(Press-News.org) Plants adapt to the local weather and soil conditions in which they grow, and these environmental adaptations are known to evolve over thousands of years as mutations slowly accumulate in plants' genetic code. But a University of Rochester biologist has found that at least some plant adaptations can occur almost instantaneously, not by a change in DNA sequence, but simply by duplication of existing genetic material.
Justin Ramsey's findings are published in the current Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
While nearly all animals have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from the maternal parent and the other inherited from the paternal parent—many plants are polyploids, meaning they have four or more chromosome sets. "Some botanists have wondered if polyploids have novel features that allow them to survive environmental change or colonize new habitats," says Assistant Professor Justin Ramsey. "But this idea had not been rigorously tested."
Plant breeders have previously induced polyploidy in crop plants, like corn and tomato, and evaluated its consequences in greenhouses or gardens. Such an experimental approach had never been taken in wild plant species, Ramsey said, so it was unknown how polyploidy affected plant survival and reproduction in nature.
Ramsey decided to perform his own test by studying wild yarrow (Achillea borealis) plants that are common on the coast of California. Yarrow with four chromosome sets (tetraploids) occupy moist, grassland habitats in the northern portion of Ramsey's study area; yarrow with six sets of chromosomes (hexaploids) grow in sandy, dune habitats in the south.
Ramsey transplanted tetraploid yarrow from the north into the southern habitat and discovered that the native hexaploid yarrow had a five-fold survival advantage over the transplanted tetraploid yarrow. This experiment proved that southern plants are intrinsically adapted to dry conditions; however, it was unclear if the change in chromosome number, per se, was responsible. Over time, natural hexaploid populations could have accumulated differences in DNA sequence that improved their performance in the dry habitats where they now reside.
To test that idea, Ramsey took first-generation, mutant hexaploid yarrow that were screened from a tetraploid population, and transplanted them to the sandy habitat in the south. Ramsey compared the performance of the transplanted yarrows and found that the hexaploid mutants had a 70 percent survival advantage over their tetraploid siblings. Because the tetraploid and hexaploid plants had a shared genetic background, the difference of survivorship was directly attributable to the number of chromosome sets rather than the DNA sequences contained on the chromosomes.
Ramsey offers two theories for the greater survivorship of the hexaploid plants. It may be that DNA content alters the size and shape of the cells regulating the opening and closing of small pores on the leaf surface. As a result, the rate at which water passes through yarrow leaves may be reduced by an increase in chromosome set number (ploidy). Another possibility, according to Ramsey, is that the addition of chromosome sets masks the effects of plant deleterious genes, similar to those that cause cystic fibrosis and other genetic diseases in humans.
"Sometimes the mechanism of adaptation isn't a difference in genes," said Ramsey, "it's the number of chromosomes." While scientists previously believed polyploidy played a role in creating gene families—groups of genes with related functions—they were uncertain whether chromosome duplication itself had adaptive value.
Now, Ramsey says scientists "should pay more attention to chromosome number, not only as an evolutionary mechanism, but as a form of genetic variation to preserve rare and endangered plants."
### END
Genome duplication encourages rapid adaptation of plants
2011-05-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
It's a jungle out there
2011-05-04
Tallahassee, FL-- The most comprehensive study of 20th century children's books ever undertaken in the United States has found a bias towards tales that feature men and boys as lead characters. Surprisingly, researchers found that even when the characters are animals, they tend to be male.
The findings, published in the April issue of Gender & Society, are based on a study of nearly 6,000 books published from 1900 to 2000. While previous studies have looked at the representation of male and female characters in children's books, they were often limited in scope. "We looked ...
Student Visas: F1 Visa Requirements
2011-05-04
Student Visas: F1 Visa Requirements
The F1 visa allows students from around the world to study full time in the United States at accredited primary, secondary or postsecondary academic institutions. The F1 is a nonimmigrant visa, meaning it is intended for temporary visitors who do not intend to become permanent residents.
However, F1 recipients are usually eligible for 12 months of practical training (employment authorization or permission to work) during and after completing their studies. Students who take advantage of this training or other similar opportunities ...
