(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, September 16, 2010—Not only do undergraduate students gain valuable hands-on experience by participating in scientific research projects, but they also make meaningful contributions, examples of which are highlighted in the current special issue of DNA and Cell Biology, a peer-reviewed journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The issue is available free online.
This special issue features a collection of papers reporting on successful research projects in which undergraduate students played a significant role, "and undoubtedly learned much in the process," writes Jo Handelsman, PhD, Editor-in-Chief of DNA and Cell Biology and Howard Hughes Medical Institute Professor in the Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology at Yale University (New Haven, CT), in an accompanying Editorial. Dr. Handelsman notes that "novices bring a fresh perspective" and their "lack of entrenched bias can bring new insights to old problems."
"This issue of DNA and Cell Biology is a testament to the creativity and hard work that undergraduates invest in research projects. And implicit in these publications is evidence of the power of research as an instrument of education," says Dr. Handelsman.
Included in the issue is a paper by Cristina Cardemil and colleagues from Swarthmore College (Pennsylvania) and DuPont Company (Wilmington, DE), describing the development of a bioluminescence-based test that uses a bacterium to measure the amount of ammonia and phosphate in water samples. The researchers showed that this method yields as good or better results as commonly used analytical chemistry test kits that have limited sensitivity.
Laura Bergner and coworkers from Davidson College (North Carolina) authored an article on their research to map and clone a mutant gene associated with male sterility in fruit flies. In Drosophila carrying this mutant gene, sperm begin to form too early, before chromosome replication has taken place. The authors identified a novel protein coded for by the gene of interest.
Exploring the regulation of telomerase, a protein that maintains the integrity of the ends of mammalian chromosomes and is typically silenced in normal human cells but reactivated in 90% of cancers, Diana Tran and coauthors from Harvey Mudd College (Claremont, CA), identified a gene region that is highly conserved among mammalian species and may play an important role in regulating telomerase activity.
Irene Cho and colleagues from University of Maryland Baltimore County and University of Alabama at Birmingham studied the effects of variation in the fruit fly S6 kinase gene—which appears to regulate fat storage—on the metabolism, fitness, and immune system health, and life span of Drosophila.
INFORMATION:
DNA and Cell Biology, led by Editor-in-Chief Jo Handelsman, PhD, publishes peer-reviewed papers, short communications, reviews, and laboratory methods dealing with eukaryotic or prokaryotic gene structure, organization, expression, cell biology, biochemistry, immunology, virology, and evolution. A complete table of contents and free sample issue may be viewed online.
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. is a privately held, fully integrated media company known for establishing authoritative peer-reviewed journals in many promising areas of science and biomedical research, including Human Gene Therapy, Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, and AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses. Its biotechnology trade magazine, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 60 journals, books, and newsmagazines is available at our website.
Undergraduate research highlighted in DNA and Cell Biology Journal
2010-09-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bacteria identified that may lead to inflammatory bowel disease in certain individuals
2010-09-16
Certain bacteria that inhabit the intestine provide the environmental trigger that initiates and perpetuates chronic intestinal inflammation in individuals who are genetically susceptible to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a study led by Harvard School of Public Health researchers has found.
Inflammatory bowel disease results from a loss of homeostasis, or balance, between the immune system and the microbes that inhabit the intestine. "In this study, we identified two microbes that instigate gut inflammation that leads to inflammatory bowel disease in mice," said ...
UCSB, Texas A&M scientists document fate of deep hydrocarbon plumes in Gulf oil spill
2010-09-16
SANTA BARBARA, Calif., Sept. 16, 2010 — In the aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon disaster in the Gulf of Mexico, a team of scientists led by UC Santa Barbara's David Valentine and Texas A&M University's John Kessler embarked on a research cruise with an urgent mission: determining the fate and impact of hydrocarbon gases escaping from a deep-water oil spill.
The spill provided a rare opportunity for Valentine, a professor in the Department of Earth Science at UCSB, and Kessler, an assistant professor in the Department of Oceanography at Texas A&M, to study the behavior ...
