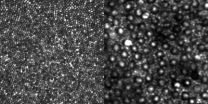
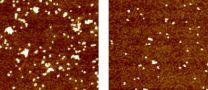
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Sheffield have discovered valuable insight into how people develop B-cell lymphoma, one of the most common cancers in the UK.
The team, from the University's Institute for Cancer Studies and funded by Leukaemia and Lymphoma Research, Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) and Yorkshire Cancer Research, found that a mechanism different to that previously thought to be the cause of lymphoma may be responsible for the development of the disease.
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that affects the blood, originating in the lymph glands. B-cells are the immune cells in the human body that are responsible for producing antibodies to fight infections and provide long-term immunity. B-cell lymphomas include both Hodgkin's lymphomas and most non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.
Prior to this research, the main theory to explain the origins of lymphoma was the malfunction of a mechanism (somatic hypermutation) used by B-cells to modify the genes coding for antibodies. This mechanism is required to produce highly specific antibodies, but it also accidentally alters other genes, leading to lymphoma.
However, the team from the University knew that this theory only accounted for affecting a handful of genes, and the model could only explain certain types of lymphoma.
Led by Dr Thierry Nouspikel, the researchers discovered another mechanism, which potentially affects many more genes and can account for a wider palette of lymphomas. The research found that B-cells actually do not repair the bulk of their DNA and only take care of the few genes they are using. When the B-cells are inert in the blood flow, this is not a problem. However, when they receive a stimulation (e.g. an infection) they start to proliferate and then produce antibodies.
To proliferate they must replicate their DNA, and replication of damaged DNA results in the introduction of mutations, the accumulation of which can lead to lymphoma. Dr Nouspikel's team have designed a novel method to specifically detect such mutations, and have proved that they do occur in genes that have been implicated in lymphoma.
The researchers demonstrated that B-cells are deficient in one of the main DNA repair pathways, known as Nucleotide Excision Repair. This pathway repairs a lot of different DNA lesions, including UV-induced damage and chemical adducts (e.g. from air pollution and cigarette smoke). Their model therefore explains why strong UV exposure (e.g. unprotected sun bathing) is the number one environmental risk factor for lymphoma and also supports the evidence that exposure to air pollution and smoking are also risk factors.
Dr Nouspikel said: "Lymphoma is one of the ten most frequent cancers in adults in the UK, and the third among children. If we want to come up with efficient strategies for prevention and therapy, it is crucial to understand what causes it. The novel mechanism we have discovered potentially accounts for the development of many different types of lymphoma. It may also explain why strong exposure to sunlight is the main environmental risk factor for this cancer."
###
Notes for editors:
The research is due for publication in Blood on 9 June 2011 and will also be published in Cell Cycle on 15 July 2011. To view the full research paper online, visit:
http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/content/early/2011/04/08/blood-2010-12-326637.long
To find out more about the University of Sheffield's Institute for Cancer Studies, visit:
http://www.shef.ac.uk/medicine/oncology/units/ics
For further information please contact: Amy Stone, Media Relations Officer, on 0114 2221046 or email a.f.stone@sheffield.ac.uk
To view this news release and images online on 09 June 2011, visit http://www.shef.ac.uk/mediacentre/2011/cancer-research-discovery.html
To read other news releases about the University of Sheffield, visit http://www.shef.ac.uk/mediacentre/
New research provides breakthrough in understanding common cancer
2011-06-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds shingles may be related to elevated risk of multiple sclerosis
2011-06-09
Taiwanese investigators have found that there can be a significantly higher risk of multiple sclerosis (MS) occurring in the year following a shingles, or herpes zoster, attack. The findings, which support a long-held view on how MS may develop, are published in The Journal of Infectious Diseases and now available online (http://jid.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2011/06/07/infdis.jir239.abstract).
MS is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord, leading to inflammation and nerve damage as the body's immune cells attack the nervous system. Possible ...
Immediate use of an IUD following abortion more likely to prevent unintended pregnancies
2011-06-09
PORTLAND, Ore. — Women who receive a contraceptive known as an intrauterine device or IUD immediately following a first trimester abortion experience few complications and are less likely to have an unintended pregnancy than those who delay getting an IUD by several weeks, according to a new study at Oregon Health & Science University.
The findings are published in the June 9 New England Journal of Medicine.
Research has shown that IUDs are safe, highly effective, long-term reversible contraceptives that don't require active use once they've been inserted. IUDs are ...
