(Press-News.org) Antibiotics can work miracles, knocking out common infections like bronchitis and tonsillitis. But according to the Center for Disease Control, each year 90,000 people in the U.S. die of drug-resistant "superbugs" ― bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a deadly form of staph infection resistant to normal antibiotics. Although hospital patients are particularly susceptible as a result of open wounds and weakened immune systems, the bacteria can infect anyone.
Dr. Micha Fridman of Tel Aviv University's Department of Chemistry is now developing the next generation of antibiotics designed to overcome this kind of bacteria. And the key, he says, is in the bacteria itself.
"We took the mechanism of bacterial resistance and used this mechanism itself to generate antibiotics," explains Dr. Fridman. "It's thanks to these bacteria that we can develop a better medication." Conducted in collaboration with Prof. Sylvie Garneau-Tsodikova from the University of Michigan at Ann Arbor, Dr. Fridman's research was highlighted recently in the journal ChemBioChem.
Fighting from within
According to Dr. Fridman, certain bacterial strains include enzymes which help the bacteria to inactivate antibiotics. When the enzymes meet with these antibiotics, they chemically alter the drug, making the antibiotic ineffective and unable to recognize its target.
Turning this powerful mechanism against the bacteria itself, the team isolated the antibiotic-inactivating enzymes from the bacteria, then integrated them into the drugs. With this alteration, the modified antibiotics proved to be effective against typically resistant bacterial strains.
At the heart of this development, says Dr. Fridman, was the chemical modification of the parent drug. Once the researchers identified how the bacteria incapacitated the antibiotics, they were able to create a drug that could block bacterial resistance while maintaining the integrity of the antibiotic.
Killing bacteria, saving lives
These new antibiotics will be a vast improvement on today's drugs, says Dr. Fridman. When fully developed, they could be used to treat infections that are now considered difficult if not impossible to treat with current antibiotics.
Dr. Fridman says that, while the new antibiotics are a few years away from the marketplace, the ability to beat bacterial resistance will be invaluable for the future of health care.
###
American Friends of Tel Aviv University (www.aftau.org) supports Israel's leading and most comprehensive and most sought-after center of higher learning. Ranked #114 in the world in independent rankings, TAU's innovations and discoveries are cited more often by the global scientific community than all but 20 other universities worldwide.
Internationally recognized for the scope and groundbreaking nature of its research programs, Tel Aviv University consistently produces work with profound implications for the future.
Outsmarting killer bacteria
Tel Aviv University develops next generation of antibiotics to combat drug-resistant 'superbugs'
2010-09-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Last strongholds for tigers identified in new study
2010-09-15
NEW YORK (Embargoed until September 14, 2010: 5:00 p.m. U.S. Eastern Time)— A new peer-reviewed paper by the Wildlife Conservation Society and other groups reveals an ominous finding: most of the world's last remaining tigers—long decimated by overhunting, logging, and wildlife trade—are now clustered in just six percent of their available habitat. The paper identifies 42 'source sites' scattered across Asia that are now the last hope and greatest priority for the conservation and recovery of the world's largest cat.
The securing of the tiger's remaining source sites ...
False memories of self-performance result from watching others' actions
2010-09-15
Did I turn off the stove, or did I just imagine it? Memory isn't always reliable. Psychological scientists have discovered all sorts of ways that false memories get created, and now there's another one for the list: watching someone else do an action can make you think you did it yourself.
The team of psychological scientists who found the new way to create false memories weren't setting out to make a big discovery. They were trying to learn more about imagination, another way that false memories get created. But then in an experiment, they found that people who had watched ...
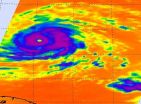
Stunning NASA infrared imagery of Hurricane Igor reveals a 170 degree temperature difference
2010-09-15
NASA satellites provide infrared images to forecasters that show temperature, and today's imagery of powerful Hurricane Igor showed the storm's perfect form and the warm ocean waters around it that are keeping it fueled. NASA's infrared data also revealed a huge difference of 170 degrees between the cold cloud tops in Hurricane Igor and the warm sea surface temperatures powering it below.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Igor on Sept. 14 at 14:47 UTC (10:47 a.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured icy cold cloud top temperatures in ...
