and have succeeded in generating three-dimensional images with the aid of innovative ...
Nassau County Crime Lab Shut Down
2011-04-21
Prosecutors trust that the information they receive from crime labs is correct and accurate. The results from tests run at the lab are used to help build cases against those accused of crimes. When this information is inaccurate it can lead to questions for both past and future cases, and in some instances, lead to innocent people being convicted of crimes they did not commit. The Nassau County crime lab recently became the only police lab in the nation to completely close its doors due to its inability to follow procedures.
The lab's troubles started in December 2010. ...
How can we measure infants' pain after an operation?
2011-04-21
It turns out to be difficult to find out exactly how much a child who cannot yet speak suffers after a surgical operation. Researchers at the University Hospital of La Paz, in Madrid, have validated the 'Llanto' scale, the first, and only, tool in Spanish which measures infant pain rapidly and simply.
"The lack of appropriate tools prevents health professionals from knowing if a pre-verbal child who cannot tell us how much a surgical wound hurts, is being treated correctly", explains Francisco Reinoso, lead author of the study and head of the section of Paediatric Anaesthesia ...
Shades of gray: LSU researcher studies South Louisiana's historical ties to the oil industry
2011-04-21
BATON ROUGE – On the one year anniversary of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill that took the lives of 11 men and devastated the livelihoods of many residents of coastal Louisiana, it's difficult to put the complicated relationship between people and oil into perspective. While the environmental impacts have thus far not been as pervasive as originally feared, most scientists are in agreement that it is still simply too early to tell. However, dependence upon oil has not lessened over the past year, laying the groundwork for some very significant debates between environmentalists ...
Bus Accidents In Northeast The Most Recent In A Decade Long List
2011-04-21
The Northeast has seen three tour bus accidents in less than a month. On March 21, a New Jersey-based PRT tour bus rolled over in New Hampshire, seriously injuring five people.
The bus was travelling to Boston from Quebec, carrying 25 Koreans. The driver apparently lost control on a snowy highway.
On March 15, a bus headed from Chinatown to Philadelphia crashed on the New Jersey Turnpike in East Brunswick, killing two, the driver and a passenger.
The worst accident of the three happened on March 12, with 15 passengers killed when a Worldwide Tours Bus headed to ...
Rotten meat doesn't stand a chance
2011-04-21
Is the vacuum-packed chicken leg really still fresh and edible? Looks alone do not tell the whole story. And the "best-before" date is no guarantee, either. Scandals involving the sale of rotten meat have added to the uncertainty, and the customer him- or herself may be shortening the shelf life through improper storage. This is an area in which a sensor film developed by the Fraunhofer Research Institution for Modular Solid State Technologies EMFT in Munich can immediately give a green – or rather: yellow light, or warn of spoiled goods. EMFT developed the film in a project ...
California Family Courts: Take a Number ... A Very Large Number
2011-04-21
California Family Courts deal with a huge volume of traffic every year. Just the Los Angeles Superior Court -- Family Law handles 100,000 filings per year.
The high number of filings combined with the fact that over 70 percent of litigants in family law are unrepresented -- meaning they don't have an attorney -- many courts have adopted local rules and procedures in an attempt to more efficiently process the high volume of family law cases.
While some of these rules and procedures help speed up the process, the price that efficiency comes at was the virtual elimination ...