(Press-News.org) In the first study of its kind on K-12 Christian education in North America, University of Notre Dame sociologist David Sikkink, in partnership with Cardus – a public policy think tank – found that while Protestant Christian school graduates show uncommon commitment to their families and churches, donate more money than graduates of other schools, and divorce less, they also have lower incomes, less education, and are less engaged in politics than their Catholic and non-religious private school peers.
The two-year study surveyed a representative sample of religious school graduates in the U.S. (ages 24 to 39) to determine the impact of Christian schools on adults in today's society as well as understand how Christian schools are attempting to define themselves in today's socio-cultural and economic landscape. The research team also sampled more than 150 Catholic and Protestant school administrators in Canada and the U.S. to assess the aspirations of Christian schools.
Also among the findings:
In addition to divorcing less, Protestant Christian school graduates are having more children than their Catholic and non-religious private school peers;
Protestant Christian school graduates participate in more relief and development service trips than their Catholic and non-religious private school peers;
Protestant Christian school graduates were more thankful for what they have in life;
Protestant Christian school graduates attend less competitive colleges than Catholic and non-religious private school peers;
Protestant Christian school graduates are not engaging in higher education any more than their public school peers;
Protestant Christian school graduates talk less about politics, participate less in political campaigns and donate less to political causes than their Catholic and non-religious private school peers;
Graduates of Catholic and non-religious private schools have a significant advantage in the number of years of education;
More Catholic school administrators ranked university as the top priority, while more Protestant school administrators ranked family as the top emphasis of the school.
Preliminary results of the study will be presented Wednesday (May 25) at the Willard Hotel in Washington, D.C., where representatives of Cardus and lead researcher Sikkink will discuss the study's findings.
### END
New research on Christian school graduates yields surprising results
2011-05-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
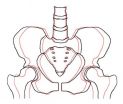
Pelvic widening continues throughout a person's lifetime, UNC study
2011-05-26
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – By the age of 20, most people have reached skeletal maturity and do not grow any taller. Until recently it was assumed that skeletal enlargement elsewhere in the body also stopped by age 20.
But a new study by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has found evidence that, even though you're not getting taller anymore, the pelvis ("hipbones") does continue to widen as people advance in age from 20 years to 79 years.
"I think it's a fairly common human experience that people find themselves to be wider at the age of 40 or 60 ...
Mating rivalry among furred and feathered: Variety is spice of life
2011-05-26
This press release is available in French.Montreal, May 25, 2011 – Birds do it. Bees do it. Fish, lobsters, frogs and lizards do it, too. But when it comes to securing a mate in the animal world, variety is literally the spice of life.
A group of scientists from Simon Fraser University, Concordia University and Dalhousie University has found flexibility in mating rituals is the key to reproductive success when males outnumber females.
The research team pored through hundreds of investigations on mating trends in mammals, insects, fish, crustaceans, amphibians and reptiles. ...
Defect in graphene may present bouquet of possibilities
2011-05-26
A class of decorative, flower-like defects in the nanomaterial graphene could have potentially important effects on the material's already unique electrical and mechanical properties, according to researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and Georgia Tech. In a new paper,* the team for the first time describes a family of seven defects that could occur naturally or be induced to occur in graphene, one of which already has been observed.
Graphene is renowned for its strength and conductivity, both of which are a result of its structure. For ...
New software tool helps evaluate natural cooling options for buildings
2011-05-26
A new, free software tool from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) could prove to be a breath of fresh air for architects and designers of ventilation systems for "green" commercial buildings.
With the Climate Suitability Tool,* building design teams can evaluate whether the local climate is suitable for cooling a prospective building with natural ventilation or requires a hybrid system that supplies supplemental cooling capacity. The tool is based on a model of the heat-related characteristics of a building configured to take full advantage of ambient ...
NIST 'nanowire' measurements could improve computer memory
2011-05-26
A recent study* at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) may have revealed the optimal characteristics for a new type of computer memory now under development. The work, performed in collaboration with researchers from George Mason University (GMU), aims to optimize nanowire-based charge-trapping memory devices, potentially illuminating the path to creating portable computers and cell phones that can operate for days between charging sessions.
The nascent technology is based on silicon formed into tiny wires, approximately 20 nanometers in diameter. ...
Fish species discovered by LSU researcher makes 2011 top 10 list
2011-05-26
BATON ROUGE – The International Institute for Species Exploration at Arizona State University and a committee of taxonomists from around the world announced their picks for the top 10 new species described in 2010. Among their top picks is Halieutichthys intermedius, a pancake batfish recently discovered by Prosanta Chakrabarty, curator of fishes at LSU's Museum of Natural Science, and colleagues.
Halieutichthys intermedius, more commonly referred to as the Louisiana pancake batfish, gained some notoriety during the spring and summer of 2010, when the Deepwater Horizon ...
Public universities place greater focus on internal research services than public ones do
2011-05-26
Research expenditure has increased in Spain, as has the focus on research performance. However, the internal services that universities provide to support research, both in terms of infrastructure and staff, have not improved, according to a study published in the journal The Service Industries Journal, which also shows that public universities outperform private ones in this respect.
"The Ministry of Science and Innovation provides Spanish universities with access to databases. However, we have seen that in many cases there are no research support staff to explain how ...
New study provides global analysis of seagrass extinction risk
2011-05-26
A team of 21 researchers from 11 nations, including professor Robert "JJ" Orth of the Virginia Institute of Marine Science, has completed the first-ever study of the risk of extinction for individual seagrass species around the world.
The 4-year study, requested by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), shows that 10 of the 72 known seagrass species (14%) are at an elevated risk of extinction, while 3 species qualify as endangered.
The authors caution that loss of seagrass species and seagrass biodiversity will seriously impact marine ecosystems ...
Improved prognosis for esophageal cancer
2011-05-26
In recent years, the number of cases of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (or gullet) has been on the rise. At the same time, however, new ways of treatment are improving the outlook for patients. In the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Artzebl Int 2011; 108[18]: 313), Angelika Behrens and her working group report on innovations in diagnosis and treatment.
The main cause of this cancer is reflux of gastric acid from the stomach, with heartburn as the main symptom. Other risk factors are being male, being overweight, and having relatives ...
New bandwidth management techniques boost operating efficiency in multi-core chips
2011-05-26
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed two new techniques to help maximize the performance of multi-core computer chips by allowing them to retrieve data more efficiently, which boosts chip performance by 10 to 40 percent.
To do this, the new techniques allow multi-core chips to deal with two things more efficiently: allocating bandwidth and "prefetching" data.
Multi-core chips are supposed to make our computers run faster. Each core on a chip is its own central processing unit, or computer brain. However, there are things that can slow these ...