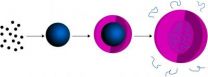
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have designed a multiple-compartment gel capsule that could be used to simultaneously deliver drugs of different types. The researchers used a simple "one-pot" method to prepare the hydrogel capsules, which measure less than one micron.
The capsule's structure -- hollow except for polymer chains tethered to the interior of the shell -- provides spatially-segregated compartments that make it a good candidate for multi-drug encapsulation and release strategies. The microcapsule could be used to simultaneously deliver distinct drugs by filling the core of the capsule with hydrophilic drugs and trapping hydrophobic drugs within nanoparticles assembled from the polymer chains.
"We have demonstrated that we can make a fairly complex multi-component delivery vehicle using a relatively straightforward and scalable synthesis," said L. Andrew Lyon, a professor in the School of Chemistry and Biochemistry at Georgia Tech. "Additional research will need to be conducted to determine how they would best be loaded, delivered and triggered to release the drugs."
Details of the microcapsule synthesis procedure were published online on July 5, 2011 in the journal Macromolecular Rapid Communications.
Lyon and Xiaobo Hu, a former visiting scholar at Georgia Tech, created the microcapsules. As a graduate student at the Research Institute of Materials Science at the South China University of Technology, Hu is co-advised by Lyon and Zhen Tong of the South China University of Technology. Funding for this research was provided to Hu by the China Scholarship Council.
The researchers began the two-step, one-pot synthesis procedure by forming core particles from a temperature-sensitive polymer called poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). To create a dissolvable core, they formed polymer chains from the particles without a cross-linking agent. This resulted in an aggregated collection of polymer chains with temperature-dependent stability.
"The polymer comprising the core particles is known for undergoing chain transfer reactions that add cross-linking points without the presence of a cross-linking agent, so we initiated the polymerization using a redox method with ammonium persulfate and N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine. This ensured those side chain transfer reactions did not occur, which allowed us to create a truly dissolvable core," explained Lyon.
For the second step in the procedure, Lyon and Hu added a cross-linking agent to a polymer called poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide) to create a shell around the aggregated polymer chains. The researchers conducted this step under conditions that would allow any core-associated polymer chains that interacted with the shell during synthesis to undergo chain transfer and become grafted to the interior of the shell.
Cooling the microcapsule exploited the temperature-sensitivities of the polymers. The shell swelled with water and expanded to its stable size, while the free-floating polymer chains in the center of the capsule diffused out of the core, leaving behind an empty space. Any chains that stuck to the shell during its synthesis remained. Because the chains control the interaction between the particles they store and their surroundings, the tethered chains can act as hydrophobic drug carriers.
Compared to delivering a single drug, co-delivery of multiple drugs has several potential advantages, including synergistic effects, suppressed drug resistance and the ability to tune the relative dosage of various drugs. The future optimization of these microcapsules may allow simultaneous delivery of distinct classes of drugs for the treatment of diseases like cancer, which is often treated using combination chemotherapy.
INFORMATION:
Unique gel capsule structure enables co-delivery of different types of drugs
2011-07-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bigger than football: Study shows sports can help communities recover from disaster
2011-07-07
Research from North Carolina State University shows that organized sports can be a powerful tool for helping to rebuild communities in the wake of disasters. The research focused specifically on the role of professional football in the wake of Hurricane Katrina.
"Sports, and by extension sports media, can be a powerful force for good. It can bring people together. It can provide hope, even in the midst of great destruction," says Dr. Ken Zagacki, co-author of a paper describing the research and a professor of communication at NC State. "But we have to be careful that ...
SEO Specialist Release Comprehensive SEO Guide
2011-07-07
SEO Specialist hear many small and medium sized companies complain about transparency in the online marketing industry. Not every SEO company reveal what's included in the services to make websites be found in top of Google, Yahoo and Bing.
In an attempt to reveal what's included in SEO Specialist's services, a comprehensive guide to search engine optimisation (SEO) was released.
The popular guide to SEO covers all areas of website optimisation and it is divided into four chapters;
- SEO analysis: Discuss how to analyse a website and it's competitors.
- On-Page ...
Transcription factor is potential target for liver cancer treatment
2011-07-07
AUGUSTA, Ga. – Altering the body's metabolism could be an effective treatment for deadly liver cancer, researchers report.
