(Press-News.org) A wall painting (fresco) of Tyche, the Greek goddess of fortune, was exposed during the 11th season of excavation at the Sussita site, on the east shore of the Sea of Galilee, which was conducted by researchers of the University of Haifa. Another female figure was found during this season, of a maenad, one of the companions of the wine god Dionysus.
"It is interesting to see that although the private residence in which two goddesses were found was in existence during the Byzantine period, when Christianity negated and eradicated idolatrous cults, one can still find clear evidence of earlier beliefs," said Prof. Arthur Segal and Dr. Michael Eisenberg of the Zinman Institute of Archaeology at the University of Haifa, who headed the excavation. The city of Sussita is located within the Sussita National Park under the management of the Israel Nature and Parks Authority, which has accompanied and assisted the excavation teams this season in enabling the continuation of excavation work and the conservation of the archaeological finds.
During the course of the excavations conducted by the team from the University of Concordia under the direction of Prof. Mark Schuler, in a residence that appeared, by the quality and complexity of its construction, to belong to one of the city notables, the excavators reached an inner courtyard with a small fountain at its center. Near the fountain they found a fresco of Tyche, who was apparently deified as the city's goddess of fortune. Her head is crowned, her youthful gaze is focused, and she has abundant brown hair beneath her crown. According to the researchers, artistic analysis has indicated that the wall painting may be dated to the end of the Roman period or the beginning of the Byzantine period (3rdth centuries C.E.).
The goddess Tyche was not the only mythological figure to be discovered in this compound. Found on a bone plate was a wonderfully etched relief of a maenad, one of a group of female followers of Dionysus, the god of wine. According to Greek mythology, the maenads accompanied Dionysus with frenzied dances while holding a thyrsus, a device symbolizing sexuality, fertility, and the male sexual organ associated with sexual pleasure. The maenad of Sussita was also depicted as being in the midst of a frenzied dance. The researchers believe that both manifestations of the cult of Graeco-Roman female goddesses can be dated to the end of the Roman period, but there is no doubt that the residence in which they were found continued to exist even after Christianity triumphed over idolatry.
In this season the city's Roman period basilica (1stnd centuries CE) began to be exposed. This is a large-sized building that incorporated the city's central commercial, social and judicial areas. Besides the excellent architectural marble items that were unearthed there, the researchers also found decorations made of "stucco", molded plaster used in the imitation of marble. "We could not fail to wonder how a relatively plebeian city could employ first-class builders and artisans. The stucco decorations demonstrate that despite everything, the city rulers were certainly not sparing of the costs and expenditure of construction," the researchers noted.
Sussita was erected on a mountain top rising to the east of the Sea of Galilee during the 2nd century B.C.E. by the Seleucid rulers who then controlled the country. The city existed during the Hellenist, Roman, Byzantine and Umayyad periods, until it was destroyed by a violent earthquake in the year 749 C.E. Together with Beth Shean and other cities on the eastern bank of the Jordan River, Sussita was one of the cultural-geographical group of Decapolis cities – a region within which Jesus conducted some of the miracles described in the New Testament.
INFORMATION:
For more details contact Rachel Feldman • Tel: +972-4-8288722
Communications and Media Relations
University of Haifa
press@univ.haifa.ac.il
Goddess of fortune found in Sussita
A wall painting (fresco) of Tyche, the Greek goddess of fortune, was exposed during the 11th season of excavation at the Sussita site, on the east shore of the Sea of Galilee, which was conducted by researchers of the University of Haifa
2010-09-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cardiac imaging breakthrough developed at the University of Western Ontario
2010-09-16
VIDEO:
New imaging technique developed by cardiologist, Dr. James A. White and colleagues at The University of Western Ontario shows 3-D image of the heart vasculature and myocardial scar tissue.
Click here for more information.
Cardiologists and surgeons may soon have a new tool to improve outcomes for patients requiring pacemakers, bypass surgery or angioplasties. Research led by Dr. James White and his colleagues at The University of Western Ontario has led to a new imaging ...
Discovery of key pathway interaction may lead to therapies that aid brain growth and repair
2010-09-16
WASHINGTON, DC—Researchers at the Center for Neuroscience Research at Children's National Medical Center have discovered that the two major types of signaling pathways activated during brain cell development—the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway and the Notch pathway—operate together to determine how many and which types of brain cells are created during growth and repair in developing and adult brains. This knowledge may help scientists design new ways to induce the brain to repair itself when these signals are interrupted, and indicate a need for further research ...