Scripps scientists develop test providing new pathway for identifying obesity, diabetes drugs
2010-09-16
La Jolla, CA, September 15, 2010 – Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute have designed a new molecular test that will allow researchers to look for potential drugs targeting a human metabolic enzyme believed to stimulate the appetite and play a role in diabetes.
The new test, which the scientists call a simple assay, will allow researchers to look through hundreds of thousands of compounds for those that have potential to block the action of an enzyme known as ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT). If drugs can be found that safely suppress the action of GOAT, they ...
Fat stem cells safe for breast reconstruction when cancer is dormant, says Pitt team
2010-09-16
PITTSBURGH, Sept. 15 – Fat-derived stem cells can be safely used to aid reconstruction of breast tissue after mastectomy as long as there is no evidence of active cancer, according to researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. Their findings are available in Tissue Engineering Part A.
Plastic surgeons have long moved fat from one part of the body into the breasts for reconstruction, but with some complications and a varying success rate, explained senior author Vera S. Donnenberg, Ph.D., assistant professor of surgery, Pitt School of Medicine. More ...
Significant weight-loss from surgery decreases risk for cardiovascular disease in women
2010-09-16
Significant weight loss not only improves daily life of morbidly obese woman but also decreases the risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, many people can not lose weight or can not maintain weight loss without help. Bariatric surgery is emerging as a valuable procedure to help morbidly obese individuals lose weight, as studies have shown; it can improve many health profiles and lower mortality. Now, researchers have found another positive impact of significant weight loss after bariatric surgery: it can significantly improve the lipoprotein profiles of women within ...
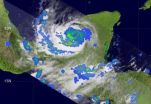
NASA eyes Karl, now a hurricane in the Gulf of Mexico
2010-09-16
NASA's Aqua and TRMM satellites have been watching Karl's clouds and rainfall as he moved across Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula and into the Gulf of Mexico today, powering up into a hurricane.
Infrared imagery of Karl's cloud temperatures from NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument this morning, Sept. 16 at 0753 UTC (3:53 a.m. EDT) showed strong convective activity in his center as indicated by high thunderstorms that were as cold as -63 Fahrenheit. That strong convection was an indication that the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico were strengthening the storm. ...
Developing countries may not benefit from adopting international treaties
2010-09-16
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A new study by an Oregon State University business professor has found that developing countries that adopt major international economic treaties do not necessarily gain more foreign direct investment.
In fact, in some cases adopting these treaties can hurt, not help a developing country, contrary to what agencies such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) espouse. The study, published in the current online version of the Journal of World Business, has major implications for Latin American and Caribbean intellectual policy reform
Ted Khoury, an assistant ...
GOES-13 sees a weaker Hurricane Julia in the 'tropical trio'
2010-09-16
GOES-13 satellite imagery this morning showed the "tropical trio": Tropical Storm Karl over the Gulf of Mexico, Hurricane Igor in the central Atlantic, and a waning Hurricane Julia in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. Hurricane Julia has now lost her Category 4 Hurricane status, and is currently a Category 2 hurricane in the eastern Atlantic and weakening. Wind shear, cooler sea surface temperatures and warmer cloud top temperatures all spell a weaker Julia.
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite known as GOES-13 that monitors weather over the U.S. East Coast ...
Study: How Palestinian and Israeli children are psychologically scarred by exposure to war
2010-09-16
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---As another round of talks continues between Israelis and Palestinians, a new University of Michigan study documents the impact the violence has been inflicting on the region's children.
Palestinian and Israeli children not only suffer the direct physical consequences of violence, they are also being psychologically scarred by the high levels of violence they witness, according to the study, presented earlier this summer at the International Society for Research on Aggression.
Nearly 50 percent of Palestinian children between the ages of 11 and 14 ...
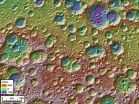
NASA'S LRO exposes moon's complex, turbulent youth
2010-09-16
The moon was bombarded by two distinct populations of asteroids or comets in its youth, and its surface is more complex than previously thought, according to new results from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) spacecraft featured in three papers appearing in the Sept. 17 issue of Science.
In the first paper, lead author James Head of Brown University in Providence, R.I., describes results obtained from a detailed global topographic map of the moon created using LRO's Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA). "Our new LRO LOLA dataset shows that the older highland impactor ...