The finding that inhibiting heat shock transcription factor 1, or HSF1, prevents liver cancer in mice also is another wake-up call that a low-fat, healthy diet is an effective cancer deterrent, said Dr. Demetrius Moskophidis, Cancer Virologist/Immunologist at Georgia Health Sciences University. HSF1 and its target genes are important to metabolism regulation.
"The principle that we demonstrated is that if we change the metabolism, we can interfere ...
Rewards Flow At River Nile Casino with 109.01% in May Payouts
2011-07-07
River Nile Casino, a top online casino has reported an increase in payouts for the month of May, 2011. Payouts rose to 109.01% on Poker games. This ultimately means that more players won more during this period.
Games at the casino are divided into four main categories, these being Table Games, Poker Games, Slot Games and Unique Games. Each category is monitored and analysed individually and reports are generated on each category for the casino by an independent auditing association. Once the reports are generated, the casino makes these public for all users to view ...
Experiment aboard shuttle Atlantis will test novel therapy to build bone during space travel
2011-07-07
BOSTON – Astronauts lose a significant amount of bone mass during space travel and with long duration flights there is concern that this bone loss could lead to an increased risk of fractures. When the final mission of NASA's 30-year Space Shuttle program is launched on July 8, an animal experiment to test a novel therapy to increase bone mass will be on board.
Led by a consortium of scientists from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), Amgen, Inc., UCB, BioServe Space Technologies and the University of North Carolina, and funded by NASA's Ames Research Center, ...
Researchers identify early biomarker for future atopy in asymptomatic children
2011-07-07
The signs of atopy may be present long before symptoms begin, even in month-old babies, according to a new research study from Denmark. The study found that the level of urinary eosinophil protein-X (u-EPX), a marker of inflammatory cells, in newborn babies was linked to higher risk of allergic sensitization, nasal eosinophilia and eczema at six years.
The study appeared online in advance of the print publication of the American Thoracic Society's American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
"We asked whether the allergic disease process may be active ...
Maple Casino Tops 100% in May Payouts
2011-07-07
Online Casino, Maple Casino has just reported paying out 100.15% during the month of May for Table Games. There are four main divisions in the casino gaming, and the other three also reported payouts in the high nineties.
On a monthly basis, the casino payouts are independently audited and a report is compiled by a separate organization. This report has just been released by the casino, and payouts for May were running high!
Casino Manager, Charlotte Jackson, said, "We are very proud to announce that our Table Game Payouts for May have peaked at 100.15%. This ...
With a simple coating, nanowires show a dramatic increase in efficiency and sensitivity
2011-07-07
Cambridge, Mass. – July 6, 2011 – By applying a coating to individual silicon nanowires, researchers at Harvard and Berkeley have significantly improved the materials' efficiency and sensitivity.
The findings, published in the May 20, 2011, issue of Nano Letters, suggest that the coated wires hold promise for photodetectors and energy harvesting technologies like solar cells.
Due to a large surface-to-volume ratio, nanowires typically suffer from a high surface recombination rate, meaning that photogenerated charges recombine rather than being collected at the terminals. ...
MadCap Software Launches Feedback Server 4.0 to Enhance Community-Based Content and Collaboration Between Technical Authors and End-Users
2011-07-07
MadCap Software, Inc. (http://www.madcapsoftware.com), the leader in multi-channel content authoring and a showcase company for Microsoft Visual Studio and Microsoft XPS, today announced that MadCap Feedback Server 4.0 is now available.
MadCap Feedback Server 4.0 (http://www.madcapsoftware.com/products/feedback/overview.aspx#introduction) is a server-based feedback system for content development teams that provides Web 2.0 features--such as blog-style comments and topic rating--to capture readers' insights and opinions on content such as knowledge bases, online Help, ...
The best hospitals are run by physicians
2011-07-07
Top-performing hospitals are typically ones headed by a medical doctor rather than a manager. That is the finding from a new study of what makes a good hospital.
The research, to be published in the elite journal Social Science and Medicine, is the first of its kind. Its conclusions run counter to a modern trend across the western world to put generally trained managers -- not those with a medical degree -- at the helm of hospitals. This trend has been questioned, particularly by the Darzi Report, which was commissioned by the U.K. National Health Service, but until ...