(Press-News.org) In summer, more dishes like gazpacho –a cold soup containing raw vegetables, bread, olive oil and vinegar– are consumed. A new study has revealed that ingredients' vitamin C content as well as other organic acids is lower in the resulting mixture, meaning that it should be eaten immediately after preparation.
Is it true that cutting fruit and boiling vegetables cause vitamin loss? A new study has examined gazpacho, one of the most popular Spanish summer dishes, comparing the levels of vitamin C (ascorbic and dehydroascorbic acid) and other organic acids (citric, oxalic, fumaric, malic and glutamic) found in each of the ingredients separately before preparation and in the resulting gazpacho.
"We found that the gazpacho showed a lower ascorbic/dehydroascorbic acid ratio than the vegetables used to prepare it," explained Elena María Rodríguez, co-author of the study conducted by the Complutense University of Madrid and the University of La Laguna (Santa Cruz de Tenerife). She added: "This suggests that some of the vegetables' antioxidant capacity is lost."
Of the ingredients, peppers had the highest vitamin C content, followed by tomatoes, and then the gazpacho itself. In general, tomatoes and garlic contained the highest levels of organic acids, whereas cucumbers presented the lowest content. Garlic and onions had the highest concentrations of the main organic acids present, glutamic and citric, than the other vegetables.
The authors therefore recommend eating gazpacho as soon as it has been prepared, or "preserving it correctly so that the vegetables maintain their antioxidant characteristics."
A drink to beat the heat
Gazpacho is a natural source of vitamins (A, C and E), carbohydrates, phosphorus, iron, calcium, magnesium, manganese, zinc, copper, potassium and sodium. It also provides fibre and antioxidant substances such as lycopene, which gives tomatoes their red colouring, and carotenoids. Given its mineral salt content, it is considered to be isotonic as it prevents over-hydration during summer.
Although there are recipes for all tastes, gazpacho generally contains bread, olive oil, vinegar and raw vegetables (tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, onions and garlic). Given its low calorie content, it is usually served cold during the hot summer months.
INFORMATION:
References:
C.M. Verde Méndez, E.M. Rodríguez Rodríguez, C. Díaz Romero, M.C. Sánchez Mata, M.C. Matallana González y M.E. Torija Isasa. "Vitamin C and organic acid contents in Spanish ''Gazpacho'' soup related to the vegetables used for its elaboration process". CyTA – Journal of Food 9(1): 71, mayo de 2011.
Gazpacho ingredients lose vitamin C during preparation
2011-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New Law Changes North Carolina Workers' Compensation Benefits
2011-08-06
A truly horrible bill that would have significantly limited injured workers' rights was introduced into the North Carolina General Assembly in early 2011. Since then, the bill underwent major changes before it eventually became law. The legislation is still generally a negative change for injured workers, but it is now much more complicated and not quite as bad.
Who Is Affected?
The new workers' compensation law went into effect on July 1, 2011. Fortunately, most of the worst provisions only apply to cases in which injuries happen after that date. However, some parts, ...
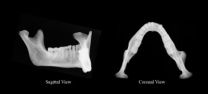
What shapes a bone?
2011-08-06
Researchers at Johns Hopkins found that use over time and not just genetics informs the structure of jaw bones in human populations. The researchers say these findings may be used to predict the diet of an ancient population, even if little evidence exists in the fossil record. It can also make it easier for scientists to pinpoint the genetic relationship between fossils.
Their results were published online June 23 in the American Journal of Physical Anthropology.
"Our research aimed to see how much of the mandible's—or jaw bone's—shape is plastic, a response to environmental ...
People With Extraordinary Abilities Can Obtain the O-1 Visa
2011-08-06
There are multiple non-immigrant visas under which dual intent is recognized by the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). Dual intent is a legal concept that describes people who maintain a proper non-immigrant status now, but intend to immigrate to the U.S. in the future. Although the eligibility and evidentiary requirements for the O-1 visa for individuals with extraordinary abilities or achievements in certain areas are strict, if non-immigrants apply for and are granted the O-1 visa, the dual intent doctrine applies.
