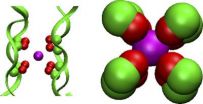
(Press-News.org) The latest Perspectives in General Physiology series examines the ion selectivity of cation-selective channels and transporters. The series appears in the May 2011 issue of the Journal of General Physiology (www.jgp.org).
According to Perspectives Editor Olaf Andersen in his introduction, a key tool in most recent studies on ion selectivity has been the so-called "toy models," which emphasize the fluid-like features of the selectivity filter and allow for the isolation of key features. Although proteins may indeed be fluid-like at small-length scales, however, they show considerable rigidity at longer-length scales. Thus, while toy models allow for important new insights, the goal is to transfer this knowledge into understanding the selectivity of the bilayer-spanning channels. This remains a challenge as it becomes necessary to consider not only the equilibrium situations but also the kinetics, and the competition among the permeant ions as they strive to make it through the channel.
As demonstrated by the Perspectives contributors in this issue, the questions surrounding ion selectivity can be approached from different, complementary directions. Alam and Jiang focus on what can be deduced from crystal structures; Nimigean and Allen consider what can be learned from a combined electrophysiological, crystallographic, and computational approach; and the last three contributors—Roux et al., Dixit and Asthagiri, and Varma et al. (appearing in the June 2011 issue of the JGP)—consider different theoretical and computational approaches based on MD simulations and quasi-chemical theory, including the use of simple "toy" models, to identify the mechanisms underlying ion selectivity.
INFORMATION:
The purpose of the Perspectives in General Physiology series is to provide an ongoing forum where scientific questions or controversies can be discussed by experts in an open manner.
About The Journal of General Physiology
Founded in 1918, The Journal of General Physiology (JGP) is published by The Rockefeller University Press. All editorial decisions on manuscripts submitted are made by active scientists. JGP content is posted to PubMed Central, where it is available to the public for free six months after publication. Authors retain copyright of their published works and third parties may reuse the content for non-commercial purposes under a creative commons license. For more information, please visit www.jgp.org.
Andersen, O.S. 2011. J. Gen. Physiol. doi:10.1085/jgp.201110651.
Alam, A., and Y. Jiang. 2011. J. Gen. Physiol. doi:10.1085/jgp.201010546.
Nimigean, C.M., and T.W. Allen. 2011. J. Gen. Physiol. doi:10.1085/jgp.201010551.
Roux, B., et al. 2011. J. Gen. Physiol. doi:10.1085/jgp.201010577.
Dixit, P.D., and D. Asthagiri. 2011. J. Gen. Physiol. doi:10.1085/jgp.201010533.
New perspectives on ion selectivity
2011-04-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cyara Solutions Continues Expansion into EMEA to Meet Growing Demand for a Better Contact Center Experience.
2011-04-26
Cyara, a pioneer of next-generation solutions for simulating, testing and monitoring interactive voice response (IVRs) and contact center systems, today announced further expansion into Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) with the opening of a dedicated EMEA office headquartered in London. The company also announced the opening of a United Kingdom-based data center and appointed Nick Duggan as director of sales EMEA to develop and support its rapidly expanding customer base in the region which includes Vodafone, Sky and Nationwide Building Society.
The Cyara Solution ...
ACC/AHA issue first clinical guidance for controlling high blood pressure in the elderly
2011-04-26
Hypertension is very common among older adults. 64 percent of older men and 78 percent of older women have high blood pressure, placing them at heightened risk for heart disease including heart failure, stroke, coronary artery disease and atrial fibrillation, as well as chronic kidney disease and diabetes mellitus. Despite its prevalence, rates of blood pressure control remain substantially lower in the elderly than in younger patients. In fact, over age 80, only one in three men and one in four women have adequate control of their blood pressure. Faced with an aging patient ...
Protein levels could signal that a child will develop diabetes
2011-04-26
AUGUSTA, Ga. – Decreasing blood levels of a protein that helps control inflammation may be a red flag that could help children avoid type 1 diabetes, researchers say.
