8-question survey can help predict post-traumatic stress disorder
2011-07-19
(Press-News.org) A simple eight-question survey administered soon after injury can help predict which of the 30 million Americans seeking hospital treatment for injuries each year may develop depression or post-traumatic stress, report Therese S. Richmond, PhD, CRNP, associate professor at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, and her colleagues in General Hospital Psychiatry.
"Depression and PTSD exert a significant, independent, and persistent effect on general health, work status, somatic symptoms, adjustment to illness, and function after injury," the authors wrote, also emphasizing that even minor injuries can lead to traumatic stress responses.
The findings allow healthcare providers to identify patients at highest risk for developing these disorders and to target appropriate resources to this vulnerable group.
This screening tool – reportedly one of the first of its kind for adults in the U.S. -- could have a great impact on the judicious allocation of costly mental health resources.
Using an eight-question survey, all injured patients can be rapidly assessed for risk in the hospital. Healthcare providers can then provide patients classed as high-risk for developing depression or PTSD with information about symptoms to look for and advise them to contact their primary care provider should symptoms surface. This intervention can facilitate early diagnosis of these disabling disorders.
The study reported nearly 100 percent accuracy in negative results. Only five percent of injured patients who tested negative for risk of depression on the screening survey developed depression and no patients who tested negative for PTSD risk developed PTSD. At the same time, not all patients who screen positive will develop these disorders. The researchers do not suggest that all patients who screen positive receive mental health services, but rather that this finding prompt systematic provision of information and additional follow-up.
The authors caution that while the findings of this initial study are most promising, they need to be replicated in an independent sample.
INFORMATION:
With Dr. Richmond, the study authors are: Josef Ruzek, PhD; Theimann Ackerson, MSSW; Douglas J. Wiebe, PhD; Flaura Winston, MD, PhD; Nancy Kassam-Adams, PhD.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-07-19
In a study published recently in the journal Science Signaling Van Andel Research Institute (VARI) scientists demonstrate on the molecular level how the anti-malaria drug chloroquine represses inflammation, which may provide a blueprint for new strategies for treating inflammation and a multitude of autoimmune diseases such as arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and certain cancers.
Chloroquine is a widely used anti-malaria drug that inhibits the growth of parasites. For decades, chloroquine and its derivative amodiaquine have also been used as anti-inflammation drugs to treat ...
2011-07-19
Business users take advantage of trial software so they can understand exactly what they are purchasing, but they still have to buy support plans on blind faith. One company is changing that. MadCap Software, Inc. (http://www.madcapsoftware.com), the leader in multi-channel content authoring and a showcase company for Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT) Visual Studio and Microsoft XPS, today announced that every 30-day free trial version of its technical communications software now also comes with a 30-day free trial of MadCap's Gold Level technical support. Gold Level support during ...
2011-07-19
Research published recently in PLoS One delivers new insight about rapid toxin evolution in venomous snakes: pitvipers such as rattlesnakes may be engaged in an arms race with opossums, a group of snake-eating American marsupials. Although some mammals have long been known to eat venomous snakes, this fact has not been factored into previous explanations for the rapid evolution of snake venom. Instead, snake venom is usually seen as a feeding, or trophic, adaptation. But new molecular research on snake-eating opossums by researchers affiliated with the American Museum of ...
2011-07-19
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Quantum dots made from cadmium and selenium degrade in soil, unleashing toxic cadmium and selenium ions into their surroundings, a University at Buffalo study has found.
The research, accepted for publication in the journal Environmental Science and Technology, demonstrates the importance of learning more about how quantum dots -- and other nanomaterials -- interact with the environment after disposal, said Diana Aga, the chemistry professor who led the study.
Quantum dots are semiconductor nanocrystals with diameters of about 2 to 100 nanometers. ...
2011-07-19
Howard H. Collens, attorney at the probate and estate planning law firm of Galloway and Collens, PLLC, spoke at a professional training seminar on The Probate Process From Start to Finish for Paralegals, sponsored by the Institute for Paralegal Education (IPE).
The seminar, which took place on June 7, 2011, aimed to increase the understanding and effectiveness of paralegals, legal assistants and legal secretaries during the legal process which may be required after a person dies. Howard H. Collens spoke about topics related to the probate process including the ethical ...
2011-07-19
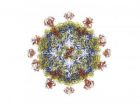
HOUSTON -- (July 18, 2011) -- Rice University scientists have defined the structure -- down to the atomic level -- of a virus that causes juvenile diarrhea. The research may help direct efforts to develop medications that block the virus before it becomes infectious.
The new paper by Professor Yizhi Jane Tao, postdoctoral researcher Jinhui Dong and their colleagues was published in today's online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Tao's Rice lab specializes in gleaning fine details of viral structures through X-ray crystallography and computer ...
2011-07-19
PRONicaragua recently announced the organization of the premier investment forum titled Nicaragua, Let's Grow Together!, which will showcase the country's sustainable growth in various economic sectors and its competitive advantages as an attractive destination for foreign direct investment (FDI).
The event will take place on August 16th and 17th in Managua, Nicaragua, and will focus on specialized sectors such as apparel, footwear, food processing and manufacturing, as well as world-class bilingual business process outsourcing (BPO) services. Participants will be coming ...
2011-07-19
The Westie Foundation of America (WFA) announced
today preliminary findings in two major studies involving the health of West Highland White Terriers also
known as Westies. Findings in these and other studies of Westies and other dogs
may hold answers for similar human conditions like Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). The studies are
jointly funded by the WFA and the AKC Canine Health Foundation (CHF).
In one study, researchers are looking at the role of a mucosal gene driving inflammation Canine IBD, a
chronic intestinal disorder that creates a bacterial-driven ...
2011-07-19
We all make numerous decisions everyday; unconsciously or consciously, sometimes doing it automatically with little effort or thinking and yet, at other times, we agonize for hours over another. Why do we make these choices – be it from deciding what to have for lunch or whether to say yes to that job offer halfway round the world. Sometimes we make choices on our own, and at other times, the choice is made for us. Exercising control (by making choices) is adaptive and now, a new study, which will be published in an upcoming issue of Psychological Science, a journal of ...
2011-07-19
What does a passionate founder of a domestic violence charity do when he wants to raise awareness and promote a daily fitness program? Rich Tola, Founder and Chairman of the yoga-inspired nonprofit, The Boulevard Zen Foundation, would say "We're going on a 30,000 mile fundraiser, visiting all 50 states in 100 days. That's 100 cities in 100 days, producing trivia-filled travelogue videos including fat burning workouts that are based on yoga". Ambitious? Yes. Impossible? "Certainly not," says the former Wall Streeter turned actor-filmmaker whose film, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 8-question survey can help predict post-traumatic stress disorder