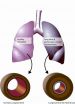
(Press-News.org) Patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension struggle with severe symptoms, which include shortness of breath, exhaustion and a lack of vitality. Moreover, the disease, which is more common in women, often claims the patient's life within a few years of its development. The currently available methods of treatment can slow down the progression of the disease and improve the symptoms; a cure, however, has thus far been unavailable. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research and Giessen University have now succeeded - for the first time in an animal model - in not only halting the progression of the disease, but also in reversing it with the help of an inhalation therapy.
A malfunction of the vascular endothelium arises at an early stage in the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension. The endothelium is the interior layer of blood vessels, which has an optimal smooth surface and hence ensures low-friction blood flow. In addition, the endothelium regulates the diameter of the blood vessels and adapts the distribution of the blood to the body's functional requirements. The blood vessel growth is also controlled by the endothelium. With pulmonary arterial hypertension, the malfunctioning of the vascular epithelium results in the contraction and narrowing of the blood vessels. In addition, the blood vessel walls thicken as a result of the pathological proliferation of the blood vessel wall cells, which leads to the further obstruction of blood flow. The heart must pump harder to counteract this resistance thus causing, in turn, pathological changes in the right ventricle that ultimately lead to the development of the condition known as right heart failure.
Under normal circumstances, the entire system is held in balance by just a few factors; nitric oxide plays a central role in the maintenance of this balance. "We have been aware of the exceptional importance of this gas for the functionality of blood vessels for some years now. It is one of the components that regulate the width of blood vessels and cell proliferation," explains Ralph Schermuly, a research group leader at the MPI. The sudden decline in the production of nitric oxide by the endothelium plays an important role in the development of pulmonary hypertension. This gives rise to the aforementioned effects on the functioning of the blood vessels.
Nitric oxide production takes place as a result of various biochemical reactions, the regulation of which is extremely complex. The Bad Nauheim-based scientists and their colleagues from the University of Giessen attempted to intervene at a key point in this system. To this end, they had rats, in which pulmonary hypertension had been experimentally induced, repeatedly inhale a nasal spray containing the active ingredient over a period of four weeks. "The effect was impressive. Not only was the disease progression halted, we were also able to observe a clear improvement in all areas," explains Soni Pullamsetti, first author of the study. The normal function of the endothelium was thus restored, cell proliferation in the blood vessel walls decreased significantly and the narrowing of the blood vessels reversed. According to Pullamsetti, these combined effects caused a reduction in the arterial hypertension.
The scientists would now like to carry out further research on the therapeutic potential of their findings. Werner Seeger, Director of the Department of Lung Development and Remodelling at the MPI and Director of the Department of Internal Medicine at University Hospital Giessen sees the potential of the study as relating to the fact that "for the first time, the progression of the disease was not only halted but the structural changes in the blood vessels were also reversed using a locally administered substance." The administration of the treatment in the form of a nasal spray would offer a relatively effortless form of therapy. Moreover, as Seeger goes on to explain, the local administration of the substance would eliminate the otherwise severe side effects. Other studies would have to show, however, whether the results achieved in the animal model are also applicable to human patients. The scientists hope that the basis for the clinical application of the treatment can be established within the next five years.
INFORMATION:
Soni Savai Pullamsetti, Rajkumar Savai, Martina Barbara Schaefer, Jochen Wilhelm, Hossein Ardeschir Ghofrani, Norbert Weissmann, Christian Schudt, Ingrid Fleming, Konstantin Mayer, James Leiper, Werner Seeger, Friedrich Grimminger and Ralph Theo Schermuly
cAMP Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors Increases Nitric Oxide Production by Modulating Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolases
DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.941484
Circulation published online 7 March, 2011
When the lungs come under pressure
2011-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
eQuoteMD Releases a Comprehensive Guide on What Doctors Need to Know When Purchasing Medical Malpractice Insurance
2011-05-08
As part of an ongoing commitment to empower physicians who purchase medical malpractice insurance, eQuoteMD.com is a releasing a comprehensive white paper delineating the most important topics and factors associated with a doctor's decisions when purchasing and maintaining medical malpractice insurance coverage. This exposition into the world of physician's liability coverage will serve to educate medical professionals who must make important decisions about this type of insurance in an effort to protect the practice's they have built.
This literary resource will assist ...
