(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C. — Neuroscientists at Georgetown University Medical Center (GUMC) have defined, for the first time, three different processing stages that a human brain needs to identify sounds such as speech — and discovered that they are the same as ones identified in non-human primates.
In the June 22 issue of the Journal of Neuroscience, the researchers say their discovery — made possible with the help of 13 human volunteers who spent time in a functional MRI machine — could potentially offer important insights into what can go wrong when someone has difficulty speaking, which involves hearing voice-generated sounds, or understanding the speech of others.
But more than that, the findings help shed light on the complex, and extraordinarily elegant, workings of the "auditory" human brain, says Josef Rauschecker, PhD, a professor in the departments of physiology/ biophysics and neuroscience and a member of the Georgetown Institute for Cognitive and Computational Sciences at GUMC.
"This is the first time we have been able to identify three discrete brain areas that help people recognize and understand the sounds they are hearing," says Rauschecker. "These sounds, such as speech, are vitally important to humans, and it is critical that we understand how they are processed in the human brain."
Rauschecker and his colleagues at Georgetown have been instrumental in building a unified theory about how the human brain processes speech and language. They have shown that both human and non-human primates process speech along two parallel pathways, each of which run from lower to higher functioning neural regions.
These pathways are dubbed the "what" and "where" streams and are roughly analogous to how the brain processes sight, but in different regions. The "where" stream localizes sound and the "what" pathway identifies the sound.
Both pathways begin with the processing of signals in the auditory cortex, located inside a deep fissure on the side of the brain underneath the temples - the so-called "temporal lobe." Information processed by the "what" pathway then flows forward along the outside of the temporal lobe, and the job of that pathway is to recognize complex auditory signals, which include communication sounds and their meaning (semantics). The "where" pathway is mostly in the parietal lobe, above the temporal lobe, and it processes spatial aspects of a sound — its location and its motion in space — but is also involved in providing feedback during the act of speaking.
Auditory perception - the processing and interpretation of sound information - is tied to anatomical structures; signals move from lower to higher brain regions, Rauschecker says. "Sound as a whole enters the ear canal and is first broken down into single tone frequencies, then higher-up neurons respond only to more complex sounds, including those used in the recognition of speech, as the neural representation of the sound moves through the various brain regions," he says.
In this study, Rauschecker and his colleagues — computational neuroscientist Maximilian Riesenhuber, Ph.D., and Mark Chevillet, a student in the Interdisciplinary Program in Neuroscience — identified the three distinct areas in the "what" pathway in humans that had been seen in non-human primates. Only two had been recognized before in previous human studies.
The first, and most primary, is the "core" which analyzes tones at the basic level of simple frequencies. The second area, the "belt", wraps around the core, and integrates several tones, "like buzz sounds," that lie close to each other, Rauschecker says. The third area, the "parabelt," responds to speech sounds such as vowels, which are essentially complex bursts of multiple frequencies.
Rauschecker is fascinated by the fact that although speech and language are considered to be uniquely human abilities, the emerging picture of brain processing of language suggests "in evolution, language must have emerged from neural mechanisms at least partially available in animals," he says. "There appears to be a conservation of certain processing pathways through evolution in humans and nonhuman primates."
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by a National Science Foundation grant awarded to Rauschecker and Riesenhuber.
About Georgetown University Medical Center
Georgetown University Medical Center is an internationally recognized academic medical center with a three-part mission of research, teaching and patient care (through MedStar Health). GUMC's mission is carried out with a strong emphasis on public service and a dedication to the Catholic, Jesuit principle of cura personalis -- or "care of the whole person." The Medical Center includes the School of Medicine and the School of Nursing & Health Studies, both nationally ranked; Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, designated as a comprehensive cancer center by the National Cancer Institute; and the Biomedical Graduate Research Organization (BGRO), which accounts for the majority of externally funded research at GUMC including a Clinical Translation and Science Award from the National Institutes of Health. In fiscal year 2009-2010, GUMC accounted for nearly 80 percent of Georgetown University's extramural research funding.
END
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Fat substitutes used in popular snack foods to help people control weight may have the opposite effect, according to Purdue University research.
"These substitutes are meant to mimic the taste of fat in foods that are normally high in fat while providing a lower number of calories, but they may end up confusing the body," said Susan E. Swithers, professor of psychological sciences. "We didn't study this in people, but we found that when rats consumed a fat substitute, learned signals that could help control food intake were disrupted, and the rats ...