Georgia Health Sciences University researchers are looking at blood levels of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, or IL-1ra, in children being closely followed because their genes put them at risk for type 1 diabetes. They also are looking at diabetic mice missing IL-1ra to see how the protein deficiency affects immune function and destruction of insulin-producing islet beta cells.
"We want to know if we ...
Researchers report widespread use of medications among pregnant women
2011-04-26
(Boston) – Researchers from Boston University's Slone Epidemiology Center, in collaboration with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Harvard School of Public Health, have reported widespread and increasing medication use among pregnant women. The study, which currently appears online in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, also found that medication use varied by socioeconomic status, maternal age, race/ethnicity and state of residence.
Although a number of antenatal medication exposures are known to cause birth defects, there is insufficient ...
Conservation of coastal dunes is threatened by poorly designed infrastructure
2011-04-26
Although the dune ecosystem is unusual, fragile and is protected by the "habitats" directive of the network Natura 2000, its conservation is very vulnerable to the proliferation of car parks, nearby buildings and inadequate boardwalks installed for protection or beach access.
Researchers at the University of Seville (UoS) have published a study in the Journal of Coastal Research of human impact on the natural dunes at two sites in the Gulf of Cádiz, specifically in the protected areas of La Flecha Litoral in El Rompido and Enebrales in Punta Umbria, both in Huelva province. ...
Wild hogs: Researchers examine impact of feral pigs in eastern N.C.
2011-04-26
The nation's feral pig population continues to expand, increasing the potential for interaction with humans and domestic swine - and for spreading diseases. Researchers at North Carolina State University examined feral pigs from eastern North Carolina to determine exposure to two parasites that can be transmitted from animals to people – Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) and Trichinella.
The study found that wild pigs host a significant number of these parasites.
"If ingested by humans, these parasites can invade muscle tissue and organs, causing flu-like symptoms – with ...
Fighting HIV in South Africa should focus on couples, study finds
2011-04-26
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A new study of sexual risk behaviors within long-term couples in South Africa finds that HIV-positive people take almost as much risk in their sexual behavior when they know their partner is HIV-negative or don't know their status, as when they know their partner is already infected. At the same time, HIV-positive partners who are on antiretroviral therapy and in intensive counseling do engage in less risky behavior. The Brown University researchers who led the study say both findings suggest that more couples-based HIV counseling is ...
Beetle bling: Researchers discover optical secrets of 'metallic' beetles
2011-04-26
WASHINGTON, April 25—Costa Rica was once regarded as the poorest of all the colonies of the Spanish Empire, sadly deficient in the silver and gold so coveted by conquistadors. As it turns out, all of the glittering gold and silver those explorers could have ever wanted was there all along, in the country's tropical rainforests—but in the form of two gloriously lustrous species of beetle.
Today, the brilliant gold- (Chrysina aurigans) and silver-colored (Chrysina limbata) beetles have given optics researchers new insights into the way biology can recreate the appearance ...
Laying bare the not-so-sweet tale of a sugar and its role in the spread of cancer
2011-04-26
BETHESDA, Md., April 25, 2011 – Cancer has a mighty big bag of tricks that it uses to evade the body's natural defense mechanisms and proliferate. Among those tricks is one that allows tumor cells to turn the intricate and extensive system of lymphatic vessels into something of a highway to metastasis. Yet research unveiled this week may aid in the development of therapeutics that will put the brakes on such cancer spread, and the researchers who completed the study say the findings may extend to other lymphatic disorders.
In the latest issue of the Journal of Biological ...
Researchers identify novel pathophysiologic mechanism responsible for autoimmunity
2011-04-26
(Boston) – Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have discovered that human proteins with an affinity for Dermatan Sulfate (DS) have the propensity to become autoantigens. In a companion article, the researchers also found that DS physically interacts with dead cells and that the resulting DS–autoantigen complexes drive autoreactive B-1a cell responses and autoantibody production both in-vitro and in mouse models. These findings, which appear in two back-to-back papers in the May issue of the American Journal of Pathology, provide a promising tool ...