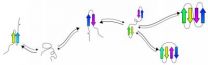
(Press-News.org) Protein folding has nothing to do with laundry. It is, in fact, one of the central questions in biochemistry. Protein folding is the continual and universal process whereby the long, coiled strings of amino acids that make up proteins in all living things fold into more complex three-dimensional structures. By understanding how proteins fold, and what structures they are likely to assume in their final form, researchers are then able to move closer to predicting their function.
This is important because incorrectly folded proteins in humans result in such devastating diseases as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Huntington's, emphysema and cystic fibrosis. Developing better modelling techniques for protein folding is crucial to creating more effective pharmaceutical treatments for these and other diseases.
Computational methods of modelling protein folding have existed for a couple of decades. But what McGill researcher Jérôme Waldispühl of the McGill Centre for Bioinformatics has done, working with collaborators from MIT, is to develop algorithms that can work from a laptop computer to examine a protein's fundamental chemical properties and then scan a number of possible protein shapes before predicting the final form that the protein is likely to take.
The results have been impressive. Whereas classical techniques for predicting protein folding pathways required hundreds of thousands of CPU hours to compute the folding dynamics of 40 amino acids proteins, the program tFolder implemented by Solomon Shenker – a former McGill under-graduate student now at Cornell – has been able to predict correctly in 10 minutes on a single laptop, a coarse-grained representation of the folding pathways of a protein with 60 amino acids.
Waldispühl and his students continue to work on their algorithm to improve its success rate at predicting protein folding with broader categories of proteins including some that are important in DNA-binding. The research was recently presented at the 15th Annual International Conference in Research in Computational Molecular Biology (RECOMB 2011).
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by McGill and the NSERC discovery grant program.
For more information: http://csb.cs.mcgill.ca/tfolder
Protein folding made easy
McGill researcher develops speedier technique for predicting vital process
2011-06-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Paved surfaces can foster build-up of polluted air
2011-06-08
BOULDER—New research focusing on the Houston area suggests that widespread urban development alters wind patterns in a way that can make it easier for pollutants to build up during warm summer weather instead of being blown out to sea.
The international study, led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), could have implications for the air quality of fast-growing coastal cities in the United States and other midlatitude regions overseas. The reason: the proliferation of strip malls, subdivisions, and other paved areas may interfere with breezes needed to ...
The heat is on for sodium-manganese oxide rechargeable batteries
2011-06-08
RICHLAND, Wash. -- By adding the right amount of heat, researchers have developed a method that improves the electrical capacity and recharging lifetime of sodium ion rechargeable batteries, which could be a cheaper alternative for large-scale uses such as storing energy on the electrical grid.
To connect solar and wind energy sources to the electrical grid, grid managers require batteries that can store large amounts of energy created at the source. Lithium ion rechargeable batteries -- common in consumer electronics and electric vehicles -- perform well, but are too ...
Glaciations may have larger influence on biodiversity than current climate
2011-06-08
An investigation by the Spanish Scientifc Council (Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, CSIC) reveals that the large impacts occurred during the last ice age maintain their effects on the current distribution of dung beetles of the scarab family (Scarabaeidae). The presence of these beetles in Europe seems to be more influenced by the climate of that glaciation than by the present one.
The study, published yesterday in the journal Ecology Letters, analyzed the species richness and the structure of their communities throughout the different regions of the European ...
Your attention please: 'Rewarding' objects can't be ignored
2011-06-08
The world is a dazzling array of people, objects, sounds, smells and events: far too much for us to fully experience at any moment. So our attention may automatically be snagged by something startling, such as a slamming door, or we may deliberately focus on something that is important to us right then, such as locating our child among the happily screaming hordes on the school playground. We also know that people are hard-wired to seek out and pay attention to things that are rewarding, such as food when we are hungry, or water when we are thirsty.
So what happens ...
Chicago Plastic Surgeon Makes Appearance on Popular Show, The Doctors
2011-06-08
Dr. Kotis, a Chicago plastic surgeon, made an appearance on the popular daytime television show The Doctors. He and the show's host, Dr. Drew Ordon, scrubbed in to demonstrate a cutting-edge procedure that can end the pain and limitations caused by rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
In the May 24th airing of The Doctors take on Chicago, Dr. Kotis performed a surgery to replace a thumb joint which has been worn down on a woman due to a terrible car accident. The damaged joint caused the bones in the thumb to rub together causing severe rheumatoid as well as osteoarthritis. ...
Brown and Crouppen Welcomes FDA Study
2011-06-08
Metal-on-Metal ("MoM") hip replacements have come under scrutiny lately. On May 6, 2011, the Food and Drug Administration ordered 21 manufacturers of 145 different MoM hip replacements to study and report the outcomes of patients who have received these devices. Such a study is called a "postmarket surveillance study."
Attorney Ron Brown, of St. Louis-based law firm Brown and Crouppen, welcomed the development saying, "I'm very glad to see the FDA's action on this."
Recent years have seen growing concern in both the United States and ...
Smithsonian study: Stranding records are faithful reflection of live whale and dolphin populations
2011-06-08
Whales are the earth's largest creatures, yet they are incredibly hard to study in the open ocean. For decades scientists have used boats, aircraft and even high cliffs to conduct visual surveys and gather data on whale and dolphin populations. Today, these live surveys form the basis of our knowledge of these marine mammals—what species live where in the world, which ones tend to live together and how abundantly they are represented.
Now, recent work by paleobiologist Nick Pyenson of the Smithsonian's National Museum of Natural History, has revealed a second, equally ...
Atlanta Perimeter Hotel Near Philips Arena Provides Close Accommodations to Fans Attending New Kids on the Block and Back Street Boys in Concert
2011-06-08
The Holiday Inn Express & Suites Atlanta Perimeter Hotel (North), near Perimeter Mall, provides close accommodations to the fans attending New Kids on the Block and Back Street Boys in concert. The show will take place on June 22, 2011 at Philips Arena in downtown Atlanta. It will feature members of both American vocal groups, who will performances of many of their music hit as well as and new joint songs, "Don't Turn Out the Lights" and "All in My Head".
The two groups first appeared together in November, 2010 at the American Music Awards. The ...
Native ants use chemical weapons to turn back invading Argentine ants
2011-06-08
Argentine ants are taking over the world – or at least the nice temperate parts. They've spread into Mediterranean and subtropical climates across the globe in sugar shipments from Argentina, and no native ant species has been known to withstand their onslaught – until now. A group of Stanford University undergraduate students working on a class project have discovered that a native species, the plucky winter ant, has been using chemical warfare to combat the Argentine tide.
The winter ants – named for their unusual ability to function in cold weather, rather than grind ...
Saxo Bank Launches Retail FX Trading Platform ForexTrading.com
2011-06-08
Saxo Bank, the online trading and investment specialist, has announced the launch of ForexTrading.com which will offer retail investors a select range of FX crosses and CFDs with variable spreads - as low as 0.8 pips. ForexTrading.com provides investors with a range of basic functionalities designed to make trading flexible and straightforward.
ForexTrading.com is powered by Saxo Bank, which is renowned for aggregating liquidity from the world's leading FX dealers. ForexTrading.com gives traders the ability to trade in the world's most liquid currency pairs and global ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Protein folding made easyMcGill researcher develops speedier technique for predicting vital process