(Press-News.org) Operations research models developed by a team at the Georgia Institute of Technology helped CARE International pick three locations worldwide to supply relief quickly to victims of earthquakes, floods, and other natural disasters, according to a paper in a journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS®).
"Pre-Positioning of Emergency Items for CARE International" is by Serhan Duran, currently at the Middle East Technical University in Ankara Turkey, and by Marco A. Gutierrez and Pinar Keskinocak of the H. Milton Stewart School of Industrial and Systems Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology. It appears in a special issue of the INFORMS journal Interfaces that is dedicated to the new, growing field of humanitarian logistics, which relies on industrial concepts like supply chain management to benefit the public sector.
The special issue is edited by Ozlem Ergun, Prof. Keskinocak, and Julie Swann, who are directors of the Georgia Tech Center for Health and Humanitarian Logistics.
A podcast interview with Professors Keskinocak and Swann is at http://www.scienceofbetter.org/podcast/swann.html and at www.scienceofbetter.org/podcast.
"The team's work not only gave us excellent recommendations regarding locations, inventory levels, and an expansion strategy for the network, but is also serving as the basis for funding proposals for the network," writes Rigoberto Giron, Associate Vice President, Strategic Initiatives and Supply Chain Management, CARE, in a post-script to the study. "By pre-positioning we expect to reduce response time from weeks to 48-72 hours, reduce procurement costs by buying in larger quantities, reduce freight costs by using transportation resources more efficiently and improve coordination with other responding organizations."
The models created by the team helped CARE International review 12 suggested international locations for opening new CARE warehouses and finalize three, in Dubai, Panama, and Cambodia. They also helped CARE determine that, although more is better, the benefits of multiple relief-supply warehouses declines after the number reaches three to four, thus helping CARE make maximum use of its limited resources.
In their research, the authors considered two kinds of capacity constraints: the number of warehouses to open and the inventory amounts to keep throughout the pre-positioning network. They ran their model for the option of opening between one and nine warehouses and for three levels of inventory – high, medium, and low.
With funding limited, they also helped make the critical decision which warehouse location would be most valuable to open first. They recommended that CARE open its first depot in the Middle East, expand to Central America, and then to Southeast Asia. Given a gradual roll-out plan, they were able to determine that once all three warehouses were operational, the supplies should be divided 35% in Dubai, 15% in Central America, and 50% in Cambodia.
If CARE obtains the resources to open a fourth warehouse in Africa and a fifth in Europe, the authors' sensitivity analysis shows that the relief organizational will be at its highest possible state of readiness to respond to unforeseen disasters anywhere in the world.
The authors were able to make recommendations by modeling the frequency, location, and magnitude of future demand based on historical data about earlier CARE relief operations.
One of the first applications of the research took place during the 2010 Haitian earthquake. With a million water purification kits and other supplies at depots, CARE was able to rapidly deliver water purification tablets to victims of the earthquake from its Panama warehouse.
The team's model is a mixed integer program that was run on a 4 x 900 MHz processor using ILOG OPL Studio with the CPLEX solver.
INFORMATION:
About INFORMS
The Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS®) is an international scientific society with 10,000 members, including Nobel Prize laureates, dedicated to applying scientific methods to help improve decision-making, management, and operations. Members of INFORMS work in business, government, and academia. They are represented in fields as diverse as airlines, health care, law enforcement, the military, financial engineering, and telecommunications. INFORMS serves the scientific and professional needs of operations research analysts, experts in analytics, consultants, scientists, students, educators, and managers, as well as their institutions, by publishing a variety of journals that describe the latest research in operations research. INFORMS Online (IOL) is at www.informs.org. Further information about operations research can be found at www.scienceofbetter.org.
END
COLUMBIA, Mo. ¬— While some members of Congress and others are trying to repeal the healthcare reform law that was passed in 2010, known as the "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act," medical providers have begun to implement requirements as the law slowly phases in over the next several years. For reform to be successful, one University of Missouri public health expert has determined that professional associations for psychologists and other medical providers need to be at the forefront of the planning stages, and that everyone, including providers and patients, ...