Alabama Dram Shop Act
2011-05-04
Alabama Dram Shop Act
In Alabama it had long been the rule, with cases going back to 1876, that one cannot recover for negligence in the dispensing of alcohol.
The legislature modified Alabama case law, which provided no remedy for the unlawful dispensing of alcohol, by the creation the Civil Damages Act and the Dram Shop Act.
The Dram Shop Act
The language of the Alabama Dram Shop Act states:
-Every wife, child, parent, or other person who shall be injured in person, property, or means of support by any intoxicated person or in consequence of the intoxication ...
MIT: New system for flat-panel solar power combines with hot water systems for greater performance
2011-05-04
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- MIT researchers and their collaborators have come up with an unusual, high performance and possibly less expensive way of turning the sun's heat into electricity.
Their system, described in a paper published online in the journal Nature Materials on May 1, produces power with an efficiency roughly eight times higher than ever previously reported for a solar thermoelectric device — one that produces electricity from solar heat. It does so by generating and harnessing a temperature difference of about 200 degrees Celsius between the interior of the device ...
Protein identified as enemy of vital tumor suppressor PTEN
2011-05-04
HOUSTON - A protein known as WWP2 appears to play a key role in tumor survival, a research team headed by a scientist at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center reports in an advance online publication of Nature Cell Biology.
Their research suggests that the little-studied protein binds to the tumor-suppressing protein PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10), marking it for destruction by proteasomes, which degrade proteins and recycle their components.
PTEN plays a role regulating the cellular reproduction cycle and prevents rapid ...
Safety Rule Requiring Backup Cameras Paused
2011-05-04
Safety Rule Requiring Backup Cameras Paused
Two year old Cameron Gulbransen died in a tragic and preventable accident, a type of accident that occurs too often -- Cameron was accidentally backed over by his father while playing in the driveway. In response to Cameron's death, Congress passed the Cameron Gulbransen Kids Transportation Safety Act of 2007.
The act sets out to end backup accidents by trying to "eliminate" vehicles' blind spots. As part of the act, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) set out to implement a rule requiring ...
Mouse study turns fat-loss/longevity link on its head
2011-05-04
SAN ANTONIO (May 3, 2011) — Since the 1930s scientists have proposed food restriction as a way to extend life in mice. Though feeding a reduced-calorie diet has indeed lengthened the life spans of mice, rats and many other species, new studies with dozens of different mouse strains indicate that food restriction does not work in all cases.
Diet and fat loss
Researchers at the UT Health Science Center San Antonio's Barshop Institute for Longevity and Aging Studies, with colleagues at the University of Colorado, studied the effect of food restriction on fat and weight ...
Thinking of Leaving the Hospital Before You Are Discharged? Do So at Your Own Risk
2011-05-04
Thinking of Leaving the Hospital Before You Are Discharged? Do So at Your Own Risk
A recent report released by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality shows an alarming rise in the number of patients who are leaving hospitals, emergency rooms and urgent care clinics before they are properly discharged. The agency examined data dating back to 1997 and found that the number of patients leaving against medical advice has increased nearly 40 percent since then. Hospital discharge information for 2008 -- the most recent year such data was available -- show that roughly ...
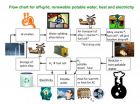
Portable tech might provide drinking water, power to villages
2011-05-04
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Researchers have developed an aluminum alloy that could be used in a new type of mobile technology to convert non-potable water into drinking water while also extracting hydrogen to generate electricity.
Such a technology might be used to provide power and drinking water to villages and also for military operations, said Jerry Woodall, a Purdue University distinguished professor of electrical and computer engineering.
The alloy contains aluminum, gallium, indium and tin. Immersing the alloy in freshwater or saltwater causes a spontaneous reaction, ...
Survey Reveals High Rate of Criminal Convictions Among Nursing Home Employees
2011-05-04
Survey Reveals High Rate of Criminal Convictions Among Nursing Home Employees
In an unprecedented examination of the nursing home industry, the federal Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) surveyed hundreds of nursing homes around the country to find that a whopping 92 percent of them employed at least one worker with a criminal conviction. Perhaps even more disturbing is the fact that almost half of all nursing home facilities in the country employ five or more people with at least one conviction each.
An extreme example of the problem is seen in one particular ...