(Press-News.org) DeKalb, Ill. – Scientists at Northern Illinois University say they have discovered a simple method for producing high yields of graphene, a highly touted carbon nanostructure that some believe could replace silicon as the technological fabric of the future.
The focus of intense scientific research in recent years, graphene is a two-dimensional material, comprised of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. It is the strongest material ever measured and has other remarkable qualities, including high electron mobility, a property that elevates its potential for use in high-speed nano-scale devices of the future.
In a June communication to the Journal of Materials Chemistry, the NIU researchers report on a new method that converts carbon dioxide directly into few-layer graphene (less than 10 atoms in thickness) by burning pure magnesium metal in dry ice.
"It is scientifically proven that burning magnesium metal in carbon dioxide produces carbon, but the formation of this carbon with few-layer graphene as the major product has neither been identified nor proven as such until our current report," said Narayan Hosmane, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry who leads the NIU research group.
"The synthetic process can be used to potentially produce few-layer graphene in large quantities," he said. "Up until now, graphene has been synthesized by various methods utilizing hazardous chemicals and tedious techniques. This new method is simple, green and cost-effective."
Hosmane said his research group initially set out to produce single-wall carbon nanotubes. "Instead, we isolated few-layer graphene," he said. "It surprised us all."
"It's a very simple technique that's been done by scientists before," added Amartya Chakrabarti, first author of the communication to the Journal of Materials Chemistry and an NIU post-doctoral research associate in chemistry and biochemistry. "But nobody actually closely examined the structure of the carbon that had been produced."
INFORMATION:
Other members of the research group publishing in the Journal of Materials Chemistry include former NIU physics postdoctoral research associate Jun Lu, NIU undergraduate student Jennifer Skrabutenas, NIU Chemistry and Biochemistry Professor Tao Xu, NIU Physics Professor Zhili Xiao and John A. Maguire, a chemistry professor at Southern Methodist University.
The work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation, Petroleum Research Fund administered by the American Chemical Society, the Department of Energy and Robert A. Welch Foundation.
Northern Illinois University scientists find simple way to produce graphene
2011-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genius of Einstein, Fourier key to new humanlike computer vision
2011-06-21
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Two new techniques for computer-vision technology mimic how humans perceive three-dimensional shapes by instantly recognizing objects no matter how they are twisted or bent, an advance that could help machines see more like people.
The techniques, called heat mapping and heat distribution, apply mathematical methods to enable machines to perceive three-dimensional objects, said Karthik Ramani, Purdue University's Donald W. Feddersen Professor of Mechanical Engineering.
"Humans can easily perceive 3-D shapes, but it's not so easy for a computer," ...
Bacteria develop restraint for survival in a rock-paper-scissors community
2011-06-21
It is a common perception that bigger, stronger, faster organisms have a distinct advantage for long-term survival when competing with other organisms in a given community.
But new research from the University of Washington shows that in some structured communities, organisms increase their chances of survival if they evolve some level of restraint that allows competitors to survive as well, a sort of "survival of the weakest."
The phenomenon was observed in a community of three "nontransitive" competitors, meaning their relationship to each other is circular as in ...
Picower: 1 skull + 2 brains = 4 objects in mind
2011-06-21
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. — In the 1983 movie "A Man with Two Brains," Steve Martin kept his second brain in a jar. In reality, he had two brains inside his own skull — as we all do, one on the left and one on the right hemisphere. When it comes to seeing the world around us, each of our two brains works independently and each has its own bottleneck for working memory.
Normally, it takes years or decades after a brand new discovery about the brain for any practical implications to emerge. But this study by MIT neuroscientists could be put to immediate use in designing more effective ...
Increase in survival when AED used less than 10 seconds after CPR pause
2011-06-21
TORONTO, Ont., June 20, 2011--Every second counts when performing CPR.
A new study has found the number of people who survive after suffering a cardiac arrest outside a hospital drops significantly if the pause between stopping CPR and using a defibrillator to administer an electric shock is longer than 20 seconds.
The number of people who survive rises significantly if the pause is less than 10 seconds.
"If your pre-shock pause is over 20 seconds, the chances of surviving to reach a hospital, be treated and be discharged are 53 per cent less than if the pause is ...
Energy drinks linked to substance use in musicians, study shows
2011-06-21
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Frequent use of energy drinks is associated with binge drinking, alcohol-related social problems and misuse of prescription drugs among musicians, according to researchers at the University at Buffalo's Research Institute on Addictions.
In survey results published in the Journal of Caffeine Research this spring, UB research scientists Kathleen E. Miller and Brian M. Quigley examined substance use by 226 Western New York professional and amateur musicians aged 18-45. In the sample, 94 percent were caffeine users and 57 percent reported use of energy ...
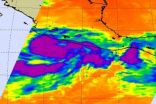
Thunderstorms in Beatriz show strengthening toward hurricane status
2011-06-21
Tropical Storm Beatriz developed from a low pressure area that NASA was watching last week. Beatriz is now expected to reach hurricane force and hit western coastal Mexico today and tomorrow. NASA satellite imagery today revealed powerful thunderstorms bubbling within, indicating further strengthening is occurring.
Beatriz formed from the low pressure area System 92E that NASA and JAXA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) was watching last week. The low pressure area was coming together on Friday, June 17 and had some isolated areas of heavy rainfall. Those areas ...
Fastest sea-level rise in 2 millennia linked to increasing global temperatures
2011-06-21
The rate of sea level rise along the U.S. Atlantic coast is greater now than at any time in the past 2,000 years--and has shown a consistent link between changes in global mean surface temperature and sea level.
The findings are published this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The research, funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF), was conducted by Andrew Kemp, Yale University; Benjamin Horton, University of Pennsylvania; Jeffrey Donnelly, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution; Michael Mann, Pennsylvania State University; ...
Husband's employment status threatens marriage, but wife's does not, study finds
2011-06-21
A new study of employment and divorce suggest that while social pressure discouraging women from working outside the home has weakened, pressure on husbands to be breadwinners largely remains.
The research, led by Liana Sayer of Ohio State University and forthcoming in the American Journal of Sociology, was designed to show how employment status influences both men's and women's decisions to end a marriage.
According to the study, a woman's employment status has no effect on the likelihood that her husband will opt to leave the marriage. An employed woman is more ...
Researchers find process of cervical ripening differs between term and preterm birth
2011-06-21
DALLAS – June 21, 2011 – Cervical ripening that instigates preterm labor is distinct from what happens at the onset of normal term labor, researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have found.
The findings challenge the conventional premise that premature cervical ripening and remodeling is likely just an accelerated version of the term labor process, and that normal term ripening is caused primarily by activation of inflammatory responses.
Cervical remodeling is the process by which the cervix is transformed to open sufficiently during the birth process.
"Premature ...
TRGroup, Inc Achieves Maryland Minority Business Enterprise (MBE) Certification
2011-06-20
TRGroup, Inc., one of Maryland's fastest growing Information Technology (IT) consulting and solutions firms, announced today that it has achieved certification as a Minority Business Enterprise with the state of Maryland. This certification makes the TRGroup, Inc. eligible to compete on the more than $80 million dollars of Maryland contracts for Information Technology services awarded through the MDOT MBE program.
"As a certified MBE in the state of Maryland, we will now have a greater ability to expand our IT services, providing support to state and local government ...