Reptile 'cousins' shed new light on end-Permian extinction
2011-05-08
An international team of researchers studied the parareptiles, a diverse group of bizarre-looking terrestrial vertebrates which varied in shape and size. Some were small, slender, agile and lizard-like creatures, while others attained the size of rhinos; many had knobbly ornaments, fringes, and bony spikes on their skulls.
The researchers found that, surprisingly, parareptiles were not hit much harder by the end-Permian extinction than at any other point in their 90 million-year history.
Furthermore, the group as a whole declined and diversified time and time again ...
Combination of ADHD and poor emotional control runs in families
2011-05-08
A subgroup of adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) also exhibit excessive emotional reactions to everyday occurrences, and this combination of ADHD and emotional reactivity appears to run in families. A study from a Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH)-based research team finds that siblings of individuals with both ADHD and deficient emotional self-regulation (DESR) had a significantly greater risk of having both conditions than did siblings of those with ADHD alone. The study, which will appear in the American Journal of Psychiatry, has received ...
World's blueberries protected in unique, living collection
2011-05-08
Familiar blueberries and their lesser-known wild relatives are safeguarded by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists and curators at America's official blueberry genebank. The plants, collected from throughout the United States and more than two dozen foreign countries, are growing at the USDA Agricultural Research Service National Clonal Germplasm Repository in Corvallis, Ore.
The blueberries are maintained as outdoor plants, potted greenhouse and screenhouse specimens, tissue culture plantlets, or as seeds, according to research leader Kim E. Hummer.
The ...
Mom or dad has bipolar disorder? Keep stress in check
2011-05-08
This release is available in French.
Montreal May 5, 2011 – Children whose mother or father is affected by bipolar disorder may need to keep their stress levels in check. A new international study, led by Concordia University, suggests the stress hormone cortisol is a key player in the mood disorder. The findings published in Psychological Medicine, are the first to show that cortisol is elevated more readily in these children in response to the stressors of normal everyday life.
"Previous research has shown that children of parents with bipolar disorder are four times ...
Artful dodgers: Responding but not answering often undetected
2011-05-08
WASHINGTON -- How can some people respond to a question without answering the question, yet satisfy their listeners? This skill of "artful dodging" and how to better detect it are explored in an article published by the American Psychological Association.
People typically judge a speaker with the goal of forming an opinion of the speaker, which can make them susceptible to dodges, according to the study published online in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied. Limited attention capacity is another reason people fall for dodges, said the authors, citing a previous ...
Surgery reduces risk of mortality due to prostate cancer even for low-risk groups
2011-05-08
A Swedish research team partly consisting of researchers from Uppsala University followed a group of prostate cancer patients in the Nordic region for 15 years. The study found, among other things, that surgery reduces the risk that men with prostate cancer (even those with low-risk tumours) will die within 15 years. The results were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The researchers followed Swedish, Finnish and Icelandic prostate cancer patients. Radical prostatectomy (surgical removal of the prostate gland) was performed on 347 randomly chosen ...
Quantum simulation with light: Frustrations between photon pairs
2011-05-08
Researchers from the Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology at the University of Vienna and the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information at the Austrian Academy of Sciences used a quantum mechanical system in the laboratory to simulate complex many-body systems. This experiment, which is published in Nature Physics, promises future quantum simulators enormous potential insights into unknown quantum phenomena.
Already the behavior of relatively small quantum systems cannot be calculated because quantum states contain much more information than their ...
Normal stem cells made to look and act like cancer stem cells
2011-05-08
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, after isolating normal stem cells that form the developing placenta, have given them the same properties of stem cells associated with an aggressive type of breast cancer.
The scientific first opens the door for developing novel targeted therapies aimed at triple negative breast cancer. Known also as TNBC, this is a highly recurrent tumor that spreads aggressively beyond its original site in the breast and carries a poor prognosis for patients who have it.
The study ...
Scientists sequence genomes of 2 major threats to American food and fuel
2011-05-08
An international team of researchers co-led by a University of Minnesota scientist has sequenced the genomes of two fungal pathogens -- one that threatens global wheat supplies and another that limits production of a tree crop valued as a future source for biofuel.
The sequencing of the genetic codes of wheat stem rust pathogen (Puccinia graminis) and poplar leaf rust pathogen (Melampsora larici-populina) is expected to help researchers develop control strategies to address worldwide threats to wheat fields and tree plantations. The study, which was published this week ...