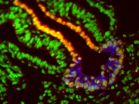
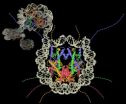
(Press-News.org) Mammals first evolved their characteristic large brains to enable a stronger sense of smell, according to a new study published this week in the journal Science by paleontologists from The University of Texas at Austin, Carnegie Museum of Natural History and St. Mary's University in San Antonio.
This latest study is the first to use CT technology, similar to medical scanners, to reconstruct the brains of two of the earliest known mammal species, both from the Jurassic fossil beds of China. The 3D scans revealed that even these tiny, 190-million-year-old animals had developed brains larger than expected for specimens of their period, particularly in the brain area for smell.
Among living animals, mammals have the largest brains relative to body size. Scientists have proposed many explanations, but because fossil skulls of early mammals are extremely rare, have been reluctant to cut them open for closer study, thus destroying the fossils. Scientists have mostly relied on comparative studies of living mammals.
"We studied the outside features of these fossils for years," said Tim Rowe, professor in the Jackson School of Geosciences and director of the Vertebrate Paleontology Laboratory at The University of Texas at Austin, and lead author of the new study. "But until now, studying the brains meant destroying the fossils. With CT technology, we can have our cake and eat it, too."
According to the study, other factors leading to larger brains in early mammals included greater tactile sensitivity and enhanced motor coordination. Fossils of some of the earliest mammals, such as Hadrocodium, bore full coats of fur, explaining the need for enhanced tactile sensitivity.
Rowe's co-authors are Thomas E. Macrini, assistant professor of biological sciences at St. Mary's University in San Antonio, and Zhe-Xi Luo, curator and associate director for research and collections at the Carnegie Museum of Natural History.
Macrini conducted much of this research for his doctoral dissertation at The University of Texas at Austin, in which he scanned the heads of numerous fossil and living species to visualize the size and shape of their brains.
"This is the most comprehensive study yet undertaken using computed tomography to study the evolution of the mammalian skull," said Macrini. "And it is exciting to see these new insights emerging from years of intense labor."
Luo was involved in the discovery and research on the fossils for this study. When he first described the paper clip-sized mammal Hadrocodium ten years ago, he named it for its relatively large cranium despite its appearance so early in the mammalian lineage ("hadro" means "fullness" in Latin and "codium" means "head").
"I have spent years studying these fossils, but until they were scanned it was impossible to see the internal details," said Luo. "I was absolutely thrilled to see what the brains of our 190-million-year old relatives were like."
###
For this study, the team CT scanned more than a dozen early fossil mammals and more than 200 living species over the past 10 years at the High-Resolution X-ray Computed Tomography Facility at The University of Texas at Austin, a facility supported by the National Science Foundation for researchers around the world. The scans, including interactive 3D fly-throughs, are archived online and available to the public along with nearly 1,000 other specimens on the DigiMorph Web site (www.digimorph.org).
For a gallery of press images related to this release, please visit: http://www.jsg.utexas.edu/galleries/mammalbrain051911/
Mammals first evolved big brains for better sense of smell
2011-05-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Predicting the fate of personalized cells next step toward new therapies
2011-05-20
PHILADELPHIA – Discovering the step-by-step details of the path embryonic cells take to develop into their final tissue type is the clinical goal of many stem cell biologists.
To that end, Kenneth S. Zaret, PhD, professor of Cell and Developmental Biology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, and associate director of the Penn Institute for Regenerative Medicine, and Cheng-Ran Xu, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the Zaret laboratory, looked at immature cells called progenitors and found a way to potentially predict their fate. They base ...
Large brains in mammals first evolved for better sense of smell
2011-05-20
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania… Paleontologists have often wondered why mammals—including humans—evolved to have larger brains than other animals. A team of paleontologists now believe that large brains may have developed in mammals to facilitate an acute sense of smell, according to a new paper published today in the prestigious journal Science. The team also noticed enlargement in the areas of the brain that correspond to the ability to sense touch through fur; this sense is acutely developed in mammals.
Scientists used high-resolution CT scans to study rare 190-million-year-old ...
Death of Osama bin Laden Highlights Importance of the Zadroga Act, Says New York Personal Injury Lawyer
2011-05-20
After the death of Osama bin Laden, New York personal injury lawyer David Perecman reaffirmed his commitment to help the heroes who are still battling illnesses connected to 9/11.
