(Press-News.org) (Boston) – A new study conducted by a team of researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) sheds light on a possible new approach to treat the bone marrow disease known as myelofibrosis by inhibiting an enzyme that connects extracellular fibers. The study, published online in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, was conducted under the direction of Katya Ravid, PhD, professor of medicine and biochemistry and director of the Evans Center for Interdisciplinary Biomedical Research at BUSM.
Myelofibroisis, which currently affects between 16,000 and 18,500 Americans, occurs when bone marrow is replaced by scar tissue, resulting in a disruption in blood cell production.
Blood cells originate from precursor stem cells, which typically reside in the bone marrow. Red and white blood cells are categorized as cells with a myeloid lineage, which also includes megakaryocytic cells that give rise to blood-clotting platelets. An excess proliferation of myeloid cells causes a surplus production of fibers outside of the cell, which forms a dense matrix within the bone marrow that disrupts the formation of these blood cells.
Previous research has shown that the enzyme lysyl oxidase links and stabilizes the extracellular fibers, but as of yet, a treatment aimed at inhibiting the formation of these fibers has not been successful. Ravid's team demonstrated that inhibiting that enzyme using pharmacologic agents resulted in a significant decrease in the burden of myelofibrosis.
The team's investigation, which used a mouse model with a dense matrix, showed that while the megakaryotic cells that proliferate express high levels of lysyl oxidase, the normal, mature megakaryotic cells express scarce levels of the enzyme. The group also determined that lysyl oxidase boosts the proliferation of these cells, and also identified the mechanism that causes that to happen.
"This study uncovers a potential new approach aimed at controlling and treating myelofibrosis," said senior author Ravid. "This discovery will allow additional research in the field of leukemia to follow a new avenue with the potential of finding new treatments against the disease."
INFORMATION:
Other BUSM researchers involved with this study include Alexia Eliades, PhD, Nicholas Papadantonakis, MD, Ajoy Bhupatiraj, PhD, Kelly Burridge , PhD, Hillary Johnston-Cox, BA, Hector Lucero, PhD and Philip Trackman, PhD. Anna Rita Migliaccio, PhD, from Mt. Sinai School of Medicine and John Crispino, PhD, from Northwestern University Medical School, also contributed to the study. Funding for this study was provided by the National Institutes of Health's National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute.
About Boston University School of Medicine
Originally established in 1848 as the New England Female Medical College, and incorporated into Boston University in 1873, Boston University School of Medicine today is a leading academic medical center with an enrollment of more than 700 medical students and more than 800 masters and PhD students. Its 1,246 full and part-time faculty members generated more than $335 million in funding in the 2009-2010 academic year for research in amyloidosis, arthritis, cardiovascular disease, cancer, infectious disease, pulmonary disease and dermatology among others. The School is affiliated with Boston Medical Center, its principal teaching hospital, the Boston and Bedford Veterans Administration Medical Centers and 16 other regional hospitals as well as the Boston HealthNet.
END
RICHLAND, Wash. – A new computer model of blue-green algae can predict which of the organism's genes are central to capturing energy from sunlight and other critical processes.
Described in a paper published in the journal Molecular BioSystems, the model could advance efforts to produce biofuel and other energy sources from blue-green algae, known as cyanobacteria. Researchers from the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Washington University in St. Louis and Purdue University developed the model, which was made for the single-celled marine ...
A Brooklyn purveyor of unlocked cell phones is celebrating the arrival of summer with the latest releases from Nokia, Samsung, HTC, and more. In the spirit of Spring Break, Cellification.com is offering price breaks of ten percent or more on select phones and models on a first-come/first-served basis for a limited time only.
The sale is also being held to honor the upcoming one-year anniversary of an FCC ruling that finds unlocked cell phones to be entirely legal.
It was only last year that the FCC released their revised rules governing a number of intellectual property ...
If the obvious reasons for avoiding recreational drug use aren't off-putting enough, physicians have yet another detrimental consequence to add to the list – crusty, purplish areas of dead skin that are extremely painful and can open the door to nasty infections.
The condition is called purpura. Typical causes include a range of rare disorders, but it is also associated with the use of cocaine. Not just any cocaine, though: Physicians, researchers and health officials believe cocaine contaminated with a de-worming drug commonly used by veterinarians is the culprit. ...
DALLAS – June 23, 2011 – UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers have identified compounds that appear to inhibit a signaling pathway in Huntington's disease, a finding that may eventually lead to a potential drug therapy to help slow the progression of degenerative nerve disorders.
"Our studies have uncovered a new therapeutic target for Huntington's disease treatment and possibly for other neurodegenerative diseases," said Dr. Ilya Bezprozvanny, professor of physiology and senior author of the study, published in today's issue of Chemistry and Biology. "In addition, ...
Children love to succeed and do well in school. Watch a child being praised, and you will see his or her face light up with pride. Have you noticed when children do good and receive positive feedback, they want to continue to do good? Unfortunately the opposite is true as well. If young children are not consistently reminded of their manners, they often tend to get in trouble, which can lead to feelings of embarrassment and sadness. In a recent survey, more than 70 percent of U.S. adults said they thought people are ruder now than they were 20 years ago. Guaranteed Success ...
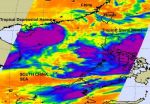
The Northwestern Pacific Ocean is active with two tropical cyclones today, Tropical Storm Meari near the Philippines, and Tropical Depression Haima moving over China and now toward Vietnam. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the region on June 22 and captured an infrared image of both storms in one image.
One of the instruments onboard NASA's Aqua satellite is the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS). AIRS captures cloud top temperatures in tropical cyclones to determine the strength of convection and thunderstorms. The strongest thunderstorms have cloud tops with icy cold ...
LOS ALAMOS, New Mexico, June 23, 2011—Two papers in this week's issue of Science report the first oxygen and nitrogen isotopic measurements of the Sun, demonstrating that they are verydifferent from the same elements on Earth. These results were the top two priorities of NASA's Genesis mission, which was the first spacecraft to return from beyond the Moon, crashing in the Utah desert in 2004 after its parachute failed to deploy during re-entry.
Most of the Genesis payload consisted of fragile solar-wind collectors, which had been exposed to the solar particles over a ...
Boston, MA—Researchers have discovered a new mechanism for the origin of Barrett's esophagus, an intestine-like growth in the esophagus that is triggered by chronic acid reflux and often progresses to esophageal cancer. Studying mice, the researchers found that Barrett's esophagus arises not from mutant cells in the esophagus but rather a small group of previously overlooked cells present in all adults that can rapidly expand to cancer precursors when the normal esophagus is damaged by acid.
This research will be published online in the June 24th issue of Cell.
Decades ...
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who use inhaled corticosteroids to improve breathing for more than six months have a 27 percent increased risk of bone fractures, new Johns Hopkins-led research suggests.
Because the research subjects were mostly men age 60 and older, the findings raise perhaps more troubling questions about the medication's effects on women with COPD, a group already at a significantly higher risk than men for fractures.
"There are millions of COPD patients who use long-term inhaled corticosteroids in the United States and ...
Suburban Hobby Farmer asked us what was the most important lesson children have learned in a garden in my classes. My answer comes from our walks through the forest, an empty lot, a patch of earth on a farm, a small tract of woodland while wearing a pair of Daddy's socks. At the end of these walks the children plant the socks into a flat full of potting soil and a magic journey full of promise and faith begins. From here on out every child who plants their daddy's socks after walking through a forest with the socks over their tennis shoes is intimately connected to any ...