Venice to suffer fewer storm surges
Australia's CSIRO has found that the frequency of extreme storm surge events generated by Adriatic Sea tempests could fall by about 30 percent by 2100
2011-06-11
(Press-News.org) Venice – the City of Dreams – may have one less nightmare to deal with following a finding that the frequency of extreme storm surge events generated by Adriatic Sea tempests could fall by about 30 per cent by 2100.
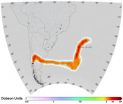
A team of international scientists led by CSIRO's Dr Alberto Troccoli studied atmospheric circulation in the Mediterranean region to assess climate impacts through changes in storm surge frequency in Venice – a World Heritage-listed city built on 117 small islands and considered vulnerable to high sea levels (locally known as Acqua Alta).
Dr Troccoli said predictions of such extreme and small-scale events are exceedingly challenging, even for relatively short time horizons.
"The survival of Venice and its lagoon is seriously questioned under the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) global sea level rise scenarios and the results of this study, published in the journal Climatic Change, emphasise the need for location-by-location studies to determine coastal flooding impacts.
"While some assessment of the vulnerability of Venice to extreme high-water events have been carried out in the past, possible future changes in storm surge occurrences critical to flooding events remain largely unexplored. It is important to understand how these events will evolve since a moderate to strong storm surge event is required to cause serious flooding.
"We found that the frequency of extreme storm surge events affecting Venice is projected to decrease by about 30 per cent by the end of the 21st century which would leave the pattern of flooding largely unaltered under 21st Century climate simulations," Dr Troccoli said.
The research team – from CSIRO, the University of Padova and the University of Reading – used data from observations of storms, analysis of atmospheric and surface conditions, and climate scenario simulations. Storm surges in the northern part of the Adriatic Sea are driven by the passage of deep low-pressure systems, which cause sea level pressure gradients and strong Sirocco (South-Easterly) winds along the Adriatic Sea. These forces combine to push water into the northern end of the basin where Venice is located.
Dr Troccoli said an implication of the finding is that alterations in extreme tidal levels under climate change must be considered on a location-by-location basis in spite of the projected increase in global sea level.
"Thus the projected change in the storm surge contribution, combined with the projected change of mean water levels in the Adriatic Sea indicates that tidal flooding events might not be exacerbated over the current century, with potential beneficial consequences for the conservation of the city.
"Our paper presents an alternative analysis for storm surges and we believe our findings could have important implications on the way future storm surge and high tide events are interpreted," he said.
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-06-11
Clinically ascertained reports suggest that boys and girls with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may differ from each other in their vulnerability to substance use problems, say the researchers of the University of Helsinki and University of Jyväskylä, Finland.
A total of 1545 Finnish adolescents were assessed for DSM-IV-based ADHD symptoms by their parents and classroom teachers using standardized rating scales at age 11-12 years. At age 14, substance use disorders and psychiatric co-morbidity were assessed with the Semi-Structured Assessment for the ...
2011-06-11
A report issued by the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights (IACHR) examines the use of detention centers for immigration cases. The report criticized the operation of system that is overly penal in nature, resorting to prison-like conditions for administrative detentions.
The IACHR was prompted to investigate the detention systems by complaints human rights advocates, according to a New York Times story.
Findings of the Report
The Inter-American Commission found that:
- In many if not the majority of cases, detention is a disproportionate measure and the ...
2011-06-11
This image shows the huge plume of sulphur dioxide that spewed from Chile's Puyehue-Cordón Caulle Volcanic Complex, which lies in the Andes about 600 km south of Santiago.
After lying dormant for more than 50 years, a series of rumbling earthquakes signalled the beginnings of this major volcanic eruption. On 4 June, a fissure opened, sending a towering plume of volcanic ash and gas over 10 km high.
Several thousand people were evacuated as a thick layer of ash and pumice fell and blanketed a wide area. Airports in Chile and Argentina were closed as a result.
The ...
2011-06-11
Side-impact crashes account for 13 percent of all car accidents and 18 percent of all fatal car accidents, according to a 2009 study conducted by the University of Michigan. These types of crashes, also known as T-bone accidents, can result in serious injuries to drivers and passengers, who may be able to file personal-injury lawsuits following side-impact car accidents in California.
Automotive Experts Test Side-Impact Safety
While front-impact collisions have been the focus of automotive safety improvements for decades, researchers and auto engineers are turning ...
2011-06-11
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Voters in states with early primary races such as Iowa and New Hampshire have up to five times the influence of voters in later states in selecting presidential candidates, according to research by Brown University economist Brian Knight. The paper, the first to quantify the effects of early victories in the race for the presidential nomination, is co-authored by Nathan Schiff and published in The Journal of Political Economy.
Knight and Schiff developed a statistical model that examines how daily polling data responds to returns ...
2011-06-11
People lose 30% of their muscle strength between the ages of 50 and 70 years. However, maintaining muscle strength in old age is enormously important in order to maintain mobility and to be able to lead an independent life and manage everyday tasks independently. In the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, Frank Mayer and colleagues from the University of Potsdam conclude that progressive strength (resistance) training counteracts muscular atrophy in old age (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2011; 108(21): 359-64).
The authors investigated the extent of the effects that ...
2011-06-11
The U.S. Supreme Court has heard several cases regarding acceptable behavior by law enforcement, and this term is no exception. One of the cases involves Albert Florence, a New Jersey resident who alleged that his civil rights were violated after being subject to strip searches when being booked into two local jails.
Florence was stopped in 2005 while riding in his vehicle with his wife and daughter. The police ran a search for the vehicle's registration, and discovered that it belonged to Florence, who had an outstanding warrant for an unpaid fine from a 2003 non-indictable ...
2011-06-11
Just a few genes make enterohaemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) extremely dangerous to humans. If it were not for these genes, EHEC would hardly differ from harmless enteric bacteria. Bioinformatics scientists from the Saarbrücken Cluster of Excellence want to exploit this similarity to find starting points for effective drugs against the EHEC pathogen. In a very short time, the scientists have constructed EhecRegNet, a database and analysis platform that incorporates all known interactions between enteric E. coli genes. Using integrated simulations, genetic switches for the dangerous ...
2011-06-11
Patti Flynn is a disabled mother locked in a legal battle with her ex-boyfriend for custody of their five-year-old son. The parties currently share custody, but Flynn's ex-boyfriend is seeking full custody of the child. While this is an intense emotional fight, she has been through such struggles before.
A week before she was to be married, Flynn suffered a stroke and fell in the shower, leaving her unable to speak or move her right side. Unfortunately, that relationship deteriorated, but she endured a long road of rehabilitation and learned how to care for her toddler. ...
2011-06-11
UPTON, NY - Magnetic studies of ultrathin slabs of copper-oxide materials reveal that at very low temperatures, the thinnest, isolated layers lose their long-range magnetic order and instead behave like a "quantum spin liquid" - a state of matter where the orientations of electron spins fluctuate wildly. This unexpected discovery by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and collaborators at the Paul Scherrer Institute in Switzerland may offer support for the idea that this novel condensed state of matter is a precursor to the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Venice to suffer fewer storm surges
Australia's CSIRO has found that the frequency of extreme storm surge events generated by Adriatic Sea tempests could fall by about 30 percent by 2100