(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – Researchers may have discovered one reason that African Americans are at increased risk for heart attacks and other cardiovascular events.
According to a new study published online in the journal Radiology, African Americans have increased levels of non-calcified plaque, which consists of buildups of soft deposits deep in the walls of the arteries that are not detected by some cardiac tests. Non-calcified plaque is more vulnerable to rupturing and causing a blood clot, which could lead to a heart attack or other cardiovascular event.
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, African American adults are more likely to be diagnosed with coronary heart disease and are at greater risk of death from heart disease than white adults. In 2007, African American men were 30 percent more likely than non-Hispanic white men to die from heart disease.
"For a long time, physicians have searched for explanations as to why African Americans have higher rates of heart disease and higher cardiac death rates, but less coronary artery calcium than Caucasians," said U. Joseph Schoepf, M.D., professor of radiology and medicine and director of cardiovascular imaging at Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston. "We show that one possible explanation for the discrepancy may be found in the higher rate of less stable, non-calcified plaque in the heart vessels of African Americans."
Calcium scoring with CT is a common screening tool for patients at risk for cardiovascular disease, because increased levels of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries generally correlates with a greater risk of heart attack or other cardiovascular event. However, calcium scoring does not detect non-calcified plaque.
For the study, researchers compared 301 patients who underwent both calcium scoring with CT and contrast-enhanced coronary CT angiography (cCTA). cCTA provides a more comprehensive picture of the arteries, including the presence of non-calcified and mixed plaques.
The study group comprised 50 percent each of African American and white patients, 33 percent of whom were male (mean age 55).
Calcium scoring revealed that calcified plaque was much more prevalent in the coronary arteries of white patients than in the African Americans (45 percent, versus 26 percent). The cCTA revealed that, compared with the white patients, many more African American patients had non-calcified plaque (64 percent, versus 41 percent), and in greater amounts. The median volume of non-calcified plaque among the African American patients was 2.2 milliliters (mL), compared with 1.4 mL among white patients.
Based on these results, the researchers suggest that the value of calcium scoring as a screening tool for African Americans should be reexamined.
"The results of coronary artery calcium scoring studies are to be treated with caution in African Americans, because they may not reflect the true extent of cardiovascular disease," Dr. Schoepf said.
While cCTA does expose patients to ionizing radiation, according to Dr. Schoepf, the effective dose of this procedure has been considerably reduced over the past few years, making it a viable screening option, if other prerequisites of a successful screening test are also met.
"For African American patients, coronary CT angiography may be a more appropriate screening tool for cardiovascular risk," he said.
###
"Coronary Atherosclerosis in African American and White Patients with Acute Chest Pain: Characterization with Coronary CT Angiography." Collaborating with Dr. Schoepf were John W. Nance Jr., M.D., Fabian Bamberg, M.D., M.P.H., Doo Kyoung Kang, M.D., J. Michael Barraza, Jr., B.S., Joseph A. Abro, M.A., Gorka Bastarrika, M.D., Ph.D., Gary F. Headden, M.D., Philip Costello, M.D., and Christian Thilo, M.D.
Radiology is edited by Herbert Y. Kressel, M.D., Harvard Medical School, Boston, Mass., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (http://radiology.rsna.org/)
RSNA is an association of more than 46,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists committed to excellence in patient care through education and research. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on CT angiography, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
CT angiography improves detection of heart disease in African-Americans
2011-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds mammography screening reduces breast cancer mortality
2011-06-28
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Breast cancer screening with mammography results in a significant reduction in breast cancer mortality, according to long-term follow-up results of a large-scale Swedish trial. The results are published online in the journal Radiology.
"Mammographic screening confers a substantial relative and absolute reduction in breast cancer mortality risk in the long-term," said Stephen W. Duffy, M.Sc., professor of cancer screening at Queen Mary, University of London. "For every 1,000 to 1,500 mammograms, one breast cancer death is prevented."
The Swedish Two-County ...
Patients treated with sunitinib and sorafenib respond to flu vaccine
2011-06-28
PHILADELPHIA — Patients treated with sunitinib and sorafenib responded to the flu vaccine, which suggests the agents do not damage the immune system as much as previously feared, according to a study in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Keith Flaherty, M.D., director of developmental therapeutics at the Massachusetts General Hospital and a senior editor of Clinical Cancer Research, said the findings have broad implications beyond questions of patient management.
"The damage that chemotherapy does to normal, healthy ...
