(Press-News.org) Researchers have been examining the diverse behaviours of caterpillars to find solutions for the new generation of search and rescue soft robots.
Despite their extreme flexibility and adaptability, current soft-bodied robots are often limited by their slow speed, leading the researchers to turn to terrestrial soft-bodied animals for inspiration.
Some caterpillars have the extraordinary ability to rapidly curl themselves into a wheel and propel themselves away from predators. This highly dynamic process, called ballistic rolling, is one of the fastest wheeling behaviours in nature.
Researchers from Tufts University, Massachusetts, saw this as an opportunity to design a robot that mimics this behaviour of caterpillars and to develop a better understanding of the mechanics behind ballistic rolling.
The study, published today, Wednesday 27 April, in IOP Publishing's journal Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, also includes a video of both the caterpillar and robot in action and can be found at http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wZe9qWi-LUo.
To simulate the movement of a caterpillar, the researchers designed a 10cm long soft-bodied robot, called GoQBot, made out of silicone rubber and actuated by embedded shape memory alloy coils. It was named GoQBot as it forms a "Q" shape before rolling away at over half a meter per second.
The GoQBot was designed to specifically replicate the functional morphologies of a caterpillar, and was fitted with 5 infrared emitters along its side to allow motion tracking using one of the latest high speed 3D tracking systems. Simultaneously, a force plate measured the detailed ground forces as the robot pushed off into a ballistic roll.
In order to change its body conformation so quickly, in less than 100 ms, GoQBot benefits from a significant degree of mechanical coordination in ballistic rolling. Researchers believe such coordination is mediated by the nonlinear muscle coupling in the animals.
The researchers were also able to explain why caterpillars don't use the ballistic roll more often as a default mode of transport; despite its impressive performance, ballistic rolling is only effective on smooth surfaces, demands a large amount of power, and often ends unpredictably.
Not only did the study provide an insight into the fascinating escape system of a caterpillar, it also put forward a new locomotor strategy which could be used in future robot development.
Many modern robots are modelled after snakes, worms and caterpillars for their talents in crawling and climbing into difficult spaces. However, the limbless bodies severely reduce the speeds of the robots in the opening. On the other hand, there are many robots that employ a rolling motion in order to travel with speed and efficiency, but they struggle to gain access to difficult spaces.
Lead author Huai-Ti Lin from the Department of Biology, Tufts University, said: "GoQBot demonstrates a solution by reconfiguring its body and could therefore enhance several robotic applications such as urban rescue, building inspection, and environmental monitoring."
"Due to the increased speed and range, limbless crawling robots with ballistic rolling capability could be deployed more generally at a disaster site such as a tsunami aftermath. The robot can wheel to a debris field and wiggle into the danger for us."
###
From Wednesday 27 April 2011, the journal paper can be found at http://iopscience.iop.org/1748-3190/6/2/026007.
END
In a large, traffic-congested city in China, severe heart attack patients received treatment faster and had better long-term results when interventional physicians were taken to them, according to a study in the American Heart Association journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
The REVERSE-STEMI study involved 334 patients who had suffered a ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), a severe form of heart attack.
The patients were initially brought to one of five hospitals, all in Shanghai, China, that didn't have specialists who could perform primary ...
In contrast to previous preliminary data, use of vitamin E or the diabetes drug metformin was not superior to placebo on a measured outcome for treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents, according to a study in the April 27 issue of JAMA.
"Coincident with the rise in prevalence of childhood and adolescent obesity over the past few decades, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most common cause of chronic liver disease in children in the United States," according to background information in the article. NAFLD encompasses ...
This Mother's Day, Fort Worth restaurant, Chef Point Cafe, is giving moms a real treat with a special menu devoted to this holiday. This day, dedicated to matriarchs, is for enjoying family and what better way to do that then with a fabulous meal in a fine dining restaurant renowned for world-class cuisine? Find out what Mother's Day means, then see how dining together over a special feast celebrates each doting mother who went above and beyond her maternal duties.
The tradition of honoring mothers on a particular day is traced back to ancient Grecian times. Modern etiquette ...
An examination of medication adherence among children with newly diagnosed epilepsy found that nearly 60 percent showed persistent nonadherence during the first 6 months of therapy, and that lower socioeconomic status was associated with higher non-adherence, according to a study in the April 27 issue of JAMA.
Epilepsy, a disorder of recurrent unprovoked seizures, affects 325,000 children younger than 15 years in the United States. "Because of epilepsy's common occurrence, the narrow therapeutic and safety margins of antiepileptic medications, and the recognized complications ...
An examination of health literacy (such as understanding basic health information) among managed care patients with heart failure, a condition that requires self-management, found that nearly one in five have low health literacy, which was associated with a higher all-cause risk of death, according to a study in the April 27 issue of JAMA.
Health literacy is the degree to which individuals can obtain, process and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions, as defined by the Institute of Medicine. According to background ...
In an analysis of data from a coronary care registry in Sweden, between 1996-2007 there was an increase in the prevalence of use of evidence-based invasive procedures and pharmacological therapies for treatment of a certain type of heart attack, and a decrease in the rate of death at 30 days and one year after a heart attack for these patients, according to a study in the April 27 issue of JAMA.
Although recent population-based studies indicate a reduction in incidence, ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI; a certain pattern on an electrocardiogram following a heart ...
Among obese patients, activation of the protein biomarker CTNNB1 was associated with better colorectal cancer-specific survival and overall survival, whereas post-diagnosis physical activity was associated with better colorectal cancer-specific survival among patients negative for CTNNB1, according to a study in the April 27 issue of JAMA.
Activation of the WNT signaling pathway (a network of proteins known for their roles in cancer) and cadherin-associated protein beta-1 (CTNNB1; [beta-catenin]) plays a critical role in colorectal carcinogenesis. Accumulating evidence ...
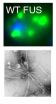
PHILADELPHIA -- Several genes have been linked to ALS, with one of the most recent called FUS. Two new studies in PLoS Biology, one from the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, and the other from colleagues at Brandeis University, both examined FUS biology in yeast and found that defects in RNA biology may be central to how FUS contributes to ALS, or Lou Gehrig's disease. These findings point to new targets for developing drugs.
Proteins aggregate to form insoluble clumps in the brain and spinal cord of ALS patients. In some instances of ALS, the clumping ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Teens are rarely described as stable, so when something about their rapidly changing brains remains placidly unaltered, neuroscientists take notice. Such is the case in a new study of electroencephalography (EEG) readings gathered from dozens of teens while they slept. Despite the major neural overhaul underway during adolescence, most individuals maintained a unique and consistent pattern of underlying brain oscillations. The work lends a new level of support to the idea, already observed in adults, that people produce a kind of brainwave ...
Hospitals and physician practices that form care-coordinating networks called "Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs)," under provisions of the new health-care law could reap cost-savings and other benefits. However, experts at Johns Hopkins and the University of Pennsylvania warn that such networks could potentially be designed to exclude minorities and widen disparities in health care.
In a commentary appearing in the April 27 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association, a Johns Hopkins physician says that as a result of new provisions in the Patient Protection ...