(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered an important enzyme molecule that may prevent fatal cardiac disorders associated with cardiac hypertrophy – the leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.
Cardiac hypertrophy is a disease of the heart muscle where a portion of the tissue is thickened without any obvious cause. It is commonly linked to high blood pressure (hypertension) and excessive exercises and results in a shrinking of the heart chamber and a reduction of its blood-pumping volume.
The condition is also associated with fatal cardiac disorders related to irregular heart beats (arrhythmias), leading to millions of deaths worldwide each year, and is perhaps the most well-known cause of sudden cardiac arrest in young sports people.
The researchers used laboratory experiments and computer simulations to show that the enzyme MKK4 is involved in preventing arrhythmias. They believe it does this by modifying another protein, connexion, which forms an electrical bridge between adjacent heart cells to ensure the conduction of electrical activity across the heart as an excitation wave, triggering synchronised mechanical contraction of the heart with a regular heartbeat rhythm.
The multidisciplinary team, writing in The Journal of Biological Chemistry, found that loss of the MKK4 protein disrupts the spatial distribution of connexin, resulting in reduced and non-uniform electrical coupling between heart cells.
This causes a fragmented excitation wave in the heart, leading to uncoordinated heart muscle contraction and irregular heart rhythm. As a result, the heart loses its power to pump blood efficiently, causing disability or sudden cardiac death.
"Using experimental measurements together with detailed computer models, we were able to simulate the electrical activity in cardiac tissue with disrupted electrical coupling between adjacent cardiac cells," said Dr Xin Wang, in Manchester's Faculty of Life Science.
"The information generated from this study will help us to identify whether the MKK4 enzyme could become a therapeutic target for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in association with cardiac hypertrophy."
Co-author Professor Henggui Zhang, a biophysicist in Manchester's School of Physics and Astronomy, added: "This research means it would be possible to identify the most important factor behind the sudden cardiac death associated with cardiac hypertrophy, which can affect people of any age with hypertension and also healthy well-trained athletes."
###
Notes for editors:
A copy of the paper is available on request.
Enzyme prevents fatal heart condition associated with athletes
2011-05-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research says 9/11 produced permanent shift to Republican party among new young US voters
2011-05-26
Research led by the University of Warwick's Centre for Competitive Advantage in the Global Economy has found that not only did the events of 9/11 produce an immediate shift in favour of the Republican party among new young US voters but that shift persisted into later years. The research shows that party strategists should focus on winning over voters when they are young.
The researchers Professor Sharun Mukand, from the University of Warwick, and Professor Ethan Kaplan, from Stockholm University and the University of Maryland, looked at whether the mere act of registering ...
Arrival of direct antiviral agent therapy for hepatitis C sparks debate of who to treat first
2011-05-26
For many patients with the hepatitis C virus (HCV), direct antiviral agents (DAA) offer a potential cure for the disease. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently approved two new DAAs, telaprevir and boceprevir, and with that clinicians must now decide who should be the first to receive this treatment. Discussion of this timely topic is now available in the June issue of Hepatology, a journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates up to 170,000 million ...
Trash to treasure: Turning steel-mill waste into bricks
2011-05-26
Scientists are reporting development and successful testing of a promising new way of using a troublesome byproduct of the global steel industry as raw materials for bricks that can be used in construction projects. Their study appears in ACS' Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.
In the report, Ana Andrés and colleagues note that steel mills around the world produce vast quantities of waste dust each year — 8 million – 12 million tons in the United States, for instance, and 700,000 tons in the European Union countries. The dust often is converted into a rock-like ...
Research study reveals profile for female drunk-drivers
2011-05-26
Female drink-drivers are more likely to be older, better-educated and divorced, widowed or separated, research has shown.
The study by academics at The University of Nottingham found that emotional factors and mental health problems were common triggers in alcohol-related offences committed by women.
And they also discovered that rehabilitation programmes that force women to face the consequences of their crime can intensify their feelings of guilt and shame, leading them to turn to alcohol and increasing the risk that they will re-offend.
In a paper to be published ...
New research on Christian school graduates yields surprising results
2011-05-26
In the first study of its kind on K-12 Christian education in North America, University of Notre Dame sociologist David Sikkink, in partnership with Cardus – a public policy think tank – found that while Protestant Christian school graduates show uncommon commitment to their families and churches, donate more money than graduates of other schools, and divorce less, they also have lower incomes, less education, and are less engaged in politics than their Catholic and non-religious private school peers.
The two-year study surveyed a representative sample of religious school ...
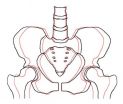
Pelvic widening continues throughout a person's lifetime, UNC study
2011-05-26
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – By the age of 20, most people have reached skeletal maturity and do not grow any taller. Until recently it was assumed that skeletal enlargement elsewhere in the body also stopped by age 20.
But a new study by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has found evidence that, even though you're not getting taller anymore, the pelvis ("hipbones") does continue to widen as people advance in age from 20 years to 79 years.
"I think it's a fairly common human experience that people find themselves to be wider at the age of 40 or 60 ...
Mating rivalry among furred and feathered: Variety is spice of life
2011-05-26
This press release is available in French.Montreal, May 25, 2011 – Birds do it. Bees do it. Fish, lobsters, frogs and lizards do it, too. But when it comes to securing a mate in the animal world, variety is literally the spice of life.
A group of scientists from Simon Fraser University, Concordia University and Dalhousie University has found flexibility in mating rituals is the key to reproductive success when males outnumber females.
The research team pored through hundreds of investigations on mating trends in mammals, insects, fish, crustaceans, amphibians and reptiles. ...
Defect in graphene may present bouquet of possibilities
2011-05-26
A class of decorative, flower-like defects in the nanomaterial graphene could have potentially important effects on the material's already unique electrical and mechanical properties, according to researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and Georgia Tech. In a new paper,* the team for the first time describes a family of seven defects that could occur naturally or be induced to occur in graphene, one of which already has been observed.
Graphene is renowned for its strength and conductivity, both of which are a result of its structure. For ...
New software tool helps evaluate natural cooling options for buildings
2011-05-26
A new, free software tool from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) could prove to be a breath of fresh air for architects and designers of ventilation systems for "green" commercial buildings.
With the Climate Suitability Tool,* building design teams can evaluate whether the local climate is suitable for cooling a prospective building with natural ventilation or requires a hybrid system that supplies supplemental cooling capacity. The tool is based on a model of the heat-related characteristics of a building configured to take full advantage of ambient ...
NIST 'nanowire' measurements could improve computer memory
2011-05-26
A recent study* at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) may have revealed the optimal characteristics for a new type of computer memory now under development. The work, performed in collaboration with researchers from George Mason University (GMU), aims to optimize nanowire-based charge-trapping memory devices, potentially illuminating the path to creating portable computers and cell phones that can operate for days between charging sessions.
The nascent technology is based on silicon formed into tiny wires, approximately 20 nanometers in diameter. ...