Do children understand irony?
2010-09-15
New research findings from the Université de Montréal reveals that children as young as four are able to understand and use irony. This study, published recently in the British Journal of Developmental Psychology, may impact the way parents communicate with their family.
"Previous studies concluded that irony wasn't understood before the age of eight or ten," says Stephanie Alexander, a postdoctoral student at the Université de Montréal's Department of Social and Preventive Medicine and senior author of the study. "However, these studies were mostly done in a laboratory ...
ORNL scientists reveal battery behavior at the nanoscale
2010-09-15
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Sept. 14, 2010 -- As industries and consumers increasingly seek improved battery power sources, cutting-edge microscopy performed at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory is providing an unprecedented perspective on how lithium-ion batteries function.
A research team led by ORNL's Nina Balke, Stephen Jesse and Sergei Kalinin has developed a new type of scanning probe microscopy called electrochemical strain microscopy (ESM) to examine the movement of lithium ions through a battery's cathode material. The research, "Nanoscale mapping ...
Legal analysis: The health insurance mandate is constitutional
2010-09-15
(Garrison, NY) The most politically charged feature of the health reform law is the mandate that legal residents have health insurance. Within weeks of the law's passage, twenty states had filed lawsuits charging that the mandate is unconstitutional because it gives the federal government more power than it actually has. The state lawsuits are widely expected to reach the Supreme Court next year. Legal scholar Lawrence O. Gostin writes that the health insurance mandate rests on firm legal ground.
Under the mandate, which goes into effect in 2014, the federal government ...
Study identifies students at risk for difficulties in medical school
2010-09-15
Students who enter medical school with high debt levels, low scores on the Medical College Admissions Test (MCAT) or who are non-white are more likely to face difficulties that may prevent graduation or hinder acceptance into a residency program if they do graduate, according to a nationwide study of students enrolled in MD programs.
The research, from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, is reported Sept. 15 in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The study of more than 84,000 students who entered U.S. medical schools from 1994-1999 showed ...
Report shows federal poverty guidelines leave state's seniors destitute
2010-09-15
Data and research on what it really takes for seniors to make ends meet in each of California's 58 counties will be released today at the state Capitol in Sacramento.
The release is the latest update of the Elder Economic Security Standard Index (Elder Index), a tool that measures the actual costs of basic necessities for older adults. The Elder Index is quickly replacing federal poverty level (FPL) guidelines as a new standard for evaluating and meeting the needs of seniors across California.
"This year, the federal government officially acknowledged it's time ...
Blood test accurately predicts death from prostate cancer up to 25 years in advance
2010-09-15
NEW YORK, September 14, 2010 – A blood test at the age of 60 can accurately predict the risk that a man will die from prostate cancer within the next 25 years, according to researchers at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, in New York, and Lund University, in Sweden. The findings, published today online in the British Medical Journal, could have important implications for determining which men should be screened after the age of 60 and which may not benefit substantially from continued prostate cancer screening.
The study analyzed blood samples from 1,167 men born ...
Adapting to darkness: How behavioral and genetic changes helped cavefish survive extreme environment
2010-09-15
VIDEO:
A cavefish (left) and surface fish (right) swimming in assay chambers in the presence of a 50 Hz vibrating rod. When the rod is vibrated, the cavefish, but not surface...
Click here for more information.
University of Maryland biologists have identified how changes in both behavior and genetics led to the evolution of the Mexican blind cavefish (Astyanax mexicanus) from its sighted, surface-dwelling ancestor. In research published in the August 12, 2010 online edition ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
[Press-News.org] Outsmarting killer bacteriaTel Aviv University develops next generation of antibiotics to combat drug-resistant 'superbugs'