(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, PA – 3 May 2011 – Developmental abnormalities in the mirror neuron system may contribute to social deficits in autism.
The mirror neuron system is a brain circuit that enables us to better understand and anticipate the actions of others. These circuits activate in similar ways when we perform actions or watch other people perform the same actions.
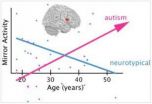
Now, a new study published in Biological Psychiatry reports that the mirror system in individuals with autism is not actually broken, but simply delayed.
Dr. Christian Keysers, lead author on the project, detailed their findings, "While most of us have their strongest mirror activity while they are young, autistic individuals seem to have a weak mirror system in their youth, but their mirror activity increases with age, is normal by about age 30 and unusually high thereafter."
This increase in function of mirror neuron systems may be related to increased capacity for social function or responsiveness to rehabilitative treatments among individuals with autism.
"The finding of late developing circuit functions could be very important. One wonders whether the recent breakthroughs in the genetics of autism could help to identify causes for the developmental delays. This type of bridge might help to identify novel treatment mechanisms for autism," said Dr. John Krystal, Editor of Biological Psychiatry.
One of the next steps in this line of research will be for researchers to examine how individuals with autism accomplish this improvement over time, and how therapeutic interventions targeting the same mechanism can help to support this important process.
INFORMATION:
Notes to Editors
The article is "Age-Related Increase in Inferior Frontal Gyrus Activity and Social Functioning in Autism Spectrum Disorder" by Jojanneke A. Bastiaansen, Marc Thioux, Luca Nanetti, Christiaan van der Gaag, Cees Ketelaars, Ruud Minderaa, and Christian Keysers. Bastiaansen, Thioux, Nanetti, and Keysers are affiliated with the Social Brain Laboratory, Department of Neuroscience, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands. Bastiaansen and Ketelaars are affiliated with Autism Team North Netherlands, Lentis, Groningen, The Netherlands. Thioux and Keysers are also with the Social Brain Laboratory, Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. van der Gaag and Minderaa are affiliated with Department of Psychiatry, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands. The article appears in Biological Psychiatry, Volume 69, Number 9 (May 1, 2011), published by Elsevier.
The authors' disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available in the article.
John H. Krystal, M.D. is Chairman of the Department of Psychiatry at the Yale University School of Medicine and a research psychiatrist at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System. His disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available at http://journals.elsevierhealth.com/webfiles/images/journals/BPS/Biological_Psychiatry_Editorial_Disclosures_03_29_11.pdf.
Full text of the article mentioned above is available upon request. Contact Chris J. Pfister at c.pfister@elsevier.com to obtain a copy or to schedule an interview.
About Biological Psychiatry
This international rapid-publication journal is the official journal of the Society of Biological Psychiatry. It covers a broad range of topics in psychiatric neuroscience and therapeutics. Both basic and clinical contributions are encouraged from all disciplines and research areas relevant to the pathophysiology and treatment of major neuropsychiatric disorders. Full-length reports of novel results, commentaries, case studies of unusual significance, and correspondence judged to be of high impact to the field are published, particularly those addressing genetic and environmental risk factors, neural circuitry and neurochemistry, and important new therapeutic approaches. Concise reviews and editorials that focus on topics of current research and interest are also published rapidly.
Biological Psychiatry (www.sobp.org/journal) is ranked 4th out of 117 Psychiatry titles and 13th out of 230 Neurosciences titles in the 2009 ISI Journal Citations Reports® published by Thomson Reuters. The 2009 Impact Factor score for Biological Psychiatry has increased to 8.926.
About Elsevier
Elsevier is a world-leading publisher of scientific, technical and medical information products and services. The company works in partnership with the global science and health communities to publish more than 2,000 journals, including The Lancet and Cell, and close to 20,000 book titles, including major reference works from Mosby and Saunders. Elsevier's online solutions include SciVerse ScienceDirect, SciVerse Scopus, Reaxys, MD Consult and Nursing Consult, which enhance the productivity of science and health professionals, and the SciVal suite and MEDai's Pinpoint Review, which help research and health care institutions deliver better outcomes more cost-effectively.
A global business headquartered in Amsterdam, Elsevier employs 7,000 people worldwide. The company is part of Reed Elsevier Group PLC, a world-leading publisher and information provider, which is jointly owned by Reed Elsevier PLC and Reed Elsevier NV. The ticker symbols are REN (Euronext Amsterdam), REL (London Stock Exchange), RUK and ENL (New York Stock Exchange).
The mirror neuron system in autism: Broken or just slowly developing?
2011-05-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Amygdala detects spontaneity in human behavior
2011-05-04
A pianist is playing an unknown melody freely without reading from a musical score. How does the listener's brain recognise if this melody is improvised or if it is memorized? Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig investigated jazz musicians to discover which brain areas are especially sensitive to features of improvised behaviour. Among these are the amygdala and a network of areas known to be involved in the mental simulation of behaviour. Furthermore, the ability to correctly recognise improvisations was not only related ...
