(Press-News.org) Athens, Ga. - A new University of Georgia study has found that select varieties of sorghum bran have greater antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties than well-known foods such as blueberries and pomegranates.
Researchers measured polyphenolic compounds, which naturally occur in plants to help fight against pests and disease, and found that the black and sumac varieties of sorghum have significant levels of antioxidants. Many fruits also contain these compounds, they said, though sorghum bran may prove to be the richest and cheapest source.
"Since most human chronic disease states are associated with chronic inflammation and high oxidative stress, a food ingredient such as sorghum bran could potentially make certain processed foods better for a healthy diet," said study co-author Diane Hartle, director of the UGA Nutraceutical Research Laboratory and an associate professor in the College of Pharmacy.
Hartle and her colleagues, whose results appear in the current issue of the Journal of Medicinal Food, measured the degree to which extracts from four different varieties of sorghum reduced inflammation in mice. They found that black and sumac varieties showed significantly higher levels of polyphenolic content and antioxidant levels than the two low-tannin varieties tested, which did not reduce inflammation.
The authors found that levels of polyphenolic compounds in the high-tannin sorghum varieties ranged from 23 to 62 mg of polyphenols per gram. For comparison, blueberries contain approximately 5 mg of polyphenolics per gram, while pomegranate juice contains 2 to 3.5 mg per gram.
The U.S. is the largest producer of sorghum in the world. Most of the sorghum grown, however, is a low-tannin variety that is fed to cattle and poultry or used to manufacture ethanol to fuel cars. "High-tannin sorghums can be of greater economy to manufacturers because of the current cost of berry and fruit sources of similar plant-based chemicals," said study co-author Phillip Greenspan, associate professor in the UGA College of Pharmacy.
High-tannin sorghum bran products have not been available in supermarket foods until recently. The researchers said they hope to generate interest in sorghum bran or its extract as an additive to food and beverages. Sorghum bran extract could be added to a variety of foods and beverages as a liquid concentrate or dried powder. The Great Plains area of the U.S. is the largest worldwide producer of sorghum, and the researchers said that the combination of its low price and high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties will make it widely useful as an inexpensive and nutritional food additive.
The researchers have already experimented with adding the extract to apple juice to make it an affordable alternative to pomegranate juice and other antioxidant-rich products. "We're hoping that some company decides to extract this bran and pull these chemicals out and put the extract into a beverage that can help you fight disease rather than promote disease," Hartle said.
Study co-author James Hargrove, associate professor in the UGA College of Family and Consumer Sciences, added that high-tannin sorghum has more antioxidant phytochemicals than other brans such as rice, wheat and oats, whose phenolic content and antioxidant values are low. He and Hartle said that the use of sorghum can become a way to reintroduce a quality food to many products that now use bleached, refined flour.
"Sorghum bran not only provides the fiber but gives you a real medicinal punch at the same time because it delivers a lot of other chemicals that a berry would give you," Hartle said.
INFORMATION: END
David H. Adams, MD, Marie-Josée and Henry R. Kravis Professor and Chairman of the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery at The Mount Sinai Medical Center, has performed the first implantation of the Medtronic Tri-Ad Semi-Flexible Tricuspid Annuloplasty Ring in the United States. Dr. Adams invented the ring, which was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The tricuspid valve lies between the right atrium and right ventricle of the heart. Tricuspid valve regurgitation occurs when the valve does not close completely and blood leaks back into the right atrium ...
A group of children who underwent fusion surgery for spondylolisthesis in the lumbar spine 30 years ago showed a clear reduction in back pain when followed up seven years later. A new study of these patients as adults has found that the benefits have lasted, reveals research from the Sahlgrenska Academy and Sahlgrenska University Hospital presented this week at the International Society of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology (SICOT) annual international conference in Gothenburg.
Spondylolisthesis (forward displacement of a vertebra) in the lumbar spine occurs in 6% ...
Today sees the presentation of a study that, for the first time, shows the results of treatment using prostheses attached to titanium implants in the bones of patients with above-the-knee amputations. It reveals that the treatment improves function and quality of life in nine out of ten patients, and is the result of research carried out at the Sahlgrenska Academy and Sahlgrenska University Hospital that is being presented this week at the International Society of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology (SICOT) annual international conference in Gothenburg.
At a symposium ...
Early childhood education can play a key role in relation to change when the world fails to adopt a sustainable approach economically, ecologically and socially.
This was highlighted at the World Congress "Children, citizens in a challenged world", which was hosted by the University of Gothenburg.
In a statement, the congress urges governments around the world to protect children's right to a childhood.
More and more people are realising that work with young children is a force for change in itself, towards creating a different society. Early childhood education has ...
Sexual conflict is not only a human phenomenon. Scientists at the University of Gothenburg have shown that females of the rough periwinkle conceal their gender identity in order to avoid excessive copulation.
The females of most species of snail excrete a substance in their mucous trails that enables males to find them more easily, since they can distinguish between trails from females and those from other males. The males follow the mucous trails laid down by females in order to find a partner for mating. However, the females of one of the species studied (Littorina ...
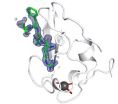
VIDEO:
This video shows UBR-box recognition of an arginine residue at the beginning of a protein (blue) targeted for degradation. The structural integrity of the UBR box depends on zinc (grey)...
Click here for more information.
Our bodies recycle proteins, the fundamental building blocks that enable cell growth and development. Proteins are made up of a chain of amino acids, and scientists have known since the 1980s that first one in the chain determines the lifetime ...
The new Premier League season has begun and in Madrid the World Cup celebrations are barely over, yet according to research in WIREs Cognitive Science the world's best players may soon be facing a new challenge from football playing robots, which their creators claim will be able to play and beat a human team. The research reveals how building robots to play football is driving the development of artificial intelligence and robotic technology which can be used for roles including search and rescue and home help.
The author, Claude Sammut, from the ARC Centre of Excellence ...
New findings from a major drug trial have brought experts a step closer to developing a drug which could prevent thousands of British deaths from heart attacks.
Dr Robert Storey, Reader at the University of Sheffield and Consultant Cardiologist at Sheffield Teaching Hospitals, was the UK lead for international trials of a new drug, ticagrelor, which have been taking place over the last six years.
The new findings from one of these studies, the ONSET/OFFSET study, revealed that the platelet function in patients taking ticagrelor recovered much quicker after the drug ...
Stroke patients who were left partially paralysed found that their condition improved after they received a simple and non-invasive method of brain stimulation, according to research in the September issue of the European Journal of Neurology.
Researchers from the Ain Shams University in Cairo, Egypt, studied 60 patients with ischaemic stroke - where the blood supply is reduced to the brain - who had been left with mild to moderate muscle weakness down one side of their body.
Twenty of the randomly assigned treatment group received repetitive transcranial magnetic ...
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. - Using carbon nanotubes (hollow tubes of carbon atoms), MIT chemical engineers have found a way to concentrate solar energy 100 times more than a regular photovoltaic cell. Such nanotubes could form antennas that capture and focus light energy, potentially allowing much smaller and more powerful solar arrays.
"Instead of having your whole roof be a photovoltaic cell, you could have little spots that were tiny photovoltaic cells, with antennas that would drive photons into them," says Michael Strano, the Charles and Hilda Roddey Associate Professor of ...