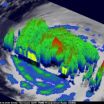
NASA's 3-D look into Hurricane Igor's heavy rainfall
2010-09-16
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite has provided a 3-D look at the power "under the hood" (of clouds) in powerful Category 4 Hurricane Igor as it heads toward Bermuda. In the meantime, Igor is creating dangerous surf in the eastern Atlantic, and it will affect the U.S. East coast later today. Igor is an extremely dangerous category four hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane wind scale today, Sept. 16, and he is expected to remain a large and powerful hurricane over the next several days.
The TRMM satellite, operated by NASA and the Japanese ...
Scientific understanding of T. rex revised by a decade of new research and discovery
2010-09-16
We've all heard this story: the Late Cretaceous of Asia and North America—about 65 million years ago—was dominated by several large-headed, bipedal predatory dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus rex and Tarbosaurus that had tiny arms. But a decade of new fossil discoveries that have more than doubled the number of known tyrannosaur species has changed this tale. Older and smaller tyrannosaurs have made the evolutionary tree of this group richer and more complex. Furthermore, a series of innovative research projects on topics like bone growth and biomechanics have added an enormous ...
Beating blood clots: Reducing your risk before hip replacement surgery
2010-09-16
Risk factors for venous thromboembolism after total hip replacement (THR) surgery were identified in a new study published in the September 2010 issue of The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (JBJS). While the rate of thromboembolism has been significantly reduced through medication, understanding the risk factors could further reduce the likelihood of patients developing this potentially fatal complication.
Two of the most common manifestations of a thromboembolism include:
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), in which the blood clot forms in a deep vein, commonly in the thigh ...
Placebo effect significantly improves women's sexual satisfaction, study shows
2010-09-16
AUSTIN, Texas — Many women with low sex drives reported greater sexual satisfaction after taking a placebo, according to new psychology research from The University of Texas at Austin and Baylor College of Medicine.
The study was conducted by Cindy Meston, a clinical psychology professor at The University of Texas at Austin, and Andrea Bradford, a 2009 University of Texas at Austin graduate and postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Family and Community Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine. They found that opening a new line of communication about sex can have a positive ...
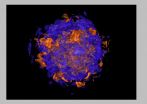
3-D computer simulations help envision supernovae explosions
2010-09-16
For scientists, supernovae are true superstars -- massive explosions of huge, dying stars that shine light on the shape and fate of the universe.
For a brief burst of time, supernovae can radiate more energy than the sun will emit in its lifetime. With the potential energy of 25 hundred trillion trillion nuclear weapons, they can outshine entire galaxies, producing some of the biggest explosions ever seen, and helping track distances across the cosmos.
Now, a Princeton-led team has found a way to make computer simulations of supernovae exploding in three dimensions, ...
Asthma and cavities both common in kids but not linked
2010-09-16
INDIANAPOLIS – There is no apparent link between asthma and tooth decay, according to a study published in the September 2010 issue of the Journal of the American Dental Association.
"Is There a Relationship between Asthma and Dental Caries?: A Critical Review of the Literature" examined the 27 separate studies which looked for a link between asthma and cavities that were reported in 29 papers published between 1976 and March 2010.
"The notion that there is a link between asthma and tooth decay may have its origin in anecdotal statements by emergency room workers who ...
Disease transmission model says media coverage cuts infection rate and pandemic extent
2010-09-16
At the first sign of a disease pandemic, public health officials should begin strongly communicating about the extent of the outbreak and the steps that can be taken by the public to avoid infection. That's the recommendation of two mathematical biologists who have modified the most widely used infectious disease transmission model to account for the impact of news media coverage.
During outbreaks of serious infectious diseases, many individuals closely follow media reports and as a result, take precautions to protect themselves against the disease. These precautions ...
October 2010 Lithosphere highlights
2010-09-16
Boulder, CO, USA – The October LITHOSPHERE examines the following key questions: (1) how do large volumes of silicic magma contribute to the growth of continental crust?; (2) how does the Tibetan Plateau grow?; (3) what are the dynamics of the lithosphere beneath the Eastern Carpathians in Romania?; (4) what's really true about the Mojave-Snow Lake fault hypothesis?; (5) can Earth's pulse be measured at its hotspots?; and (6) what is the nature of the Moho in NW Canada?
Keywords: Philipsburg Batholith, Tibetan Plateau, Carpathians, Mojave-Snow Lake fault, hotspots, Moho.
Highlights ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Goddess of fortune found in SussitaA wall painting (fresco) of Tyche, the Greek goddess of fortune, was exposed during the 11th season of excavation at the Sussita site, on the east shore of the Sea of Galilee, which was conducted by researchers of the University of Haifa