For many individuals, the death of bin Laden brought closure. The death also served to rekindle memories of those who volunteered to assist at the World Trade Center site after the 9/11 attacks.
The lives of many Ground Zero volunteers were changed in challenging ways. Rescue and recovery workers and others are still suffering from health consequences related to the World Trade Center disaster.
"People ...
Scientists discover new drug target for squamous cell carcinoma
2011-05-20
SEATTLE – Researchers at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center have discovered a new drug target for squamous cell carcinoma – the second most common form of skin cancer. Scientists in the laboratory of Valeri Vasioukhin, Ph.D., have found that a protein called alpha-catenin acts as a tumor suppressor and they also have unlocked the mechanism by which this protein controls cell proliferation.
The findings by Vasioukhin and colleagues will be published May 24 in Science Signaling.
For the study, the researchers studied mice that were bred to lack a copy of the gene that ...
Packaging process for genes discovered in new research
2011-05-20
Scientists at Penn State University have achieved a major milestone in the attempt to assemble, in a test tube, entire chromosomes from their component parts. The achievement reveals the process a cell uses to package the basic building blocks of an organism's entire genetic code -- its genome. The evidence provided by early research with the new procedure overturns three previous theories of the genome-packaging process and opens the door to a new era of genome-wide biochemistry research. A paper describing the team's achievement will be published in the journal Science ...
Senators Want DUI Applications Removed From Smartphones
2011-05-20
In March, four Democratic U.S. Senators, Harry Reid, D-Utah, Chuck Schumer, D-N.Y., Frank Lautenberg, D-N.J., and Tom Udall, D-N.M., drafted a letter requesting that Apple, Google and Research in Motion (or RIM) eliminate the applications (user-friendly computer programs for specific tasks) on mobile communication devices that warn drivers of the locations of drunk-driving checkpoints.
The next day, RIM, the manufacturer of the BlackBerry agreed to the removal of driving-under-the-influence (DUI/DWI) checkpoint functionality on its BlackBerry devices.
Google later ...
What Causes the Metal Skin on an Airliner to Tear Apart?
2011-05-20
On Friday, April 1, 2011, a Southwest Airlines Boeing 737-300 experienced a rapid decompression when the metal fuselage skin tore apart, leaving a 5X1 foot hole. This kind of event is rare, but can, and has been, catastrophic when it does occur.
In 1988, another Boeing 737, a 200 model, experienced a similar, but much worse, event over Hawaii. In that case, the skin on the entire front section of the aircraft cabin was denuded, leaving the passengers sitting in the first several rows completely exposed, with the aircraft being held together by two metal spars running ...
Of frogs, chickens and people
2011-05-20
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have uncovered new details of an unusual biological mechanism in the brains of diverse species that not only helps regulate how their brains develop, but also how they function later in life. The discovery could lead to new biomarkers for specific neurological diseases in humans and, possibly, the development of drugs to cure them.
The research, by Miles F. Wilkinson, PhD, professor of reproductive medicine and a member of the UCSD Institute for Genomic Medicine, and colleagues, is published in ...
Preparing for a Prenuptial Agreement
2011-05-20
Thinking about, let alone preparing for, divorce before you are even married is not what most of us want to do. Whether we believe that divorce will never happen to us or whether we just choose to ignore the possibility, the fact remains that almost half of all marriages in the United States end in divorce.
One way to enter into a marriage prepared for all outcomes is to create a prenuptial agreement. Creating this agreement doesn't mean that your marriage will eventually come to an end. Rather, creating a prenuptial agreement is just a way for you and your spouse to ...
Looking deep into a huge storm on Saturn
2011-05-20
The atmosphere of the planet Saturn normally appears placid and calm. But about once per Saturn year (about thirty Earth years), as spring comes to the northern hemisphere of the giant planet, something stirs deep below the clouds that leads to a dramatic planet-wide disturbance (eso9014 - http://www.eso.org/public/news/eso9014/).
The latest such storm was first detected by the radio and plasma wave science instrument on NASA's Cassini spacecraft [1], in orbit around the planet, and also tracked by amateur astronomers in December 2010. It has now been studied in detail ...