New study finds rise in global malaria R&D funds leads to largest ever pipeline of new products
2011-06-28
This press release is available in French.LONDON (28 JUNE 2011)—A new analysis of progress in the global fight against malaria finds a four-fold increase in annual funding for malaria research and development (R&D) in just 16 years—increasing from US$121 million in 1993 to US$612 million in 2009, with a particularly rapid increase since 2004. The funding has generated the strongest pipeline of malaria control and prevention products in history.
The report warns, however, that even a small decline in annual funding could jeopardize this pipeline, derail development of ...
Alameda Services Receives National Healthcare Association (NHA) Approval; Prepares Students for Certified Electronic Health Record Specialists (CEHRS) Exam
2011-06-28
Alameda Services, a Health Information Technology (HIT) consulting and training organization specializing in workforce development, has been recognized as a training affiliate for the CEHRS Exam, administered by the National Healthcare Association (NHA). As an affiliate, Alameda Services is able to prepare students for the rigorous national certification as part of its program. Students and healthcare providers often report a higher level of recruitment, retention and placement among those who obtain the electronic health record (EHR) certification. More information about ...
Study shows long-term benefits of breast screening
2011-06-28
Results from the longest running breast screening trial show that screening with mammography reduces the number of deaths from breast cancer.
The study*, by researchers at Queen Mary, University of London, shows that the number of deaths that are prevented goes up year after year.
The results are new evidence of the long-term benefits of regular breast screening.
Senior author, Professor Stephen Duffy explained: "Breast cancer can take many years to develop so to tell if screening is effective, we need to see how women fair in the long-term.
"In this study, we've ...
Team approach reduces urinary tract infections in rehab patients
2011-06-28
Baltimore, Maryland, June 28, 2011 – Nurses, occupational and physical therapists, case managers and education staff, all working together at a 300-bed Nebraska rehabilitation hospital, have successfully implemented a team approach to dramatically reduce infections from urinary catheters, the most prevalent type of infection acquired in healthcare settings.
The interdisciplinary team at Madonna Rehabilitation Hospital in Lincoln, one of the largest free-standing rehabilitation hospitals in the country, reduced catheter associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) by 89 ...
triCerat Takes On IT Decisions 2011 in London
2011-06-28
triCerat is excited to announce its debut at IT decisions in London, June 28-29 at the QEII Conference Centre in Westminster, London.
IT decisions addresses the current, significant developments affecting IT systems in the real world. The two-day program includes sessions on virtualization, storage, cloud computing, software-as-a-service (SaaS), mobile and wireless accessibility, security, green IT, and more. The 30-minute sessions and roundtable discussions were designed with time-efficiency in mind for the busy IT executive. Keynote speaker Tim Jennings, Research Fellow ...
Intensive, hands-on effort reduces bloodstream infections in critically ill patients
2011-06-28
Baltimore, Maryland, June 28, 2011 – Nurses on a surgical intensive care unit (SICU) at a large academic medical center cut bloodstream infections to zero and saved more than $200,000 during a six-month period.
The University of Maryland Medical Center SICU sustained a rate of zero central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs) for a 25-week period, eliminating 14 CLABSIs and saving 2-3 lives when compared to the same time period in the previous year, according to results of an intensive, six-month nursing initiative presented today at the 38th Annual Educational ...
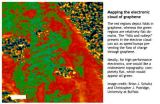
Researchers image graphene electron clouds, revealing how folds can harm conductivity
2011-06-28
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- A research team led by University at Buffalo chemists has used synchrotron light sources to observe the electron clouds on the surface of graphene, producing a series of images that reveal how folds and ripples in the remarkable material can harm its conductivity.
The research, scheduled to appear June 28 in Nature Communications, was conducted by UB, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the Molecular Foundry at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), and SEMATECH, a global consortium of semiconductor manufacturers.
Graphene, ...
Gothic Cabinet Craft Releases iPhone App for Furniture Shoppers
2011-06-28
Gothic Cabinet Craft (http://www.gothiccabinetcraft.com), one of the largest manufacturers and retailers of real wood furniture in the North Eastern United States, today announces the release of their new iPhone app for furniture shoppers, ShopGothic. A free app, ShopGothic was designed to aid in the furniture shopping process of Gothic Cabinet Craft's customers.
"No more guessing what color will best match existing furniture," says Aristidis Zaharopoulos, President of Gothic Cabinet Craft, Inc. "We found that to be a problem for many of our customers. ...