A recent report by the Social Security and Medicare Board of Trustees gave some devastating news to existing and future social security benefit recipients. Projections show that Social Security Trust Funds will reach complete depletion in 2036, leaving eligible Social Security Disability recipients without any benefits to receive. While the report was expected to deliver bad news, the projections were even worse than what most experts anticipated.
The rapidly depleting Social Security Disability Trust Funds funds are the casualty of fiscal irresponsibility in Washington; ...
VIDEO:
Dr. George W. Holden, a psychologist and parenting expert at Southern Methodist University, Dallas, discusses a new corporal punishment study based on actual audio recordings.
Believed to be the first study...
Click here for more information.
In one recording, a mom spanks her 3-year-old 11 times for fighting with his sister. In another, a mom slaps her son for turning the page of a book while she reads to him. In still another, a mom spanks her 5-year-old when he ...
Saxo Bank and Bjarne Riis, owner and manager of Riis Cycling A/S, have announced that Saxo Bank, a sponsor for the cycling team since 2008, will remain co-title sponsor in 2012 with SunGard, one of the world's leading software and technology services companies.
Bjarne Riis said: "It is indeed a great day for our cycling team. Saxo Bank is an extremely professional company, so I am proud that Saxo Bank has a strong faith in our work and continues to see the commercial benefits in sponsoring our team."
"Since 2008 we have shown in both words and actions ...
NEW YORK (June 23, 2011) -- The drug telaprevir (Incivek) provides a dramatic improvement in the treatment of the most common form of hepatitis C infection, says an international team of investigators led by Dr. Ira M. Jacobson of NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center.
Their study, published in today's edition of the New England Journal of Medicine, led to approval of the agent for patient use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on May 23.
Results of the ADVANCE trial showed that telaprevir combined with standard therapy (pegylated-interferon ...
TORONTO, ON – A new study by psychologists at the University of Toronto and Tufts University shows that a woman can more accurately identify a man's sexual orientation when looking at his face, when she is closest to her time of peak ovulation. Further, having romantic thoughts or a mating goal heightens a woman's ability to discriminate between straight and gay men.
"This effect is not apparent when a woman is judging another female's orientation," says Professor Nicholas Rule of the Department of Psychology at the University of Toronto, lead author of a new study published ...
Burton has been a staple on the British high street for well over 100 years, with a heritage steeped in history, with this in mind, the brand is proud to announce the launch of its new Montague Burton Collection which draws on its history, looks at its archives for inspiration; and ultimately creates a capsule wardrobe for autumn winter that is proud to be British.
The range (named after Montague Burton, the founding father of the company in 1904) builds on the resurgence of national pride as the UK approaches the 2012 Olympics. With a nation united there has never been ...
In a new article published in the journal Molecular Neurodegeneration, researchers at the University of Missouri School of Medicine take some of the first steps toward unraveling the molecular dysfunction that occurs when proteins are exposed to environmental toxins. Their discovery helps further explain recent NIH findings that demonstrate the link between Parkinson's disease and two particular pesticides – rotenone and paraquat.
"Fewer than 5 percent of Parkinson's cases are attributed to genetics, but more than 95 percent of cases have unknown causes," said Zezong ...
Burton has announced the creation of its new 24 Hour Suit. New technology has been developed to ensure the 24 Hour Suit range keeps its wearer looking sharp 24/7.
These suits are all stain repellent, crease resistant and also shape retaining meaning that whatever life throws at the wearer, they will be able to keep calm, look good and carry on.
The blazers are all fitted with a selection of mesh material as part of the lining in the under arms to ease movement and have been carefully designed to create a comfortable and wearable tailored look. There is a secret 'security' ...
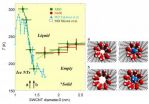
COLLEGE PARK, MD (June 22, 2011)—Water and ice may not be among the first things that come to mind when you think about single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), but a Japan-based research team hoping to get a clearer understanding of the phase behavior of confined water in the cylindrical pores of carbon nanotubes zeroed in on confined water's properties and made some surprising discoveries.
The team, from Tokyo Metropolitan University, Nagoya University, Japan Science and Technology Agency, and National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, describes ...