Importantly, holders of O-1 visas ...
Sentinel node biopsy safe, effective in head and neck melanomas, U-M study finds
2011-08-06
This release is available in Spanish.
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — A common technique for determining whether melanoma has spread can be used safely and effectively even in tumors from the head and neck area, according to a new study from the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy involves injecting a special dye to identify the first node where cancer would likely spread. If that node is clean, patients can avoid further debilitating surgery to remove multiple lymph nodes. If that node shows cancer, patients know they need the more extensive ...
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Common among Car Accident Victims
2011-08-06
Most people think of military personnel returning from combat as individuals who commonly experience the mayhem of anxiety known as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). However, civilians experience PTSD just as much. Individuals who sustain injuries from car accidents, in particular, often suffer from PTSD.
What is PTSD?
In more specific terms, PTSD is an anxiety disorder many people experience after undergoing a traumatic or life-threatening event like a car or motorcycle accident, pedestrian-vehicle accident or a fall from a significant height. Many PTSD sufferers ...
Study suggests increase in public health spending results in healthier people
2011-08-06
LEXINGTON, Ky. (August 1, 2011) — A groundbreaking new study published in the journal, Health Affairs, suggests that increases in public health spending result in healthier people, especially in communities with fewer resources.
The study was co-authored by Glen P. Mays, the new F. Douglas Scutchfield Endowed Professor in Health Services and Systems Research at the University of Kentucky College of Public Health. At UK, Mays is affiliated with the National Coordinating Center for Public Health Services and Systems Research, funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. ...
Montana State researcher discovers link between Montana weather, ocean near Peru
2011-08-06
BOZEMAN, Mont. – A Montana State University researcher who analyzed 100 years of data has found a significant link between extreme Montana weather and the ocean temperatures near Peru.
Montanans who want to know what to expect from the weather should look to the Pacific Ocean in the fall or maybe find a way to chat with some Peruvian fishermen, according to Joseph Caprio, professor emeritus in MSU's Department of Land Resources and Environmental Sciences and former Montana State Climatologist.
If the average surface temperature of the ocean near Peru is warmer than ...
UCLA study shows man-made fat may limit damage to heart attack victims
2011-08-06
FINDINGS:
A man-made fat called Intralipid, which is currently used as a component of intravenous nutrition and to treat rare overdoses of local anesthetics, may also offer protection for patients suffering from heart attacks.
Current treatment for a heart attack focuses on limiting the duration of the ischemic period, when blood flow to tissues is reduced, and on subsequently opening arteries to reestablish normal coronary blood flow. It is well known that injury to the heart muscle can occur after oxygen and nutrients in the blood flow back to deprived cells, a ...
What do Facebook and Rembrandt have in common? Everything
2011-08-06
Los Angeles, CA (August 5, 2011) Facebook and artists like Rembrandt have much in common, says the author of "Friending the Virgin: some thoughts on the pre-history of Facebook" in the open access journal SAGE Open.
The main commonality lies in the act of portraiture, which consists of more than just the realistic depiction of a subject, but also a number of rhetorical decisions closely intertwined with evolving ideas of identity and society, according to author Larry Friedlander. The article points out the complex negotiations that artists had to make when painting some ...
Attorney General: No Joint Growing Under Michigan Medical Marijuana Act
2011-08-06
In 2008, state voters adopted the Michigan Medical Marijuana Act ("MMMA"). While the MMMA did not repeal any existing Michigan laws regarding marijuana, it did carve out a specific exception to shield certain qualifying individuals from state-level criminal liability.
Until very recently, it was uncertain whether patients otherwise in compliance with MMMA could legally cooperate in marijuana plant cultivation. But, according to a new opinion from the Michigan Attorney General, only individual growing and use is contemplated by the MMMA.
Separate, Secure ...