Hebrew University researchers demonstrate why DNA breaks down in cancer cells
2011-05-04
Jerusalem, May 3, 2011 – Damage to normal DNA is a hallmark of cancer cells. Although it had previously been known that damage to normal cells is caused by stress to their DNA replication when cancerous cells invade, the molecular basis for this remained unclear.
Now, for the first time, researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have shown that in early cancer development, cells suffer from insufficient building blocks to support normal DNA replication. It is possible to halt this by externally supplying the "building blocks," resulting in reduced DNA damage ...
Controlling brain circuits with light
2011-05-04
Commenting on Edward Boyden's article, Ben Barres, Head of the Neuronal & Glial Cell Biology Section of Faculty of 1000 and Professor at Stanford University School of Medicine said: "There will probably be a Nobel prize for optogenetics someday as it has revolutionized our attempts to understand how the brain works. This article provides a fascinating insight into the birth of optogenetics and the roles of the major players."
The invention of optogenetics literally sheds light on how our brains work. Published in the May 2011 issue of F1000 Biology Reports, Edward Boyden's ...
A boring life -- the Asiatic wild ass in the Mongolian Gobi
2011-05-04
Wild asses are descendants of the original ancestors of the horse and the donkey. Unfortunately most species of wild ass are now in danger of extinction, largely as a direct result of human activities such as hunting and habitat destruction. Walzer's group has been working together with colleagues in Germany, China and Mongolia on the Asiatic wild ass, which is currently restricted to areas in Mongolia, China, India, Iran and Turkmenistan although it was formerly much more widespread. The researchers are considering the factors responsible for the decline of the species, ...
Nature of bonding determines thermal conductivity
2011-05-04
Jülich/Aachen, 3 May 2011 - Optical data carriers such as DVDs, Blu-rays and CD-RWs store data in layers of so-called "phase change materials". In the future, these materials will enable the development of fast, non-volatile and energy-saving main memories. A prerequisite for this is a low thermal conductivity. Phase change materials display a surprisingly low thermal conductivity even in the crystalline state. This is described by an international research team including scientists from Jülich and Aachen in the latest edition of the respected journal Advanced Functional ...
Climbers leave rare plants' genetic variation on the rocks
2011-05-04
Rock climbers are having a negative impact on rare cliff-dwelling plants, ecologists have found. Writing in the British Ecological Society's Journal of Applied Ecology they say that in areas popular with climbers, conservation management plans should be drawn up so that some cliffs are protected from climbers.
The Northern Franconian Jura and the Swabian Alb are two of Germany's most important climbing areas but also the last European stronghold of the rare yellow whitlowgrass (Draba azoides) – a small plant that lives on limestone cliffs where it forms cushion-like rosettes.
To ...
Curtains that 'quench' noise
2011-05-04
Noise is annoying. It interrupts communication, reduces productivity and tires people out – in extreme cases it can even make them ill. Sound absorbing surfaces are therefore needed in rooms where people work, talk to each other or are trying to relax. These decrease reverberation and so make rooms quieter. However so called acoustically «hard» materials such as glass and concrete, which are commonly used in interior design, scarcely absorb sound at all. Heavy curtains made of material such as velvet are often used to absorb sound. On the other hand, lightweight and transparent ...
Employees should build reputation before using work-family programs
2011-05-04
Employees often suspect that participating in work-family programs could harm their careers, and prior research studies have shown they are right to be worried. Employees who use the programs are at risk of fewer promotions and lower wages than those who do not.
But now, two researchers have shown how employees could gain the intended benefits of work-family programs -- such as flexible schedules with prorated pay -- without harming their careers.
Forrest Briscoe, assistant professor of management, Penn State Smeal College of Business, and Katherine Kellogg, associate ...
Study finds infection control violations at 15 percent of US nursing homes
2011-05-04
Washington, DC, May 3, 2011 – Fifteen percent of U.S. nursing homes receive deficiency citations for infection control per year, according to a new study published in the May issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of APIC - the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology.
Conducted by a team of researchers at the University of Pittsburgh's Graduate School of Public Health, the study analyzed deficiency citation data collected for the purpose of Medicare/Medicaid certification between 2000 and 2007, representing ...
Grazing as a conservation tool
2011-05-04
NEW YORK (May 3, 2011) – Rotational grazing of cattle in native pasturelands in Brazil's Pantanal and Cerrado regions can benefit both cattle and wildlife, according to a new study by the Wildlife Conservation Society.
The technique, which has been adapted for a variety of livestock worldwide, calls for cattle to graze in small areas for shorter periods of time before moving onto other pastures. The result is a greater forage base that produces larger, more valuable cattle while reducing incentives for deforestation, uncontrolled burning, and replacement ...