(Press-News.org) Animals and plants may not be able to evolve their way out of the threat posed by climate change, according to a UC Davis study of a tiny seashore animal. The work was published today (June 8) in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
The tide pool copepod Tigriopus californicus is found from Alaska to Baja California — but in a unique lab study, the animals showed little ability to evolve heat tolerance.
"This is a question a lot of scientists have been talking about," said study co-author Eric Sanford, an associate professor of evolution and ecology at UC Davis and a researcher at the university's Bodega Marine Laboratory. "Do organisms have the ability to adapt to climate change on a timescale of decades?"
UC Davis graduate student Morgan Kelly, the first author of the paper, collected copepods from eight locations between Oregon and Baja California in Mexico. The tiny shrimplike animals, about a millimeter long, live in tide pools on rocky outcrops high in the splash zone.
Kelly grew the short-lived copepods in the lab for 10 generations, subjecting them to increased heat stress to select for more heat-tolerant animals.
At the outset, copepods from different locations showed wide variability in heat tolerance. But within those populations, Kelly was able to coax only about a half-degree Celsius (about one degree Fahrenheit) of
increased heat tolerance over 10 generations. And in most groups, the increase in heat tolerance had hit a plateau before that point.
In the wild, these copepods can withstand a temperature swing of 20 degrees Celsius a day, Kelly said. But they may be living at the edge of their tolerance, she said.
Although the copepods are widespread geographically, individual populations are very isolated, confined to a single rocky outcrop where wave splash can carry them between pools. That means there is very little flow of new genes across the population as a whole.
"It's been assumed that widespread species have a lot of genetic capacity to work with, but this study shows that may not be so," said co-author Rick Grosberg, professor of evolution and ecology at UC Davis. Many other species of animals, birds and plants face stress from climate change, and their habitats have also been fragmented by human activity -- perhaps more than we realize, he said.
"The critical point is that many organisms are already at their environmental limits, and natural selection won't necessarily rescue them," Grosberg said.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by the National Science Foundation.
Can evolution outpace climate change?
2011-06-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UAB first in US with cell-processing workstation
2011-06-09
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – The University of Alabama at Birmingham has taken a significant step toward making sophisticated cell therapy a part of patient care with its acquisition of the first cell-processing workstation (CPWS) from SANYO North America Corporation (SANYO) in the United States.
Richard Marchase, Ph.D., vice president for Research and Economic Development at UAB, says "UAB has a rich history of breaking ground in the cell-therapy arena. We are thrilled that we were able to be the first in the United States to use SANYO's CPWS. This will add to our world-class ...
A double-satellite NASA-style view of the first tropical storm in eastern Pacific: Adrian
2011-06-09
The first tropical depression in the Eastern Pacific Ocean is now the first tropical storm, and two satellites are providing NASA insights into its thunderstorms, rainfall, and intensity. NASA satellite data on newly born Tropical Storm Adrian shows high cloud tops and moderate rainfall, indications that the storm is getting stronger, triggering a tropical storm watch in Mexico.
Tropical Depression 1E is the first tropical depression of 2011 and formed in the eastern Pacific Ocean early on June 7. By the morning of June 8 it had strengthened into Tropical Storm Adrian, ...
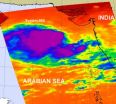
NASA imagery sees a reawakening of system 98A in the Arabian Sea
2011-06-09
System 98A has been bringing rains, gusty winds and churning up the surf along the Arabian Seacoast of west-central India for days, and NASA satellite imagery confirms that it is getting organized now that it has moved into open waters.
NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument onboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image on June 8 at 08:47 UTC (4:47 a.m. EDT) of the hundreds of thunderstorms that make up the low pressure area called System 98A. The low pressure area has now moved to the west-southwest and away from Mumbai, India. In fact, today it is located ...
Stable temperatures boost biodiversity in tropical mountains
2011-06-09
Durham, NC — We often think of rainforests and coral reefs as hotspots for biodiversity, but mountains are treasure troves for species too —especially in the tropics, scientists say. But what drives montane biodiversity? The diversity of plants and animals in tropical mountain ranges may have something to do with the stable seasonal temperatures found in the tropics relative to higher latitudes, says a new study by scientists working at the US National Evolutionary Synthesis Center.
The study, based on nearly 200 species of bats, birds, frogs, lizards and snakes, also ...
The diving bell and the water spider: How spiders breathe under water
2011-06-09
Gazing into the depths of a pond, it's hard to miss the insects that whirl and zip beneath the surface. However, only one species of spider has joined them: the diving bell spider, Argyroneta aquatica. 'It is an iconic animal; I had read about the spider as a small boy in popular literature about ponds,' says Roger Seymour from the University of Adelaide. According to Seymour, each spider constructs a net of silk in vegetation beneath the surface and fills it with air carried down on its abdomen. The spiders spend their entire lives submerged and even lay their eggs in ...
Study suggests police officer wrongfully convicted for missing the 'obvious'
2011-06-09
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In a new study, researchers tested the claims of a Boston police officer who said he ran past a brutal police beating without seeing it. After re-creating some of the conditions of the original incident and testing the perceptions of college students who ran past a staged fight, the researchers found the officer's story plausible.
The study appears in the peer-reviewed open access journal i-Perception.
Psychology professors Christopher Chabris (Union College) and Daniel Simons (University of Illinois) often explore the limits of visual attention – ...
'Decade of vaccines' has potential to save lives, but challenges ahead
2011-06-09
Bethesda, MD – Vaccinating children around the world against infectious diseases has saved the lives of millions over the past several decades. Now new opportunities exist to overcome remaining challenges—and save another 6.4 million lives over the current decade, according articles in the June 2011 edition of Health Affairs. The issue was produced under the journal's grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Last year, the Gates Foundation committed an additional $10 billion over the current decade to make life-saving vaccines available to millions of children. ...
Pioneering hospital pay-for-performance program falls short of its goals
2011-06-09
Massachusetts' innovative use of "pay-for-performance" bonuses to try to reduce racial and ethnic disparities in the case of Medicaid patients has turned up no evidence of the problem at any of the state's 66 acute-care hospitals, according to a new study that raises questions about the effectiveness of the state's novel approach.
While the study, published in the June edition of Health Affairs (June 9, 2011), found that racial and ethnic inequities for disadvantaged patients may well exist, it also determined that the hospital "pay-for-performance" approach – typically ...
Dramatic fall in cases of meningitis A in 3 west African nations after new vaccine introduction
2011-06-09
Contact: Preeti Singh
psingh@burnesscommunications.com
301-280-5722
Meningitis Vaccine Project
Dramatic fall in cases of meningitis A in 3 west African nations after new vaccine introduction
New immunization campaigns to protect millions more in 2011; $375 million funding shortfall hindering wider rollout; new analysis projects enormous cost benefit over next decade from adopting new vaccine over existing ones
This press release is available in French.
Ferney-Voltaire, France, June 9, 2011—Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger report the lowest number of confirmed meningitis ...
UT Southwestern research uncovers genetic link between emphysema, lung cancer
2011-06-09
DALLAS – June 9, 2011 – A gene linked to emphysema also can be a factor for developing lung cancer unrelated to cigarette smoking, UT Southwestern Medical Center research indicates. Smoking was the only known risk factor previously associated with both diseases.
In the study, mice bred to have the human gene pleiomorphic adenoma gene-like 2 (PLAGL2) all developed emphysema, and by gender also developed lung cancer at rates as high as one in every six rodents. Although the new study showed PLAGL2 as a contributing factor in emphysema and lung cancer development, the diseases ...