(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA — An international research team including University of Pennsylvania scientists has shown that the rate of sea-level rise along the U.S. Atlantic coast is greater now than at any time in the past 2,000 years and that there is a consistent link between changes in global mean surface temperature and sea level.
The research was conducted by members of the Department of Earth and Environmental Science in Penn's School of Arts and Science: Benjamin Horton, associate professor and director of the Sea Level Research Laboratory, and postdoctoral fellow Andrew Kemp, now at Yale University's Climate and Energy Institute.
Their work will be published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on June 20.
"Sea-level rise is a potentially disastrous outcome of climate change, as rising temperatures melt land-based ice and warm ocean waters," Horton said.
"Scenarios of future rise are dependent upon understanding the response of sea level to climate changes. Accurate estimates of past sea-level variability provide a context for such projections," Kemp said.
In the new study, researchers provided the first continuous sea-level reconstruction for the past 2,000 years and compared variations in global temperature to changes in sea level during this time period.
The team found that sea level was relatively stable from 200 B.C. to 1,000 A.D. During a warm climate period beginning in the 11th century known as the Medieval Climate Anomaly, sea level rose by about half a millimeter per year for 400 years. There was then a second period of stable sea level associated with a cooler period, known as the Little Ice Age, which persisted until the late 19th century. Since the late 19th century, however, sea level has risen by more than 2 millimeters per year on average, which is the steepest rate for more than 2,100 years.
To reconstruct sea level, the research team used microfossils called foraminifera preserved in sediment cores from coastal salt marshes in North Carolina. The age of these cores was estimated using radiocarbon dating and several complementary techniques.
To ensure the validity of their approach, the team members confirmed their reconstructions against tide-gauge measurements from North Carolina for the past 80 years and global tide-gauge records for the past 300 years. A second reconstruction from Massachusetts confirmed their findings. The records were also corrected for contributions to sea-level rise made by vertical land movements.
The team's research shows that the reconstructed changes in sea level during the past millennium are consistent with past global temperatures and can be described using a model relating the rate of sea-level rise to global temperature.
"The data from the past help to calibrate our model and will improve sea-level rise projections under scenarios of future temperature rise," research team member Stefan Rahmstorf said.
INFORMATION:
In addition to Horton and Kemp, the research was conducted by Jeffrey Donnelly of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Michael Mann of Pennsylvania State University, Martin Vermeer of Finland's Aalto University School of Engineering in Finland and Rahmstorf of Germany's Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research.
Support for this research was provided by the National Science Foundation, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, United States Geological Survey, the Academy of Finland, the European Science Foundation through European Cooperation in Science and Technology and the University of Pennsylvania.
END
The risk of developing venous thromboembolism (VTE) may be nearly twice as high for patients undergoing open surgery for colorectal problems, versus those undergoing laparoscopic colorectal (LC) resections, according to a report in the June issue of Archives of Surgery, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Venous thromboembolism (the formation of blood clots in the veins) occurs in up to 25 percent of patients who undergo surgery without specific steps taken to prevent the condition, according to background information in the article. The authors note that colorectal surgery ...
Most hospitals follow established practice guidelines for surgery involving Medicare beneficiaries with cancer, but in some cases their practice patterns diverge from the guidelines, according to a report published Online First today by Archives of Surgery, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
According to background information in the article, health care quality has emerged as an important concern in the United States. However, the right care is not always delivered to the right patient at the right time, the authors remark. "Currently, it is well documented that the ...
A review of tonsillectomy-technique studies found that some new methods have advantages over traditional methods, but others are equivalent, according to a report in the June issue of Archives of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
As background information, the article states that tonsillectomy is well established in terms of safety, but is often accompanied by pain, postsurgical bleeding, and a prolonged recovery. Traditionally, the operation has been performed using cold steel and/or electrocautery dissection (CS/EC). Newer methods ...
Using a fluticasone furoate nasal spray for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in children appears to reduce production of certain inflammatory cell proteins that may play a role in development of obstructive sleep apnea, according to a report in the June issue of Archives of Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
"Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is characterized by prolonged partial upper airway obstruction and/or intermittent complete obstruction with disruption of normal ventilation during sleep and normal sleep patterns," the authors ...
Not all varieties of botulinum toxin seem to be equally effective in reducing crow's feet wrinkles, according to a report published Online First today by Archives of Facial Plastic Surgery, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Botulinum toxin, a protein long considered harmful, is now known as a neuromodulator (a chemical that affects nerve impulses) that has cosmetic and medical uses, according to background information in the article. In 1989, botulinum toxin type A was approved in the United States for two muscular conditions that affect the appearance of the eyes. In ...
A newly constructed, 2,000-year history of sea level elevations will help scientists refine the models used to predict climate-change-induced sea level rise, according to an international team of climate researchers. The record also shows that the past century had the fastest recorded rate of sea level rise.
"One of the largest uncertainties in projecting the impacts of climate change involve predicting the amount and rate of future sea level rise," said Michael E. Mann, professor of meteorology, Penn State. "The societal ramifications are as great as any climate change ...
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a novel method of disguising nanoparticles as red blood cells, which will enable them to evade the body's immune system and deliver cancer-fighting drugs straight to a tumor. Their research will be published next week in the online Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The method involves collecting the membrane from a red blood cell and wrapping it like a powerful camouflaging cloak around a biodegradable polymer nanoparticle stuffed with a cocktail of small molecule ...
A surprising finding in a study comparing hepatitis C virus (HCV) with hepatitis A virus (HAV) infections in chimpanzees by a team that includes scientists from the Texas Biomedical Research Institute sheds new light on the nature of the body's immune response to these viruses.
Understanding how hepatitis C becomes chronic is very important because some 200 million people worldwide and 3.2 million people in the U.S. are chronically infected with HCV and are at risk for progression to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis C associated liver disease is the most common ...
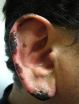
LOS ANGELES—(June 20, 2011)—Doctors warned of a potential public health epidemic in a recent report on patients in Los Angeles and New York who developed serious skin reactions after smoking or snorting cocaine believed to be contaminated with a veterinary medication drug dealers are using to dilute, or "cut," up to 70% of the cocaine in the U.S.
The report, published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, said six patients developed purple-colored patches of necrotic skin on their ears, nose, cheeks and other parts of their body and, in some instances, ...
Solartex Sun Gear, Inc., a leader in sun protective clothing in the United States, is introducing its newest line that provides the maximum (50+) SPF/UPF in sun protection. Designed in Australia, these colorful rash shirts, swimsuits and hats come in a full range of sizes from 0 to 8xl, offering something for everyone from the newborn to the plus-sized adult.
Since its founding in 1998, Solartex has specialized in locating, importing, manufacturing, and retailing sun protective UV clothing to U.S. and international consumers. It is now designing and manufacturing private ...