In the wake of the devastating Japanese tsunami, the 2010 Haitian earthquake, and the recent threat of pandemic flu, a new issue of the journal Interfaces: The INFORMS Journal on the Practice of Operations Research is dedicated to improving responses to disasters, health crises, and acute public issues, according to the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS®).
The Interfaces special issue on Humanitarian Logistics: Doing Good with Good O.R. is edited by Ozlem Ergun, Pinar Keskinocak, and Julie Swann, the directors of the Georgia Tech ...
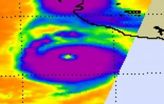
A new image and video of major Hurricane Dora were released today from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
Satellites provide a bird's eye view of a hurricane's eye, and NASA noticed Hurricane Dora's eye from several of them. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite provided forecasters with a clear view of a cloud-free eye in hurricane Dora as she strengthens near Category 5 status today. Meanwhile the GOES-11 satellite captured a movie of Dora's intensification over the last two days that clearly shows a developing eye.
The Atmospheric Infrared ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---The results of a study on candidates' use of Twitter in the 2010 midterm elections suggest that Republicans and Tea Party members used the social medium more effectively than their Democratic rivals.
The University of Michigan study, among the first to examine the Tea Party's social media strategies, also showed that analyzing Twitter activity can lead to good predictions of election winners.
Various social media tools have become a key part of campaign strategies in recent years. In 2010, nearly a quarter of online adults used social networks including ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The development of a new cell-culture system that mimics how specific nerve cell fibers in the brain become coated with protective myelin opens up new avenues of research about multiple sclerosis. Initial findings suggest that myelin regulates a key protein involved in sending long-distance signals.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by damage to the myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers. The cause remains unknown, and it is a chronic illness affecting the central nervous system that has no cure.
MS has long been considered ...
Rockville, Md. — Several reports indicate that prolonged viewing of mobile devices and other stereo 3D devices leads to visual discomfort, fatigue and even headaches. According to a new Journal of Vision study, the root cause may be the demand on our eyes to focus on the screen and simultaneously adjust to the distance of the content.
Scientifically referred to as vergence-accommodation, this conflict and its effect on viewers of stereo 3D displays are detailed in a recent Journal of Vision article, The Zone of Comfort: Predicting Visual Discomfort with Stereo Displays. ...
Stem cell researchers at UCLA have generated the first genome-wide mapping of a DNA modification called 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) in embryonic stem cells, and discovered that it is predominantly found in genes that are turned on, or active.
The finding by researchers with the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA may prove to be important in controlling diseases like cancer, where the regulation of certain genes plays a role in disease development.
"Any way you can control genes will be hugely important for human ...
Red may mean STOP or I LOVE YOU! A red splash on a toxic butterfly's wing screams DON'T EAT ME! In nature, one toxic butterfly species may mimic the wing pattern of another toxic species in the area. By using the same signal, they send a stronger message: DON'T EAT US!
Now several research teams that include Smithsonian scientists in Panama, have discovered that Heliconius butterflies mimic each other's red wing patterns through changes in the same gene.
Not only does this gene lead to the same red wing patterns in neighboring species, it also leads to a large variety ...
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (July 21, 2011) – A normal but concerning consequence of pregnancy is the fact that pregnant women are more susceptible to infection. University of Minnesota Medical School researchers have identified the underlying mechanisms for this physiologic immune suppression that may lead to new therapies to help ward off infections during pregnancy.
In pregnancy, immune system suppressing cells (called regulatory T cells) increase in number to protect the baby from attack by the mother's immune system. Because these cells are busy protecting the developing ...
A genetic study focusing on the Central American river turtle (Dermatemys mawii) recently turned up surprising results for a team of Smithsonian scientists involved in the conservation of this critically endangered species. Small tissue samples collected from 238 wild turtles at 15 different locations across their range in Southern Mexico, Belize and Guatemala revealed a "surprising lack" of genetic structure, the scientists write in a recent paper in the journal Conservation Genetics.
The turtles, which are entirely aquatic, represent populations from three different ...