Seniors abused during childhood face increased risk of sleep troubles
2011-06-09
Suffering from parental abuse as a child increases a person's chances of having poor sleep quality in old age, according to a research article in the current issue of the Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological and Social Sciences (Volume 66B, Number 3).
An analysis of data from 877 adults age 60 years and above found that early parental emotional abuse was associated with a higher number of sleep complaints in old age. It was specifically emotional abuse — rather than physical abuse or emotional neglect — that was tied to trouble in getting a good night's sleep.
"A ...
Historic first images of rod photoreceptors in the living human eye
2011-06-09
WASHINGTON, June 8—Scientists today reported that the tiny light-sensing cells known as rods have been clearly and directly imaged in the living eye for the first time. Using adaptive optics (AO), the same technology astronomers use to study distant stars and galaxies, scientists can see through the murky distortion of the outer eye, revealing the eye's cellular structure with unprecedented detail. This innovation, described in two papers in the Optical Society's (OSA) open access journal Biomedical Optics Express, will help doctors diagnose degenerative eye disorders sooner, ...
Southwest Binding & Laminating Adds PSA Overlaminates & Mounting Adhesives to Lineup
2011-06-09
Southwest Binding & Laminating, a St. Louis, MO based manufacturer and distributor of document finishing products is pleased to announce the launch of it's PSA Overlaminate (ProGuard) and Mounting Adhesives (ProBond) to service new and existing customers.
"The Wide Format Printing market has seen tremendous growth and popularity," said Mark Mercer, President and CEO of Southwest Binding & Laminating. "PSA Overlaminates and Mounting Adhesives is a great addition to Southwest's product mix, in our continued efforts to better serve our customers."For ...
NIST tunes 'metasurface' with fluid in new concept for sensing and chemistry
2011-06-09
Like an opera singer hitting a note that shatters a glass, a signal at a particular resonant frequency can concentrate energy in a material and change its properties. And as with 18th century "musical glasses," adding a little water can change the critical pitch. Echoing both phenomena, researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have demonstrated a unique fluid-tuned "metasurface," a concept that may be useful in biomedical sensors and microwave-assisted chemistry.
A metasurface or metafilm is a two-dimensional version of a metamaterial, ...
Gary Rabine Speaks at Crain's Fast Fifty Breakfast
2011-06-09
The Rabine Group is proud to announce that its CEO and founder, Gary Rabine, was invited to speak at Crain's Fast Fifty Breakfast along with other successful entrepreneurs from Crain's Fast Fifty Growing Companies list. The event will be held on Tuesday, June 14, 2011 at the Westin River North hotel in Chicago.
The prestigious Fast Fifty Growing Companies list is an annual report published by Crain's Chicago featuring the fastest-growing public and private companies in the Chicagoland area based on five-year revenue growth. Last year, the Rabine Group ranked No. 12 with ...
Distracted driving data and laws to prevent it don't match up
2011-06-09
Cell phone distractions account for more than 300,000 car crashes each year. As a result, most states have put laws in place to limit or prohibit the use of mobile devices while driving. But a new study led by Temple University finds a widening gap between the evidence on distracted driving and the laws being passed to address the problem.
The new study, published this month in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, is the first comprehensive collection and coding of state laws attempting to address the public health risk posed by distracted driving.
Lead author ...
NIST 'catch and release' program could improve nanoparticle safety assessment
2011-06-09
Depending on whom you ask, nanoparticles are, potentially, either one of the most promising or the most perilous creations of science. These tiny objects can deliver drugs efficiently and enhance the properties of many materials, but what if they also are hazardous to your health in some way? Now, scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have found* a way to manipulate nanoparticles so that questions like this can be answered.
The team has developed a method of attracting and capturing metal-based nanoparticles on a surface and releasing ...
Best Place in the USA to Celebrate July's National Ice Cream Month
2011-06-09
As the nation prepares to celebrate National Ice Cream Month this July, there's no place better to experience the creamy confection than Harrison County. Here, a trio of old-fashioned ice cream parlors and soda fountains draw sweet-toothed visitors of all ages to the southern Indiana town of Corydon.
Palate-Pleasing Prescription
Recently made famous with the wildly popular viral nature of their online commercial (http://bit.ly/cGNJuu), the classic soda fountain tucked inside Butt Drugs returns visitors to the laid-back days before cell phones and MP3s. Locals and out-of-towners ...